堆積岩の水理・物質移行特性に関するデータ取得,2; 幌延地域に産する泥岩の孔径分布・化学組成・空気浸透率と物質移行特性の検討
Data acquisition of groundwater flow and mass transport properties in sedimentary rocks, 2; Considerations of mass transport properties based on pore size distribution, chemical composition and air permeability of the Horonobe specimen
原 彰男
Hara, Akio
核燃料サイクル開発機構(現、日本原子力研究開発機構)が、幌延地域で掘削したボーリング孔(HDB-1孔,HDB-2孔,HDB-5孔)のコアより採取した声問層及び稚内層の試料について、細孔径分布,全岩化学組成,空気浸透率を測定し、声問層及び稚内層の浸透率の特徴について、珪藻化石の相変化と関連付けた検討を行った。SiO を主成分とする珪藻化石がオパールA相に属する声問層においては半径1000
を主成分とする珪藻化石がオパールA相に属する声問層においては半径1000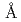 程度の細孔の集中が見られ、浸透率も稚内層と比較して高い。一方、珪藻化石がオパールCT相に相変化する稚内層においては、半径20
程度の細孔の集中が見られ、浸透率も稚内層と比較して高い。一方、珪藻化石がオパールCT相に相変化する稚内層においては、半径20 40
40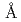 の細孔が間隙中に集中するようになり、浸透率は急激に低下する。半径20
の細孔が間隙中に集中するようになり、浸透率は急激に低下する。半径20 40
40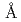 の細孔の集中の程度は、SiO
の細孔の集中の程度は、SiO 成分の含有率の高い試料ほど大きくなる。また、SiO
成分の含有率の高い試料ほど大きくなる。また、SiO 成分の含有率の高い試料ほど浸透率が低くなる傾向が認められた。半径20
成分の含有率の高い試料ほど浸透率が低くなる傾向が認められた。半径20 40
40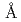 の細孔の集中は、浸透率の低下に寄与している可能性がある。今回の分析の結果、声問層・稚内層を通じて、オパールA-CT境界から200
の細孔の集中は、浸透率の低下に寄与している可能性がある。今回の分析の結果、声問層・稚内層を通じて、オパールA-CT境界から200 300mの深度の地層において浸透率が最も低くなる傾向が認められた。声問層と稚内層の地層境界から600m程度の深度において採取した稚内層の試料においては、半径100
300mの深度の地層において浸透率が最も低くなる傾向が認められた。声問層と稚内層の地層境界から600m程度の深度において採取した稚内層の試料においては、半径100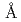 程度の細孔の集中が見られ、上位層に比べて高い浸透率が測定された。オパールA-CT境界から200
程度の細孔の集中が見られ、上位層に比べて高い浸透率が測定された。オパールA-CT境界から200 300mの深度にある稚内層は、圧力の保持や流体の移動を妨げるシール層としての機能や核種移行遅延性能を有している可能性がある。
300mの深度にある稚内層は、圧力の保持や流体の移動を妨げるシール層としての機能や核種移行遅延性能を有している可能性がある。
Pore size distribution, chemical composition and air permeability are analyzed on diatomaceous mudstone specimens of Koetoi and Wakkanai formation sampled from boreholes HDB-1, HDB-2 and HDB-5 which drilled by Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute in Horonobe area Hokkaido Japan. Permeability of Koetoi and Wakkanai formation is related to diagenetic facis changes of diatom fossils. Diatom fossils are belonging to Opal-A facies in the specimens of Koetoi formation. Pore size distribution of Koetoi formation concentrated around 1000 angstrom and permeability is higher than Wakkanai formation. In Wakkanai formation, diagenetic facies of diatomaceous fossil is changes into Opal-CT facies and pore size distribution concentrates between 20 to 40 angstrom and permeability declines abruptly. The specimen which includes high SiO content tend to have low permeability and high concentration of pore radius distribution between 20 to 40 angstrom. The degree of concentration should be caused to reducing permeability. A specimen sampled at 600m depth the formation boundary has high porosity and permeability than the specimen sampled around 200 to 300m depth below the formation boundary. The lowest permeability within the Koetoi and Wakkanai formation is observed in the Wakkanai formation at 200 to 300m depth of the formation boundary between Koetoi and Wakkanai formation. These strata have possibility of functioning as a seal rock, which can keep the high pressure and disturb ground water flow.
content tend to have low permeability and high concentration of pore radius distribution between 20 to 40 angstrom. The degree of concentration should be caused to reducing permeability. A specimen sampled at 600m depth the formation boundary has high porosity and permeability than the specimen sampled around 200 to 300m depth below the formation boundary. The lowest permeability within the Koetoi and Wakkanai formation is observed in the Wakkanai formation at 200 to 300m depth of the formation boundary between Koetoi and Wakkanai formation. These strata have possibility of functioning as a seal rock, which can keep the high pressure and disturb ground water flow.