Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Amekura, Hiroshi*; Chettah, A.*; Narumi, Kazumasa*; Chiba, Atsuya*; Hirano, Yoshimi*; Yamada, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Leino, A. A.*; Djurabekova, F.*; Nordlund, K.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.1786_1 - 1786_10, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0Injecting high-energy heavy ions in the electronic stopping regime into solids can create cylindrical damage zones called latent ion tracks. Although these tracks form in many materials, none have ever been observed in diamond, even when irradiated with high-energy GeV uranium ions. Here we report the first observation of ion track formation in diamond irradiated with 2-9 MeV C fullerene ions. Depending on the ion energy, the mean track length (diameter) changed from 17 (3.2) nm to 52 (7.1) nm. High resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy (HR-STEM) indicated the amorphization in the tracks, in which
fullerene ions. Depending on the ion energy, the mean track length (diameter) changed from 17 (3.2) nm to 52 (7.1) nm. High resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy (HR-STEM) indicated the amorphization in the tracks, in which  -bonding signal from graphite was detected by the electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS).
-bonding signal from graphite was detected by the electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS).
Zhang, A.*; Deng, K.*; Sheng, J.*; Liu, P.*; Kumar, S.*; Shimada, Kenya*; Jiang, Z.*; Liu, Z.*; Shen, D.*; Li, J.*; et al.
Chinese Physics Letters, 40(12), p.126101_1 - 126101_8, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:72.4(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Sc
Sc )
) O
O determined by single-crystal neutron diffraction
determined by single-crystal neutron diffractionTanaka, Seiya*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Amako, Yasushi*; Iiyama, Taku*; Futamura, Ryusuke*; Maruyama, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Shigenori*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(1), p.014403_1 - 014403_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kubo, Kotaro; Tanaka, Yoichi*; Ishikawa, Jun
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part O; Journal of Risk and Reliability, 11 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.66(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Matsuya, Yusuke; Kusumoto, Tamon*; Yachi, Yoshie*; Hirata, Yuho; Miwa, Misako*; Ishikawa, Masayori*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Matsuyama, Shigeo*; Fukunaga, Hisanori*
AIP Advances (Internet), 12(2), p.025013_1 - 025013_9, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:54.33(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) is a radiation therapy, which can selectively eradicate solid tumors by  -particles and Li ions generated through the nuclear reaction between thermal neutron and
-particles and Li ions generated through the nuclear reaction between thermal neutron and  B in tumor cells. With the development of accelerator-based neutron sources that can be installed in medical institutions, accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy is expected to become available at several medical institutes around the world in the near future. Lithium is one of the targets that can produce thermal neutrons from the
B in tumor cells. With the development of accelerator-based neutron sources that can be installed in medical institutions, accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy is expected to become available at several medical institutes around the world in the near future. Lithium is one of the targets that can produce thermal neutrons from the  Li(p,n)
Li(p,n) Be near-threshold reaction. Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) is a general-purpose Monte Carlo code, which can simulate a variety of diverse particle types and nuclear reactions. The latest PHITS code enables simulating the generation of neutrons from the
Be near-threshold reaction. Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) is a general-purpose Monte Carlo code, which can simulate a variety of diverse particle types and nuclear reactions. The latest PHITS code enables simulating the generation of neutrons from the  Li(p,n)
Li(p,n) Be reactions by using Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (JENDL-4.0/HE). In this study, we evaluated the neutron fluence using the PHITS code by comparing it to reference data. The subsequent neutron transport simulations were also performed to evaluate the boron trifluoride (BF
Be reactions by using Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (JENDL-4.0/HE). In this study, we evaluated the neutron fluence using the PHITS code by comparing it to reference data. The subsequent neutron transport simulations were also performed to evaluate the boron trifluoride (BF ) detector responses and the recoiled proton fluence detected by a CR-39 plastic detector. As a result, these comparative studies confirmed that the PHITS code can accurately simulate neutrons generated from an accelerator using a Li target. The PHITS code has a significant potential for contributing to more precise evaluating accelerator-based neutron fields and understandings of therapeutic effects of BNCT.
) detector responses and the recoiled proton fluence detected by a CR-39 plastic detector. As a result, these comparative studies confirmed that the PHITS code can accurately simulate neutrons generated from an accelerator using a Li target. The PHITS code has a significant potential for contributing to more precise evaluating accelerator-based neutron fields and understandings of therapeutic effects of BNCT.
 Sc
Sc )
) O
O (0
(0  x
x  0.2) hexagonal ferrite
0.2) hexagonal ferriteMaruyama, Kenichi*; Tanaka, Seiya*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Nakao, Akiko*; Moriyama, Kentaro*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Amako, Yasushi*; Iiyama, Taku*; Futamura, Ryusuke*; Utsumi, Shigenori*; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 892, p.162125_1 - 162125_8, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:15.51(Chemistry, Physical)Ishikawa, Norito; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Okubo, Nariaki
Shototsu, 18(3), p.43 - 55, 2021/05
Radiation damage mechanism in ceramics irradiated with swift heavy ions has been studied by using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). We introduce how the mechanisms are unveiled by our recent TEM studies.
 nanocubes via precise solvothermal crystal growth and their anomalous surface compositional reconstruction
nanocubes via precise solvothermal crystal growth and their anomalous surface compositional reconstructionNakashima, Koichi*; Onagi, Kaito*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Ishigaki, Toru*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Yin, S.*; Kakihana, Masato*; Sekino, Toru*
ACS Omega (Internet), 6(14), p.9410 - 9425, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:57.4(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We succeeded in synthesizing barium titanate nanocubes by hydrothermal synthesis. When the nanocubes were examined in detail using a scanning electron microscope, pulsed neutrons, and large synchrotron radiation, it was found that a reconstituted layer of titanium oxide was formed on the surface.
Miao, P.*; Tan, Z.*; Lee, S. H.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Torii, Shuki*; Yonemura, Masao*; Koda, Akihiro*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Machida, Shinichi*; Sano, Asami; et al.
Physical Review B, 103(9), p.094302_1 - 094302_18, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.4(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The layered perovskite PrBaCo O
O demonstrates a strong negative thermal expansion (NTE) which holds potential for being fabricated into composites with zero thermal expansion. The NTE was found to be intimately associated with the spontaneous magnetic ordering, known as magneto-volume effect (MVE). Here we report with compelling evidences that the continuous-like MVE in PrBaCo
demonstrates a strong negative thermal expansion (NTE) which holds potential for being fabricated into composites with zero thermal expansion. The NTE was found to be intimately associated with the spontaneous magnetic ordering, known as magneto-volume effect (MVE). Here we report with compelling evidences that the continuous-like MVE in PrBaCo O
O is intrinsically of discontinuous character, originating from an magnetoelectric transition from an antiferromagnetic insulating large-volume (AFILV) phase to a ferromagnetic less-insulating small-volume (FLISV) phase. Furthermore, the magnetoelectric effect (ME) shows high sensitivity to multiple external stimuli such as temperature, carrier doping, hydrostatic pressure, magnetic field etc. In contrast to the well-known ME such as colossal magnetoresistance and multi-ferroic effect which involve symmetry breaking of crystal structure, the ME in the cobaltite is purely isostructural. Our discovery provides a new path way to realizing the ME as well as the NTE, which may find applications in new techniques.
is intrinsically of discontinuous character, originating from an magnetoelectric transition from an antiferromagnetic insulating large-volume (AFILV) phase to a ferromagnetic less-insulating small-volume (FLISV) phase. Furthermore, the magnetoelectric effect (ME) shows high sensitivity to multiple external stimuli such as temperature, carrier doping, hydrostatic pressure, magnetic field etc. In contrast to the well-known ME such as colossal magnetoresistance and multi-ferroic effect which involve symmetry breaking of crystal structure, the ME in the cobaltite is purely isostructural. Our discovery provides a new path way to realizing the ME as well as the NTE, which may find applications in new techniques.
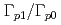 ratios of resonance states in
ratios of resonance states in  Be for deducing the
Be for deducing the  Be(
Be( ,
,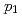 )
) Li
Li reaction rate relevant to the cosmological lithium problem
reaction rate relevant to the cosmological lithium problemIwasa, Naohito*; Ishikawa, Shunki*; Kubono, Shigeru*; Sakakibara, T.*; Kominato, Kazuya*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Matsuda, Makoto; Hirose, Kentaro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Orlandi, R.; et al.
Physical Review C, 103(1), p.015801_1 - 015801_5, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.58(Physics, Nuclear)Amekura, Hiroshi*; Toulemonde, M.*; Narumi, Kazumasa*; Li, R.*; Chiba, Atsuya*; Hirano, Yoshimi*; Yamada, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Ishikawa, Norito; Okubo, Nariaki; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.185_1 - 185_11, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:75.47(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We report the track formation of 10 nm in diameter in silicon irradiated with 6 MeV C , i.e., much lower energy than the previously reported energy threshold.
, i.e., much lower energy than the previously reported energy threshold.
Amekura, Hiroshi*; Li, R.*; Okubo, Nariaki; Ishikawa, Norito; Chen, F.*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 4(4), p.39_1 - 39_11, 2020/12
Evolution of depth profiles of the refractive index in Y Al
Al O
O (YAG) crystals were studied under 200 MeV Xe ion irradiation. The index changes were observed at three different depth regions; (i) a plateau near the surface between 0 and 3
(YAG) crystals were studied under 200 MeV Xe ion irradiation. The index changes were observed at three different depth regions; (i) a plateau near the surface between 0 and 3  m in depth, which can be ascribed to the electronic stopping Se, (ii) a broad peak at 6
m in depth, which can be ascribed to the electronic stopping Se, (ii) a broad peak at 6  m in depth, and (iii) a sharp dip at 13
m in depth, and (iii) a sharp dip at 13  m in depth, which is attributed to the nuclear stopping Sn peak.
m in depth, which is attributed to the nuclear stopping Sn peak.
Kubo, Kotaro; Zheng, X.; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2020 (ASRAM 2020) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2020/11
Dynamic probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) enables a more realistic and detailed analysis than classical PRA. However, the trade-off for these improvements is the enormous computational cost associated with performing a large number of thermal-hydraulic (TH) analyses. In this study, based on machine learning (ML), we aim to reduce these costs by skipping the TH analysis. For the ML algorithm, we selected a support vector machine; we built it using a high-fidelity/high-cost detailed model and low-fidelity/low-cost simplified model. As a result, the computational costs could be reduced by approximately 80% without significantly decreasing the accuracy under the assumed conditions.
 Sc
Sc )
) O
O single crystals
single crystalsUtsumi, Shigenori*; Tanaka, Seiya*; Maruyama, Kenichi*; Amako, Yasushi*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Nakao, Akiko*; Moriyama, Kentaro*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; 9 of others*
ACS Omega (Internet), 5(38), p.24890 - 24897, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.2(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Fabricating large, high-crystalline-quality single-crystal samples of hexagonal ferrite Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O is the first important step to elucidating its helimagnetic structure and developing it for further applications. In this study, single crystals of Ba(Fe
is the first important step to elucidating its helimagnetic structure and developing it for further applications. In this study, single crystals of Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O of various Sc concentrations
of various Sc concentrations  were successfully grown by the spontaneous crystallization method using Na
were successfully grown by the spontaneous crystallization method using Na O-Fe
O-Fe O
O flux. X-ray diffraction and elemental analysis revealed that the obtained crystals were composed of single-phase Ba(Fe
flux. X-ray diffraction and elemental analysis revealed that the obtained crystals were composed of single-phase Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O of high crystalline quality. The temperature dependence of magnetization and the magnetization curves at 77 K of the
of high crystalline quality. The temperature dependence of magnetization and the magnetization curves at 77 K of the  = 0.128 crystal exhibited behavior characteristics of helimagnetism. Neutron diffraction measurements of the
= 0.128 crystal exhibited behavior characteristics of helimagnetism. Neutron diffraction measurements of the  = 0.128 crystal exhibited magnetic satellite reflection peaks below 211K, proving evidence that Ba(Fe
= 0.128 crystal exhibited magnetic satellite reflection peaks below 211K, proving evidence that Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O behaves as a helimagnetic material.
behaves as a helimagnetic material.
Wu, P.*; Fan, F.-R.*; Hagihara, Masato*; Kofu, Maiko; Peng, K.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Lee, S.*; Honda, Takashi*; Yonemura, Masao*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 22(8), p.083083_1 - 083083_9, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:60.75(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Thermoelectric material SnSe has aroused world-wide interests in the past years, and its inherent strong lattice anharmonicity is regarded as a crucial factor for its outstanding thermoelectric performance. However, the understanding of lattice anharmonicity in SnSe system remains inadequate, especially regarding how phonon dynamics are affected by this behavior. In this work, we present a comprehensive study of lattice dynamics on Na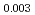 Sn
Sn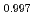 Se
Se S
S by means of neutron total scattering, inelastic neutron scattering, Raman spectroscopy as well as frozen-phonon calculations. Lattice anharmonicity is evidenced by pair distribution function, inelastic neutron scattering and Raman measurements. By separating the effects of thermal expansion and multi-phonon scattering, we found that the latter is very significant in high-energy optical phonon modes. The strong temperature-dependence of these phonon modes indicate the anharmonicity in this system. Moreover, our data reveals that the linewidths of high-energy optical phonons become broadened with mild doping of sulfur. Our studies suggest that the thermoelectric performance of SnSe could be further enhanced by reducing the contributions of high-energy optical phonon modes to the lattice thermal conductivity via phonon engineering.
by means of neutron total scattering, inelastic neutron scattering, Raman spectroscopy as well as frozen-phonon calculations. Lattice anharmonicity is evidenced by pair distribution function, inelastic neutron scattering and Raman measurements. By separating the effects of thermal expansion and multi-phonon scattering, we found that the latter is very significant in high-energy optical phonon modes. The strong temperature-dependence of these phonon modes indicate the anharmonicity in this system. Moreover, our data reveals that the linewidths of high-energy optical phonons become broadened with mild doping of sulfur. Our studies suggest that the thermoelectric performance of SnSe could be further enhanced by reducing the contributions of high-energy optical phonon modes to the lattice thermal conductivity via phonon engineering.
 and amorphizable Y
and amorphizable Y Al
Al O
O (YAG) crystals
(YAG) crystalsAmekura, Hiroshi*; Li, R.*; Okubo, Nariaki; Ishikawa, Norito; Chen, F.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 474, p.78 - 82, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:52.06(Instruments & Instrumentation)Yttrium-aluminum-garnet (YAG) and calcium fluoride (CaF ) were irradiated with 200 MeV Xe ions. YAG crystal was transformed to an amorphous phase, whereas CaF
) were irradiated with 200 MeV Xe ions. YAG crystal was transformed to an amorphous phase, whereas CaF shows the non-amorphizable nature. In spite of amorphization, YAG maintained its transparency, whereas CaF
shows the non-amorphizable nature. In spite of amorphization, YAG maintained its transparency, whereas CaF markedly loses it transparency showing a broad absorption band centered at 550 nm.
markedly loses it transparency showing a broad absorption band centered at 550 nm.
 and 200 MeV Xe ion irradiation
and 200 MeV Xe ion irradiationLi, R.*; Narumi, Kazumasa*; Chiba, Atsuya*; Hirano, Yu*; Tsuya, Daiju*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Saito, Yuichi*; Okubo, Nariaki; Ishikawa, Norito; Pang, C.*; et al.
Nanotechnology, 31(26), p.265606_1 - 265606_9, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:37.51(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)We report the elongation of embedded Au nanoparticles (NPs) in three different matrices under irradiations of 4 MeV C ions and 200 MeV Xe ions. Large elongation of Au NPs was observed for crystalline indium tin oxide (ITO) under both 4 MeV C
ions and 200 MeV Xe ions. Large elongation of Au NPs was observed for crystalline indium tin oxide (ITO) under both 4 MeV C and 200 MeV Xe irradiation. The ITO layer preserved the crystallinity even after large elongation was induced. This is the first report of the elongation of metal NPs in a crystalline matrix.
and 200 MeV Xe irradiation. The ITO layer preserved the crystallinity even after large elongation was induced. This is the first report of the elongation of metal NPs in a crystalline matrix.
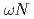 scattering length from
scattering length from  photoproduction on the proton near the reaction threshold
photoproduction on the proton near the reaction thresholdIshikawa, Takatsugu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fukasawa, Hiroshi*; Hashimoto, Ryo*; He, Q.*; Honda, Yuki*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Iwata, Takahiro*; Kaida, Shun*; Kasagi, Jirota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(5), p.052201_1 - 052201_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:43.57(Physics, Nuclear) Co
Co Fe
Fe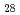 O
O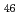
Komabuchi, Mai*; Urushihara, Daisuke*; Asaka, Toru*; Fukuda, Koichiro*; Ohara, Takashi; Munakata, Koji*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(3), p.034601_1 - 034601_5, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.38(Physics, Multidisciplinary)