Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Miyakawa, Kazuya; Yamamoto, Hajime*
JAEA-Research 2022-003, 40 Pages, 2022/05
The excavation of large-scale underground facilities, such as geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, creates an excavation damaged zone (EDZ) with cracks around the tunnel. In the EDZ, oxygen invades the bedrock through unsaturated cracks and affects environmental conditions for nuclide migration. When a tunnel is excavated in a geological formation containing a high concentration of dissolved CH , such as the Neogene marine sediments, degassed CH
, such as the Neogene marine sediments, degassed CH prevents oxygen intrusion. However, it may be promoted through gas-phase diffusion through desaturation. The purpose of this study is to illustrate the method of estimating the spatial distribution of desaturation associated with the construction and operation of underground facilities in a stratum that contains a large amount of dissolved CH
prevents oxygen intrusion. However, it may be promoted through gas-phase diffusion through desaturation. The purpose of this study is to illustrate the method of estimating the spatial distribution of desaturation associated with the construction and operation of underground facilities in a stratum that contains a large amount of dissolved CH . A sequential excavation analysis that reflected the actual process of 10-year excavation of the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) was carried out along with gas-water two-phase flow analysis. The analysis results of the amount of groundwater and gas discharged from the URL were about 100 to 300 m
. A sequential excavation analysis that reflected the actual process of 10-year excavation of the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) was carried out along with gas-water two-phase flow analysis. The analysis results of the amount of groundwater and gas discharged from the URL were about 100 to 300 m d
d and 250 to 350 m
and 250 to 350 m d
d , respectively, as of January 2017. These results showed values close to the observations (100 m
, respectively, as of January 2017. These results showed values close to the observations (100 m d
d and 300 m
and 300 m d
d , respectively). The analysis results of the saturation distribution were relatively high around the 250 m gallery and relatively low around the 350 m gallery, confirming that they are consistent with the in-situ observations. Although there were still technical issues of analysis regarding the conditions for groundwater drainage from the tunnel wall and the method of handling grout effects, the numerical calculation was generally appropriate. Although the results of the saturation distribution associated with the excavation were insufficient as the quantitative evaluation, they were almost correct from a qualitative point of view.
, respectively). The analysis results of the saturation distribution were relatively high around the 250 m gallery and relatively low around the 350 m gallery, confirming that they are consistent with the in-situ observations. Although there were still technical issues of analysis regarding the conditions for groundwater drainage from the tunnel wall and the method of handling grout effects, the numerical calculation was generally appropriate. Although the results of the saturation distribution associated with the excavation were insufficient as the quantitative evaluation, they were almost correct from a qualitative point of view.
Yoshida, Hisao*; Yamamoto, Akira*; Hosokawa, Saburo*; Yamazoe, Seiji*; Kikkawa, Soichi*; Hara, Kenji*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Tanaka, Tsunehiro*
Topics in Catalysis, 64(9-12), p.660 - 671, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.09(Chemistry, Applied)Yamamoto, Kazuya; Makino, Takayoshi; Iso, Hidetoshi; Segawa, Tomoomi; Kawaguchi, Koichi; Ishii, Katsunori
JAEA-Technology 2021-002, 31 Pages, 2021/05
In the MOX fuel fabrication process, a dry recycle technology has been developed to effectively utilize dry recovered powder obtained by crushing out of specification MOX pellets. The particle size of the dry recovery powder is divided into three classes; coarse size (about 250  m or less), medium size (about 100
m or less), medium size (about 100  m or less), and fine size (about 10
m or less), and fine size (about 10  m or less) by the current crushers, and the effect of controlling the density of sintered pellets is obtained to a certain extent by adding the dry recovered powder to the raw powder. In this report, with the aim of more finely adjusting the particle size of the dry recovery powder, a buhrstone mill and a collision plate-type jet mill were selected as grinders that can adjust the dry recovered powder within a particle size range of 250
m or less) by the current crushers, and the effect of controlling the density of sintered pellets is obtained to a certain extent by adding the dry recovered powder to the raw powder. In this report, with the aim of more finely adjusting the particle size of the dry recovery powder, a buhrstone mill and a collision plate-type jet mill were selected as grinders that can adjust the dry recovered powder within a particle size range of 250  m or less, and the particle size adjustment test was conducted to pulverize the tungsten-carbide-cobalt (WC-Co) pellets as a simulated material for the MOX pellets. The buhrstone mill can control the particle size within a certain range by adjusting the grindstone clearance, but particles with a particle size of 250
m or less, and the particle size adjustment test was conducted to pulverize the tungsten-carbide-cobalt (WC-Co) pellets as a simulated material for the MOX pellets. The buhrstone mill can control the particle size within a certain range by adjusting the grindstone clearance, but particles with a particle size of 250  m or more may be discharged. On the contrary, it is expected that the particle size of the collision plate-type jet mill can be controlled in the range of 250
m or more may be discharged. On the contrary, it is expected that the particle size of the collision plate-type jet mill can be controlled in the range of 250  m or less by adjusting the classification zone clearance. Therefore, the collision plate-type jet mill is more suitable for adjusting the particle size of the dry recovered powder than the buhrstone mill.
m or less by adjusting the classification zone clearance. Therefore, the collision plate-type jet mill is more suitable for adjusting the particle size of the dry recovered powder than the buhrstone mill.
Miyakawa, Kazuya; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Akaki, Toshifumi*; Yamamoto, Hajime*
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-002, 26 Pages, 2021/05
Investigations employing numerical simulation have been conducted to study the mechanisms of desaturation and oxygen infusion into sedimentary formations. By mimicking the conditions of the Horonobe underground research laboratory, numerical simulations aided geoscientific investigation of the effects of dissolved gas content and rock permeability on the desaturation (Miyakawa et al., 2019) and mechanisms of oxygen intrusion into the host rock (Miyakawa et al., 2021). These simulations calculated multi-phase flow, including flows of groundwater and exsolved gas, and conducted sensitivity analysis changing the dissolved gas content, rock permeability, and humidity at the gallery wall. Only the most important results from these simulations have been reported previously, because of publishers' space limitations. Hence, in order to provide basic data for understanding the mechanisms of desaturation and oxygen infusion into rock, all data for 27 output parameters (e.g., advective fluxes of heat, gas, and water, diffusive fluxes of water, CH , CO
, CO , O
, O , and N
, and N , saturation degree, water pressure, and mass fraction of each component) over a modeling period of 100 years are presented here.
, saturation degree, water pressure, and mass fraction of each component) over a modeling period of 100 years are presented here.
Kawasaki, Kohei; Shinada, Kenta; Okamoto, Naritoshi; Kageyama, Tomio; Eda, Takashi; Okazaki, Hiro; Suzuki, Hiromichi; Yamamoto, Kazuya; Otabe, Jun
JAEA-Technology 2020-025, 80 Pages, 2021/03
Plutonium Fuel Production Facility was built in 1988 for the purpose of mainly producing MOX fuel of the prototype fast breeder reactor MONJU, and large glove boxes were installed for handling unsealed nuclear fuel material remotely. The panels of these glove boxes are made of acrylic, except for those installed after December 2013. For fires inside the glove box, automatic fire extinguishing systems using halides have been introduced since the beginning of construction, but for fires outside the glove box, there have been issues with direct measures for acrylic. Therefore, we have developed a fireproof sheet that mitigates the effect of fire outside the glove box on the panels as much as possible. As a result, fire-retardant sheets have been selected and attached to the glove box panels. We conducted a flammability test of the acrylic plate attached with these fireproof sheets and a usage environment influence test of fireproof sheets, and obtained good results. In addition, we set up a working group in the Plutonium Fuel Development Center in view of reducing external exposure during the work of attaching fireproof sheets, in which we discussed and examined the work procedure, and summarized it in the basic procedure manual.
 O
O by
by  inelastic neutron scattering and their reactivity with ethylene
inelastic neutron scattering and their reactivity with ethyleneYamazoe, Seiji*; Yamamoto, Akira*; Hosokawa, Saburo*; Fukuda, Ryoichi*; Hara, Kenji*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Tsukuda, Tatsuya*; Yoshida, Hisao*; Tanaka, Tsunehiro*
Catalysis Science & Technology, 11(1), p.116 - 123, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:32.25(Chemistry, Physical)Miyakawa, Kazuya; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Akaki, Toshifumi*; Yamamoto, Hajime*
Dai-15-Kai Iwa No Rikigaku Kokunai Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), p.609 - 614, 2021/01
Desaturation is expected due to excavation of an underground repository, especially in the newly created fractures zone (EDZ). During the construction and operation of facilities, the air in the gallery infuses into the rock around the gallery though the excavation affected area and causes oxidation of host rock and groundwater, which increase nuclide mobilities. In the Horonobe underground research laboratory (HURL), which is excavated in the Neogene sedimentary formations, no pyrite dissolution or precipitation of calcium sulfates was found from the cores drilled in the rock around the gallery. The reason for no oxidation is estimated that the release of dissolved gases from groundwater due to pressure decrease flows against the air infusion. In this research, the mechanism of O intrusion into the rock was investigated by numerical multiphase flow simulation considering advection and diffusion of groundwater and gases. In the simulation, only Darcy's and Henry's laws were considered, that is, chemical reaction related to oxidation was not handled. The effects of dissolved gas and rock permeability on O
intrusion into the rock was investigated by numerical multiphase flow simulation considering advection and diffusion of groundwater and gases. In the simulation, only Darcy's and Henry's laws were considered, that is, chemical reaction related to oxidation was not handled. The effects of dissolved gas and rock permeability on O infusion into the rock were almost identical. Decreasing humidity with relatively low permeability leads to extensive accumulation of O
infusion into the rock were almost identical. Decreasing humidity with relatively low permeability leads to extensive accumulation of O into the EDZ even though with a relatively large amount of dissolved gas. In the HURL, the shotcrete attenuates O
into the EDZ even though with a relatively large amount of dissolved gas. In the HURL, the shotcrete attenuates O concentration and keeps 100% humidity at the boundary of the gallery wall, which inhibits O
concentration and keeps 100% humidity at the boundary of the gallery wall, which inhibits O infusion. Without the shotcrete, humidity at the gallery wall decreases according to seasonal changes and ventilation, which promotes O
infusion. Without the shotcrete, humidity at the gallery wall decreases according to seasonal changes and ventilation, which promotes O intrusion into the EDZ but the chemical reaction related to O
intrusion into the EDZ but the chemical reaction related to O buffering such as pyrite oxidation consumes O
buffering such as pyrite oxidation consumes O .
.
Kawaguchi, Koichi; Segawa, Tomoomi; Yamamoto, Kazuya; Makino, Takayoshi; Iso, Hidetoshi; Ishii, Katsunori
Funtai Kogakkai-Shi, 57(9), p.478 - 484, 2020/09
A collision plate type jet mill is assumed to be a pulverizer that can control the particle size for nuclear fuel fabrication. The collision plate type jet mill consists of two modules, a classifier and a mill chamber. Coarse component of powder is cycled in the equipment and finally pulverized into objective particle size. In this report, simulated crushed powders were classified and pulverized step by step, and particle size distribution were compared. The collision plate type jet mil can produce objective size particles with low overgrinding.
 -electron state of the heavy fermion superconductor NpPd
-electron state of the heavy fermion superconductor NpPd Al
Al and the isostructural family
and the isostructural familyMetoki, Naoto; Aczel, A. A.*; Aoki, Dai*; Chi, S.*; Fernandez-Baca, J. A.*; Griveau, J.-C.*; Hagihara, Masato*; Hong, T.*; Haga, Yoshinori; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 30, p.011123_1 - 011123_6, 2020/03
Rare earths (4 ) and actinides (5
) and actinides (5 ) provide variety of interesting states realized with competing interactions between the increasing number of
) provide variety of interesting states realized with competing interactions between the increasing number of  electrons. Since crystal field splitting of many-body
electrons. Since crystal field splitting of many-body  electron system is smaller than the bandwidth, (1) high resolution experiments are needed, (2) essentially no clear spectrum with well defined peaks is expected in itinerant Ce and U compounds, and (3) Np and Pu is strictly regulated. Therefore, systematic research on magnetic excitations by neutron scattering experiments of localized compounds and rare earth iso-structural reference is useful. We describe the
electron system is smaller than the bandwidth, (1) high resolution experiments are needed, (2) essentially no clear spectrum with well defined peaks is expected in itinerant Ce and U compounds, and (3) Np and Pu is strictly regulated. Therefore, systematic research on magnetic excitations by neutron scattering experiments of localized compounds and rare earth iso-structural reference is useful. We describe the  electron states of heavy electron compounds NpPd
electron states of heavy electron compounds NpPd Al
Al and actinide and rare earth based iso-structural family.
and actinide and rare earth based iso-structural family.
Miyakawa, Kazuya; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Akaki, Toshifumi*; Yamamoto, Hajime*
Proceedings of 5th ISRM Young Scholars' Symposium on Rock Mechanics and International Symposium on Rock Engineering for Innovative Future (YSRM 2019 and REIF 2019) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2019/12
The construction and operation of geological repositories require excavation and ventilation of galleries, with significant groundwater drainage. Desaturation of rock around galleries is unavoidable and may affect hydraulic properties and redox conditions. This study used numerical modeling to assess the influence of dissolved gas on the degree of saturation of rock surrounding excavated galleries, focusing on siliceous mudstone rock in the 140 m, 250 m, and 350-m-deep galleries of the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, Japan. Based on previous  electrical survey, the degree of saturation in the 250 m gallery was higher than that in the 140 m and 350 m galleries. In the Horonobe area, deep groundwater contains high concentrations of dissolved methane, and exsolution of this methane from pore water can affect desaturation. Simple numerical modeling, including simulation of multiphase flows, was undertaken for each gallery to confirm the effect of dissolved gas and rock permeability on desaturation. A sensitivity analysis was performed by varying dissolved gas contents and permeability. Results indicate that the dissolved gas content affects both the degree of saturation and its spatial extent, whereas rock permeability affects only the latter. Higher dissolved gas concentrations result in lower degrees of saturation with a greater spatial extent of desaturation, and higher permeability leads to greater extents of desaturation. It is therefore likely that gas content, rather than rock permeability, caused the observed variations in the saturation degree.
electrical survey, the degree of saturation in the 250 m gallery was higher than that in the 140 m and 350 m galleries. In the Horonobe area, deep groundwater contains high concentrations of dissolved methane, and exsolution of this methane from pore water can affect desaturation. Simple numerical modeling, including simulation of multiphase flows, was undertaken for each gallery to confirm the effect of dissolved gas and rock permeability on desaturation. A sensitivity analysis was performed by varying dissolved gas contents and permeability. Results indicate that the dissolved gas content affects both the degree of saturation and its spatial extent, whereas rock permeability affects only the latter. Higher dissolved gas concentrations result in lower degrees of saturation with a greater spatial extent of desaturation, and higher permeability leads to greater extents of desaturation. It is therefore likely that gas content, rather than rock permeability, caused the observed variations in the saturation degree.
Segawa, Tomoomi; Yamamoto, Kazuya; Makino, Takayoshi; Iso, Hidetoshi; Kawaguchi, Koichi; Ishii, Katsunori; Sato, Hisato; Fukasawa, Tomonori*; Fukui, Kunihiro*
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.738 - 745, 2019/09
In the MOX fuel fabrication process, the dry grinding technology of mixed oxide pellets have been developed for the effective use of nuclear fuel materials. To develop a technology to control the particle size of dry recovered powder, the performance of the buhrstone mill and the collision plate type jet mill were studied using a simulated powder of particle size distribution about 500  m. We found that the particle size can be controlled at the range of about 250
m. We found that the particle size can be controlled at the range of about 250  m or less by both by adjusting the clearance between the grinding wheels of the buhrstone mill, and the clearance and elevation angle of the clarification zone of the collision plate type jet mill. And furthermore, the collision plate type jet mill is considered to be suitable for particle size control because the operating parameters of the classifier can be finely adjusted.
m or less by both by adjusting the clearance between the grinding wheels of the buhrstone mill, and the clearance and elevation angle of the clarification zone of the collision plate type jet mill. And furthermore, the collision plate type jet mill is considered to be suitable for particle size control because the operating parameters of the classifier can be finely adjusted.
Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Nobuyuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Mizuno, Takashi
JAEA-Data/Code 2014-033, 43 Pages, 2015/03
Development of technologies to investigate properties (conditions) of deep geological environment and models development of geological environment have been pursued in "Geoscientific Research" in the Horonobe underground research laboratory (Horonobe URL) project. A geochemical model of groundwater evolution which is a part of geological environment model requires the data of groundwater chemistry around the Horonobe URL for the development. This report summarizes the data obtained for 3 years (i.e., from the fiscal year 2011 to 2013), especially for the results for measurement of physico-chemical parameters and analysis of groundwater chemistry, in the Horonobe URL project.
Yoshimura, Kazuya; Onda, Yuichi*; Sakaguchi, Aya*; Yamamoto, Masayoshi*; Matsuura, Yuki*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 139, p.370 - 378, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:86 Percentile:92.28(Environmental Sciences)Mitamura, Hiroyuki*; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Kaneko, Koji; Onozaki, Norimichi*; Amo, Yuta*; Kittaka, Shunichiro*; Kobayashi, Riki*; Shimura, Yasuyuki*; Yamamoto, Isao*; Suzuki, Kazuya*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 113(14), p.147202_1 - 147202_5, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:75.83(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Yamamoto, Tsuyoshi; Yonekawa, Izuru*; Ota, Kazuya*; Hosoyama, Hiroki*; Hashimoto, Yasunori*; Wallander, A.*; Winter, A.*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kusama, Yoshinori; Kawano, Yasunori; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 87(12), p.2016 - 2019, 2012/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.68(Nuclear Science & Technology)The ITER pulse scheduling system creates, approves and manage parameters that characterize plasma operation of ITER. JAEA analyzed requirements on the ITER plasma operations based on experience operating the JT-60U and designed essential functions. This system was designed to enable the change and reuse of parameters. The functions to support to check consistency between parameters and to assign parameter values are calculated by the system were proposed. These functions are useful to support operators.
Nakai, Satoru; Aoyama, Takafumi; Ito, Chikara; Yamamoto, Masaya; Iijima, Minoru; Nagaoki, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Atsuko; Onoda, Yuichi; Ohgama, Kazuya; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; et al.
Kosoku Jikkenro "Joyo" Rinkai 30-Shunen Kinen Hokokukai Oyobi Gijutsu Koenkai, 154 Pages, 2008/06
no abstracts in English
Yokoo, Kenji; Horiguchi, Hironori; Yagi, Masahiro; Nagadomi, Hideki; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Sasajima, Fumio; Oyama, Koji; Ishikuro, Yasuhiro; Sasaki, Tsutomu; Hirane, Nobuhiko; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2007-018, 104 Pages, 2007/03
Reactor operation training using JRR-4 (Japan Research Reactor No.4) was started in FY 1969, one of the curriculums of Nuclear Technology and Education Center (NuTEC). After that, the program was updated and carried out for reactor operation training, control rod calibration, and measurement of various kind of characteristics. JRR-4 has been contributed for nuclear engineer training that is over 1,700 trainees from bother domestic and foreign countries. JRR-4 can be used for experiment from zero power to 3500kW, and the trainees can make experience to operate the reactor from start up to shut down, not only zero-power experiments (critical approach, control rod calibration, reactivity measurement, etc.) but also other experiments under high power operation (xenon effect, temperature effects, reactor power calibration, etc.). This report is based on various kinds of guidance texts using for training, and collected for operation and experiments for reactor physics.
Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Kamiya, Kensaku; Shinohara, Koji; Bakhtiari, M.*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kurita, Genichi; Takechi, Manabu; Kasai, Satoshi; Sato, Masayasu; Kawashima, Hisato; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(11), p.966 - 971, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:48.1(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Kawashima, Hisato; Sengoku, Seio; Uehara, Kazuya; Tamai, Hiroshi; Shoji, Teruaki*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Shibata, Takatoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Kusama, Yoshinori; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.168 - 186, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.07(Nuclear Science & Technology)Experimental efforts on JFT-2M have been devoted to understand SOL/Divertor plasmas and to investigate power and particle controllability. Open divertor configuration was used for the first decade of JFT-2M started in 1984. We found out the SOL/Divertor plasma properties such as in/out asymmetry, heat and particle diffusivities, and SOL current at ELMs. Handling of power and particle was demonstrated by active control methods such as local pumping, edge ergodization, divertor biasing, and edge heating. For improvement of power and particle control capability of divertor, it was modified to closed configuration in 1995, which demonstrated the baffling effects with narrower divertor throat. Dense and cold divertor state (n
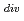 = 4
= 4 10
10 m
m and T
and T
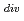 = 4 eV), compatible with the improved confinement modes (e.g. H-mode), was realized by strong gas puffing. Being related with the core confinement at H-mode, the edge plasma fluctuations were identified by an electrostatic probe. These are reviewed in this paper.
= 4 eV), compatible with the improved confinement modes (e.g. H-mode), was realized by strong gas puffing. Being related with the core confinement at H-mode, the edge plasma fluctuations were identified by an electrostatic probe. These are reviewed in this paper.