Ni膜型水素検出計設計における水素透過率の圧力依存性に関する考察小リークナトリウム水反応試験研究 第9報; 50MW蒸気発生器試験施設におけるナトリウム-水反応関係試験報告; 第3報
Study of pressure dependence of permeability in hydrogen-nickel system to the design of hydrogen detector; Studies of small leak sodium-water reaction (9): Study report of 50 MWSGTF for sodium-water reaction (3)
鐘ヶ江 直道*; 池本 一郎*; 橋口 功*; 堀 雅夫*; 法月 照芳*; 築地 道夫*; 火山 邦彦*; 高橋 忠男*
Kanegae, Naomichi*; not registered; not registered; not registered; not registered; not registered; Hiyama, Kunihiko*; Takahashi, Tadao*
期間1975年1月 1976年3月目的低圧における水素のNi膜透過現象において,透過量等がいわゆる1/2乗則に乗らないとの報告がこれまで内外でいくつかなされたが,この現象に対しSWAT-2および50MWSGTFで得られた試験結果を基に考察した。要旨水素のNi膜透過においていわゆる1/2乗則が成立し測定される1次側水素分圧P/NHと真空部圧力P/IPの間にはP/NH
1976年3月目的低圧における水素のNi膜透過現象において,透過量等がいわゆる1/2乗則に乗らないとの報告がこれまで内外でいくつかなされたが,この現象に対しSWAT-2および50MWSGTFで得られた試験結果を基に考察した。要旨水素のNi膜透過においていわゆる1/2乗則が成立し測定される1次側水素分圧P/NHと真空部圧力P/IPの間にはP/NH 1/2
1/2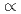 P/IPの関係が成り立つはずであるがこれまでSWAT-2からの報告も含めいくつかの報告に上式と異る測定結果が提示されている。この現象は水素検出計設計においてきわめて重要と考えられるが,50MWSGTF用水素計(Ni膜厚0.25mm,面積≒150cm
P/IPの関係が成り立つはずであるがこれまでSWAT-2からの報告も含めいくつかの報告に上式と異る測定結果が提示されている。この現象は水素検出計設計においてきわめて重要と考えられるが,50MWSGTF用水素計(Ni膜厚0.25mm,面積≒150cm 2)を用いて実施したガス中試験(水素分圧10
2)を用いて実施したガス中試験(水素分圧10 -4
-4 10
10 2mmHg.膜温度216
2mmHg.膜温度216 505
505 )から,以下のように透過度Kの低圧における圧力依存補正式を導出することができた。(1)P
)から,以下のように透過度Kの低圧における圧力依存補正式を導出することができた。(1)P 0.5mmHgでは圧刀依存性はなく,透過率Kは次式のように表わされる。K=kexp(-ERT)ここでkは定数,Eは流性化エネルギー,Rは気体定数,Tは温度である。(2)P
0.5mmHgでは圧刀依存性はなく,透過率Kは次式のように表わされる。K=kexp(-ERT)ここでkは定数,Eは流性化エネルギー,Rは気体定数,Tは温度である。(2)P 0.5mmHgにおける透他率kは次式で表わされることが判った。K=K・b・P/NH
0.5mmHgにおける透他率kは次式で表わされることが判った。K=K・b・P/NH 1/mここでKは上記1)で示した式であり,b・mは定数である。これは,低圧においてはFrecmdlichの着等温式(=b・P/NH
1/mここでKは上記1)で示した式であり,b・mは定数である。これは,低圧においてはFrecmdlichの着等温式(=b・P/NH 1/m)による補正が可能であることを示しており,試験結果から補正式中の定数は各々次の値であることが判った。b=1.25m=2.8今,測定されたP/NHとP/IPの間に1/2乗則でなくP/IP
1/m)による補正が可能であることを示しており,試験結果から補正式中の定数は各々次の値であることが判った。b=1.25m=2.8今,測定されたP/NHとP/IPの間に1/2乗則でなくP/IP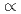 P/NH
P/NH 1/n(N
1/n(N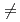 2)の関係が得られた時,mとnとの間には次の関係が成立する。1/n=1/m+1/2上記nの値に対し、SWAT-2,50MWSGTF, SCTI、およびPhenixにおけるNa中水素計より報告された結果および、本ガス中試験結果を比較すると次の範囲でよい一致を見た。.1
2)の関係が得られた時,mとnとの間には次の関係が成立する。1/n=1/m+1/2上記nの値に対し、SWAT-2,50MWSGTF, SCTI、およびPhenixにおけるNa中水素計より報告された結果および、本ガス中試験結果を比較すると次の範囲でよい一致を見た。.1 n
n 1.5
1.5
Generally, in the phenomena of hydrogen permeation or diffusion through nickel membrane, the relationship between the measured pressure P (pressure in vacuum side (mmHg)) and P
(pressure in vacuum side (mmHg)) and P (partial pressure of hydrogen in sodium (mmHg)) should be according half-power low, [P
(partial pressure of hydrogen in sodium (mmHg)) should be according half-power low, [P
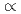 P
P
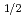 ] But some report indicated that the above equation is not realized, and the same phenomenon was also observed in our in-sodium experiments of the SWAT-2 and 50MWSGTF at PNC. This phenomenon is very important in the desigen detectors. An in gas experiment (range of P
] But some report indicated that the above equation is not realized, and the same phenomenon was also observed in our in-sodium experiments of the SWAT-2 and 50MWSGTF at PNC. This phenomenon is very important in the desigen detectors. An in gas experiment (range of P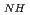 ; 10
; 10
 10
10 mmHg, temperature; 5 stages of 216
mmHg, temperature; 5 stages of 216 C
C  505
505 C) was performed using the Nickel Membrane Ionpump Type Hydrogen Detectors (Thickness:0.25m, Area:
C) was performed using the Nickel Membrane Ionpump Type Hydrogen Detectors (Thickness:0.25m, Area:  150cm
150cm ) in the 50MW Steam Generator Test Facility of PNC, and empirical results for the pressure dependence effect on the permeability K that could be employed in the design of hydrogen detectors were obtained as follow, (1)When P
) in the 50MW Steam Generator Test Facility of PNC, and empirical results for the pressure dependence effect on the permeability K that could be employed in the design of hydrogen detectors were obtained as follow, (1)When P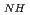
 0.5 Torr, K is found to be independent of pressure and the temperature dependence is expressed as [K=k exp (-E/RT)] Where, K is a constant, R the gas constant, E the activation energy and T the temperature. (2) When P
0.5 Torr, K is found to be independent of pressure and the temperature dependence is expressed as [K=k exp (-E/RT)] Where, K is a constant, R the gas constant, E the activation energy and T the temperature. (2) When P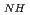
 0.5 Torr, permeability K
0.5 Torr, permeability K is expressed as [K
is expressed as [K = K
= K b P
b P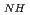
 ] Where K is the same as above equation, b and m are constants. This indicates that the pressure dependence of pemeability in the low pressure range tends to be expressed by the Freundlich's adsorption isotherm equation. From the experiments, b and m are determined as follows (these were found to be independent of temperature): [b=1.25, m=2.8] (3) If the relationship between P
] Where K is the same as above equation, b and m are constants. This indicates that the pressure dependence of pemeability in the low pressure range tends to be expressed by the Freundlich's adsorption isotherm equation. From the experiments, b and m are determined as follows (these were found to be independent of temperature): [b=1.25, m=2.8] (3) If the relationship between P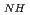 and P
and P is written as [P
is written as [P
 P
P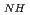
 the combination of n and m yielde the following equation [ 1/n = 1/m + 1/2] The value of n was extracted from the data of in-sodium hydrogen detectors in SCTI, Phenix, PNC(SWAT-2,
the combination of n and m yielde the following equation [ 1/n = 1/m + 1/2] The value of n was extracted from the data of in-sodium hydrogen detectors in SCTI, Phenix, PNC(SWAT-2,