Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
谷口 良徳; 三原 武; 垣内 一雄; 宇田川 豊
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 195, p.110144_1 - 110144_11, 2024/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A reactivity-initiated accident (RIA)-simulated test CN-1 on a high-burnup 64 GWd/t mixed-oxide fuel rod sheathed with M5 cladding was conducted at the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor, resulting in fuel failure. A small opening with slight ballooning deformation characterized the post-test visual appearance of the test fuel rod. Simulation using fuel performance codes FEMAXI-8/RANNS predicted rod survival under early phase loading induced by pellet-cladding mechanical interaction and subsequent boiling transition, and the cladding surface temperature measured online confirmed the occurrence of boiling transition. The experimental observation and simulation indicate that the failure was caused by a high-temperature rupture following increased rod-internal pressure. The RANNS sensitivity analysis revealed that a mechanical state parameter dedicated to predicting plastic instability might be an effective index for evaluating the risk of rupture failure during RIAs.
cladding was conducted at the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor, resulting in fuel failure. A small opening with slight ballooning deformation characterized the post-test visual appearance of the test fuel rod. Simulation using fuel performance codes FEMAXI-8/RANNS predicted rod survival under early phase loading induced by pellet-cladding mechanical interaction and subsequent boiling transition, and the cladding surface temperature measured online confirmed the occurrence of boiling transition. The experimental observation and simulation indicate that the failure was caused by a high-temperature rupture following increased rod-internal pressure. The RANNS sensitivity analysis revealed that a mechanical state parameter dedicated to predicting plastic instability might be an effective index for evaluating the risk of rupture failure during RIAs.
Li, F.; 三原 武; 宇田川 豊
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 11 Pages, 2024/00
被引用回数:0In a part of the reactivity-initiated accident (RIA) simulated tests on high-burnup fuels performed at the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor, the fuel failure caused by pellet-cladding mechanical interaction (PCMI) led to splitting into upper- and lower-part pieces or even fragmentation of the cladding tube. A massive release of fuel fragments accompanied this fracture pattern change from previously known axial cracks and thus identified as a potential concern in safety evaluation regarding core coolability. Dedicated out-of-pile mechanical tests were performed with unirradiated Zircaloy-4 cladding specimens to clarify the fracture pattern change conditions. The specimens were pre-hydrided and subjected to loading with axial-to-hoop strain ratios of 0.5-1.25, simulating the effects of hydrogen embrittlement and pellet-cladding mechanical bonding of high-burnup fuels, respectively. The results indicate that higher biaxiality of the loading and lower ductility (failure strain level) assist the fracture pattern change. This study proposes a conservative criterion that a PCMI failure splits the cladding tube into more than two pieces when strain ratio is greater than 0.75 and a concurrent hoop strain  1.7% at the failure instant.
1.7% at the failure instant.
 fuel with additives under reactivity-initiated accident conditions
fuel with additives under reactivity-initiated accident conditions三原 武; 垣内 一雄; 谷口 良徳; 宇田川 豊
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(5), p.512 - 525, 2023/05
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Fuels with additives are expected to provide enhanced fuel performance in fission gas retention owing to their large grain size, which elongates fission gas migration path. To investigate behavior of the fuels during a reactivity-initiated accident (RIA), RIA-simulated experiments OS-1 and LS-4 were performed on ADOPT (chromia- and alumina-doped UO ) fuel of 64 GWd/t and chromia-doped UO
) fuel of 64 GWd/t and chromia-doped UO fuel of 48 GWd/t, respectively. The OS-1 rod failed at a fuel enthalpy increase of 160 J/g due to pellet-cladding mechanical interaction failure, which was the lowest failure limit among the test results ever obtained at the NSRR on high-burnup fuels from 40 to 65 GWd/tU. Comparison of the hydride morphologies in the cladding metallic layer between the rods subjected to the past NSRR tests suggests the contribution of radially oriented hydrides during base irradiation to the low failure limit. The LS-4 rod survived for a peak fuel enthalpy increase of 549 J/g, which resulted in cladding deformation of
fuel of 48 GWd/t, respectively. The OS-1 rod failed at a fuel enthalpy increase of 160 J/g due to pellet-cladding mechanical interaction failure, which was the lowest failure limit among the test results ever obtained at the NSRR on high-burnup fuels from 40 to 65 GWd/tU. Comparison of the hydride morphologies in the cladding metallic layer between the rods subjected to the past NSRR tests suggests the contribution of radially oriented hydrides during base irradiation to the low failure limit. The LS-4 rod survived for a peak fuel enthalpy increase of 549 J/g, which resulted in cladding deformation of  2.4% in the residual hoop strain and FGR of 1.4%-6.1%. Whereas the low fission gas release exhibits the effect of additives, the cladding deformation is within the range explained by the deformation mechanism essentially identical to those recognized for high-burnup undoped fuels.
2.4% in the residual hoop strain and FGR of 1.4%-6.1%. Whereas the low fission gas release exhibits the effect of additives, the cladding deformation is within the range explained by the deformation mechanism essentially identical to those recognized for high-burnup undoped fuels.
Li, F.; 三原 武; 宇田川 豊
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(12), p.1455 - 1464, 2022/12
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:31.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)The mechanical properties of fuel cladding near the elastic limit are essential in considering its failure limit during a pellet-cladding mechanical interaction phase under reactivity-initiated accident (RIA) conditions. The mechanical properties of a Zircaloy-4 cladding tube, such as orthotropic elasticity and anisotropic constants for Hill's plasticity law, were evaluated based on the biaxial stress test data, focusing on the equivalent plastic strain up to ~2.5%. Samples with various fabrication conditions, such as cold-worked, recrystallized, and stress relieved after cold-work with Q-factors of 2, 3, and 4 were investigated. The cold worked samples and recrystallized samples showed high yield stress and Young's modulus, respectively. The evaluated mechanical properties of the stress relieved samples revealed a limited impact of Q-factors on mechanical behavior, including their anisotropic feature. The derived mechanical properties were applied to evaluate the fracture mechanics parameter, J-integral, based on failure limit data from biaxial-expansion-due-to-compression tests on precracked tubes. This evaluation produced systematically lower J-integral values of the stress relieved tube than previously evaluated based on the failure limit data from in-pile RIA-simulated tests.
三原 武; 垣内 一雄; 谷口 良徳; 宇田川 豊
Proceedings of TopFuel 2021 (Internet), 10 Pages, 2021/10
Test OS-1, the reactivity-initiated-accident (RIA) -simulated test on 64 GWd/tU high burnup fuel with ADOPT (chromia-and-alumina-doped UO
(chromia-and-alumina-doped UO ) pellets resulted in a failure at the lowest fuel enthalpy increase among the tests ever performed at the NSRR on high burnup fuels from 40 to 65 GWd/tU. Roles of both fuel pellets and cladding behaviours in this remarkable observation are being investigated. A comparative RIA-simulated test OS-2 was thus performed on undoped fuel that had been base-irradiated in the identical fuel assembly with the OS-1 rod. The transient records acquired during Test OS-2 indicated that the rod survived without fuel failure. Radially projected hydride lengths in the cladding metallic layer were evaluated from the metallograph images observed in the vicinity of the OS-2 test rod and compared with other failure test cases. The comparison suggested that the hydride morphologies affected the low failure limit of the OS-1 rod and also explains the survival of the OS-2 rod, to some extent. Nevertheless, as the OS-2 rod survived 100 J/g higher peak fuel enthalpy than the OS-1 failure limit, further experimental and analytical studies are desired to pursue other possible causes: additional loading specific to ADOPT
) pellets resulted in a failure at the lowest fuel enthalpy increase among the tests ever performed at the NSRR on high burnup fuels from 40 to 65 GWd/tU. Roles of both fuel pellets and cladding behaviours in this remarkable observation are being investigated. A comparative RIA-simulated test OS-2 was thus performed on undoped fuel that had been base-irradiated in the identical fuel assembly with the OS-1 rod. The transient records acquired during Test OS-2 indicated that the rod survived without fuel failure. Radially projected hydride lengths in the cladding metallic layer were evaluated from the metallograph images observed in the vicinity of the OS-2 test rod and compared with other failure test cases. The comparison suggested that the hydride morphologies affected the low failure limit of the OS-1 rod and also explains the survival of the OS-2 rod, to some extent. Nevertheless, as the OS-2 rod survived 100 J/g higher peak fuel enthalpy than the OS-1 failure limit, further experimental and analytical studies are desired to pursue other possible causes: additional loading specific to ADOPT pellets, difference in the pellet/cladding bonding condition, and so on.
pellets, difference in the pellet/cladding bonding condition, and so on.
谷口 良徳; 三原 武; 宇田川 豊
Proceedings of TopFuel 2021 (Internet), 10 Pages, 2021/10
Scattering of hydride precipitates in a fuel cladding tube was simply modeled by mapping of multiple cracks in finite element system based on the image-processed hydride morphologies observed in post-test cladding samples and the mechanical interactions of these cracks were simulated by damage mechanics calculation. This is a part of ongoing efforts to analyze the effect of the radially oriented hydride precipitates in the cladding tube on the fuel-failure limit observed in Test OS-1: a reactivity-initiated accident (RIA)-simulated test on the BWR fuel with additives irradiated to 64 GWd/tU, which resulted in a fuel failure with the lowest failure limit among the tests ever performed at the NSRR for high burnup BWR rods. The LS-1 test fuel rod, with similar burnup to the OS-1 rod, was selected as another RIA-simulated test rod to be compared with. Sensitivity was examined for damage model parameters, which dominate strain level at which a finite element becomes softened and finally loses its load-carrying capacity, and two sets of plasticity model parameters calibrated for irradiated and unirradiated materials. In the calculation, large stress concentration occurred in the regions between the tips of two adjacent cracks, and one pair of such cracks, typically one of the longest radial cracks existing in the outer periphery of the cladding, then linked to form a longer crack. The simulated macroscopic circumferential strain at failure of the OS-1 cladding model was lower than that of the LS-1 cladding model by about 40% or more. Limited sensitivity of the damage and plasticity model parameters, observed for the investigated range, suggests that the reduction of failure strain primarily reflects the difference in crack distributions between the two simulated rods. The results support the interpretation that the radially oriented hydrides contributed to the low PCMI-failure limit observed in Test OS-1.
三原 武; 宇田川 豊; 杉山 智之; 天谷 政樹
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(8), p.872 - 885, 2021/08
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:16.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)To evaluate the effects of the hydride morphology and initial temperature of fuel cladding on the pellet-cladding mechanical interaction failure under reactivity-initiated accident (RIA) conditions, RIA-simulated experiments were performed on high-burnup fuels with stress-relieved annealed (SR) and recrystallized (RX) M-MDA cladding at room and high (
cladding at room and high ( 280
280 C) temperatures. The results demonstrated that the failure-limit trend of RX-cladded fuels being lower than that of SR-cladded fuels for a similar hydrogen content holds up to at least about 700 wtppm. The observation of the fracture surfaces of failed RX cladding suggests a contribution of radially-oriented hydrides to the crack formation and/or penetration, which coincides with the aforementioned failure-limit trend. The temperature effect, namely the failure-limit rise at a high temperature, is evident irrespective of the hydride morphology, while the degree of the temperature effect decreases as the hydrogen content increases.
C) temperatures. The results demonstrated that the failure-limit trend of RX-cladded fuels being lower than that of SR-cladded fuels for a similar hydrogen content holds up to at least about 700 wtppm. The observation of the fracture surfaces of failed RX cladding suggests a contribution of radially-oriented hydrides to the crack formation and/or penetration, which coincides with the aforementioned failure-limit trend. The temperature effect, namely the failure-limit rise at a high temperature, is evident irrespective of the hydride morphology, while the degree of the temperature effect decreases as the hydrogen content increases.
Li, F.; 三原 武; 宇田川 豊; 天谷 政樹
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2020/08
Fuel cladding may be subjected to biaxial tensile stress in axial and hoop directions during pellet-cladding mechanical interaction (PCMI) of a reactivity-initiated accident (RIA). Incipient crack in the hydride rim assisted by the scattered hydrides in the metal phase may lead to failure of the cladding at small hoop strain level during PCMI. To get insight of such phenomenon, biaxial-EDC tests under axial to hoop strain ratios ranging from 0 to 1 were performed with pre-cracked (outer surface) and uniformly hydrided Zircaloy-4 cladding tube samples with final heat-treatment status of cold worked (CW), stress relieved (SR) and Recrystallized (RX). Results showed dependencies of failure hoop strain on pre-crack depth, strain ratio, hydrogen content and final heat-treatment status on fabrication, but no apparent dependencies were observed on the distribution pattern of hydrides (with similar hydrogen contents and hydrides predominantly precipitated in hoop direction) and the heat-treatment process for hydrogen charging. J integral at failure seems to be available to unify the effect of pre-crack depth.
Li, F.; 三原 武; 宇田川 豊; 天谷 政樹
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(6), p.633 - 645, 2020/06
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:24.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)To better understand the failure limit of fuel cladding during the pellet-cladding mechanical interaction (PCMI) phase of a reactivity-initiated accident (RIA), pre-cracked and hydrided cladding samples with base metal final heat-treatment status of cold worked (CW) and recrystallized (RX) were tested under biaxial stress conditions (axial to hoop strain ratios of 0 and 0.5). Displacement-controlled biaxial-expansion-due-to-compression (biaxial-EDC) tests were performed to obtain the hoop strain at failure (failure strain) of the samples. The conversion of the failure strains to J-integral at failure by finite-element analysis involving data of stress-relieved (SR) cladding specimens from our previous study revealed that the failure limit in the dimension of J-integral at failure unifies the effects of pre-crack depth. About 30 to 50 percent reduction in the J-integral at failure was observed as the strain ratio increased from 0 to 0.5 irrespective of the annealing type, pre-crack depth, and hydrogen content. the rate of fractional decreases of J-integral at failure with increase of hydrogen content are in the order of CW SR
SR RX, which are essentially independent of strain ratio for the CW and SR samples. The results were incorporated into the failure prediction model of the JAEA's fuel performance code in the form of a correction factor that considers the biaxial loading effect.
RX, which are essentially independent of strain ratio for the CW and SR samples. The results were incorporated into the failure prediction model of the JAEA's fuel performance code in the form of a correction factor that considers the biaxial loading effect.
 and chromia-alumina additive fuels under simulated reactivity-initiated accidents; A Comparative analysis with FEMAXI-8
and chromia-alumina additive fuels under simulated reactivity-initiated accidents; A Comparative analysis with FEMAXI-8宇田川 豊; 三原 武; 谷口 良徳; 垣内 一雄; 天谷 政樹
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 139, p.107268_1 - 107268_9, 2020/05
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:35.51(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper reports a computer-code analysis on the base-irradiation behavior of the chromia-and-alumina-doped BWR rod irradiated to 64 GWd/t in Oskarshamn-3, Sweden, and subjected to the reactivity-initiated-accident (RIA) test OS-1, which resulted in a fuel failure due to pellet-cladding mechanical interaction (PCMI) at the lowest fuel-enthalpy increase in all the BWR tests ever performed. The inverse calculation which utilized post-irradiation examination data as its constraint conditions revealed that the OS-1 rod had very likely experienced more intense PCMI loading due to higher swelling rate during base irradiation than other BWR rods subjected to previous RIA tests and thus had been prone to experience enhanced radial-hydride formation. The significant difference in the cladding hoop-stress more than 50 MPa discriminates the OS-1 rod from other BWR rods and supports the interpretation that enhanced radial-hydrides formation differentiated the PCMI-failure behavior observed in the test OS-1 from the previous BWR-fuel tests.
天谷 政樹; 垣内 一雄; 三原 武
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.1048 - 1056, 2019/09
New fuel cladding alloys of which composition was changed from conventional ones have been developed by nuclear fuel vendors and utilities. Since the irradiation growth of fuel cladding is one of the most important parameters which determine the dimensional stability of fuel rod and/or fuel assembly during normal operation, the irradiation growth behavior of the improved Zr-based alloys for light-water reactor fuel cladding was investigated. The coupon specimens were prepared from fuel cladding tubes with various kinds of improved Zr-based alloys. The specimens were loaded into test rigs and had been irradiated in the Halden reactor in Norway under several coolant temperature conditions up to a fast-neutron fluence of  7.8
7.8 10
10 (n/cm
(n/cm , E
, E  1 MeV). Irradiation conditions such as specimen temperatures had been continuously monitored during the irradiation. During and after the irradiation, the amount of irradiation growth of each specimen was evaluated as a part of the interim and final inspections. The effect of the difference in alloy composition on the amount of irradiation growth seemed insignificant if the other conditions e.g. the final heat treatment condition at fabrication and the irradiation temperature were the same.
1 MeV). Irradiation conditions such as specimen temperatures had been continuously monitored during the irradiation. During and after the irradiation, the amount of irradiation growth of each specimen was evaluated as a part of the interim and final inspections. The effect of the difference in alloy composition on the amount of irradiation growth seemed insignificant if the other conditions e.g. the final heat treatment condition at fabrication and the irradiation temperature were the same.
三原 武; 宇田川 豊; 天谷 政樹; 谷口 良徳; 垣内 一雄
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.544 - 550, 2019/09
In order to assess effects of additives for fuel pellet on the fuel behavior during a reactivity-initiated accident (RIA), fuels with additives irradiated in commercial light water reactors (LWRs) in Europe up to high burnup were subjected to pulse-irradiation experiments in Nuclear Safety Research Reactor (NSRR) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). Two tests were performed: test LS-4 with chromia-doped UO and Zry-2 cladding with liner and test OS-1 with ADOPT
and Zry-2 cladding with liner and test OS-1 with ADOPT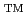 (chromia-and-alumina-doped UO
(chromia-and-alumina-doped UO ) pellet and Zry-2 cladding with liner. The test fuel rod of LS-4 did not fail. The test fuel rod of OS-1 was considered to be failed by hydride-assisted pellet-cladding mechanical interaction (PCMI). The fuel failure limit in OS-1 was the lowest among the test results ever obtained at the NSRR in similar burnup range. The morphology of the hydrides precipitated in the fuel cladding of OS-1 was investigated by metallography and compared with previous results obtained in JAEA in connection focusing fuel failure limit. It was suggested that the observed lower limit of fuel failure was related to the amount and length of the hydride precipitated along the radial direction of cladding.
) pellet and Zry-2 cladding with liner. The test fuel rod of LS-4 did not fail. The test fuel rod of OS-1 was considered to be failed by hydride-assisted pellet-cladding mechanical interaction (PCMI). The fuel failure limit in OS-1 was the lowest among the test results ever obtained at the NSRR in similar burnup range. The morphology of the hydrides precipitated in the fuel cladding of OS-1 was investigated by metallography and compared with previous results obtained in JAEA in connection focusing fuel failure limit. It was suggested that the observed lower limit of fuel failure was related to the amount and length of the hydride precipitated along the radial direction of cladding.
谷口 良徳; 宇田川 豊; 三原 武; 天谷 政樹; 垣内 一雄
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.551 - 558, 2019/09
A pulse-irradiation test CN-1 on a high-burnup MOX fuel with M5 cladding was conducted at the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor (NSRR) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). Although the transient signals obtained during the pulse-irradiation test did not show any signs of the occurrence of PCMI failure, the failure of the test fuel rod was confirmed from the visual inspection carried out after test CN-1. Analyses using fuel performance codes FEMAXI-8 and RANNS were also performed in order to investigate the fuel behavior during normal operation and pulse-irradiation regarding the test fuel rod of CN-1, and the results were consistent with this observation result. These experimental and calculation results suggested that the failure of test fuel rod of CN-1 was not caused by hydride-assisted PCMI but high-temperature rupture following the increase in rod internal pressure. The occurrence of this failure mode might be related to the ductility remained in the M5
cladding was conducted at the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor (NSRR) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). Although the transient signals obtained during the pulse-irradiation test did not show any signs of the occurrence of PCMI failure, the failure of the test fuel rod was confirmed from the visual inspection carried out after test CN-1. Analyses using fuel performance codes FEMAXI-8 and RANNS were also performed in order to investigate the fuel behavior during normal operation and pulse-irradiation regarding the test fuel rod of CN-1, and the results were consistent with this observation result. These experimental and calculation results suggested that the failure of test fuel rod of CN-1 was not caused by hydride-assisted PCMI but high-temperature rupture following the increase in rod internal pressure. The occurrence of this failure mode might be related to the ductility remained in the M5 cladding owing to its low content of the hydrogen absorbed during normal operation.
cladding owing to its low content of the hydrogen absorbed during normal operation.
三原 武; 宇田川 豊; 天谷 政樹
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(8), p.724 - 730, 2019/08
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Pellet-cladding mechanical interaction (PCMI) under reactivity-initiated accident conditions may lead to failure of high-burnup fuel rods. Zircaloy cladding tubes are subjected to biaxial stress states induced by PCMI loading. This type of stress state, specific to PCMI, presumably makes the tubes more susceptible to failure. To clarify the influence of the anisotropic mechanical properties of Zircaloy cladding tubes on their fracture behavior under biaxial stress conditions, biaxial tensile tests were performed, and the measured stresses and strains were converted to reduced parameters such as equivalent strain, equivalent stress, and stress triaxiality by using the anisotropic constants of the Hill yield function derived in our previous study. The minimum fracture strains for recrystallized (RX) and stress-relieved (SR) specimens were located where the stress ratio of axial to circumferential is 0.75 in the measured range. The equivalent plastic fracture strains tended to decrease monotonously with increasing stress triaxiality, which is a typical trend observed in ductile fracture, in the range of 0.65-0.78 for both specimens. In the case of SR specimens, however, the analysis with stress triaxiality did not reduce the fracture strains well to a single trend curve, showing that the anisotropic constants used in the present work or Hill yield function itself is not enough to describe the whole anisotropy involved in the fracture process of SR material.
Li, F.; 三原 武; 宇田川 豊; 天谷 政樹
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(5), p.432 - 439, 2019/05
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:55.67(Nuclear Science & Technology)Hydride precipitates are considered to affect cladding integrity adversely during pellet-cladding mechanical interaction (PCMI) in a reactivity-initiated accident (RIA). This study aims to clarify the role of hydride precipitates in cladding failure under the biaxial stress condition. The amount and distribution of hydride precipitates (hydride morphology) were evaluated quantitatively and hydrogen content was measured to assess its effect on the decrease in outer surface hoop strain at failure (failure strain) of the samples. The decrease in failure strain of the hydrided samples was found to be more significant under lower strain ratios in the samples with shallower pre-crack. The failure strain of sample tended to be more sensitive to hydrogen content under the strain ratio with a higher axial component in the case of samples with hydrogen contents higher than ~150 wppm.
天谷 政樹; 宇田川 豊; 成川 隆文; 三原 武; 谷口 良徳
Proceedings of Annual Topical Meeting on Reactor Fuel Performance (TopFuel 2018) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2018/10
Fuels for light water reactors (LWRs) which consist of improved cladding materials and pellets have been developed by utilities and fuel vendors to acquire better fuel performance even in the high burnup region and also raise the safety level of current nuclear power plants to a higher one. In order to evaluate adequacy of the present regulatory criteria in Japan and safety margins regarding the fuel with improved materials, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has conducted ALPS-II program sponsored by Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA), Japan. In this program, the tests simulating a reactivity-initiated accident (RIA) and a loss-of-coolant accident (LOCA) have been performed on the high burnup advanced fuels irradiated in commercial PWR or BWR in Europe. This paper presents recent results obtained in this program with respect to RIA, and main results of LOCA experiments, which have been obtained in the ALPS-II program, are summarized.
三原 武; 宇田川 豊; 天谷 政樹
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(2), p.151 - 159, 2018/02
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:67.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)Pellet-cladding mechanical interaction (PCMI) under reactivity-initiated accident conditions may lead to the failure of high-burnup fuel rods. Biaxial stress states generated by PCMI in Zircaloy cladding may make the cladding more susceptible to failure. In this study, we investigated the deformation behavior of Zircaloy cladding under biaxial stress conditions based on the concept of contours of equal plastic work. The major axis angles of the initial work contours of recrystallized (RX) and stress-relieved (SR) specimens were investigated and it was found that the shapes of the initial work contours of these kinds of specimens were almost symmetric across the direction where the ratio of axial stress to circumferential stress is 1. The shapes of subsequent work contours tended to change for the RX specimen while be the same as the initial for the SR specimen, as deformation proceeded. It was suggested that the textures and slip systems in the RX and SR specimens affect their initial work contours while the slip system in the RX specimens and the residual strain in the SR specimens influence the subsequent work contours.
天谷 政樹; 宇田川 豊; 成川 隆文; 三原 武; 谷口 良徳
Proceedings of 2017 Water Reactor Fuel Performance Meeting (WRFPM 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2017/09
JAEA has conducted a research program called ALPS-II program for advanced fuels of LWRs. In this program, the tests simulating a RIA and a LOCA have been performed on the high burnup advanced fuels irradiated in European commercial reactors. The failure limits of the high-burnup advanced fuels under RIA conditions have been obtained by the pulse irradiation tests at the NSRR in JAEA. The information about pellet fragmentation etc. during the pulse irradiations was also obtained from post-test examinations on the test rods after the pulse irradiation tests. As for the simulated LOCA test, integral thermal shock tests and high-temperature oxidation tests have been performed at the RFEF in JAEA. The fracture limits under LOCA and post-LOCA conditions etc. of the high-burnup advanced fuel cladding have been investigated, and it was found that in terms of these materials the fracture boundaries do not decrease and the oxidation does not significantly accelerate in the burnup level examined.
Li, F.; 三原 武; 宇田川 豊; 天谷 政樹
Proceedings of 25th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-25) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2017/07
The failure behavior of cladding tube was investigated by using the improved EDC test apparatus. Cold-worked, stress-relieved and recrystallized Zircaloy-4 tubes with a pre-crack were used as test specimens: this pre-crack simulated the crack which is considered to form in the hydride rim of high-burnup fuel cladding at the beginning of PCMI failure. In the EDC test, a tensile stress in axial direction was applied and displacement-controlled loading was performed to keep the strain ratio of axial/hoop as a constant. The data of cladding deformation had been achieved in the range of strain ratio of 0, 0.25, 0.5 and 0.75 and pre-crack depth of 41-87 micrometers. Failures in hoop direction were observed in all the tested samples, and a general trend that higher strain ratio and deeper crack depth lead to lower failure limit in hoop direction could be seen. Different crack propagation mode was observed between recrystallized and stress relieved and cold worked samples.
篠崎 崇*; 宇田川 豊; 三原 武; 杉山 智之; 天谷 政樹
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(9), p.1426 - 1434, 2016/09
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:79.24(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to investigate the failure behavior of fuel cladding under a reactivity-initiated accident (RIA) condition, biaxial stress tests on unirradiated Zircaloy-4 cladding tube with an outer surface pre-crack were carried out under room temperature conditions by using an improved Expansion-Due-to-Compression (improved-EDC) test method which was developed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The specimens with an outer surface pre-crack were prepared by using RAG (Rolling After Grooving) method. In each test, a constant longitudinal tensile load of 0, 5.0 or 10.0 kN was applied along the axial direction of specimen, respectively. All specimens failed during the tests, and the morphology at the failure opening of the specimens was similar to that observed in the result of post-irradiation examinations of high burnup fuel which failed during a pulse irradiation experiment. The longitudinal strain (
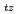 ) at failure clearly increased with increasing longitudinal tensile loads and the circumferential strain (
) at failure clearly increased with increasing longitudinal tensile loads and the circumferential strain (
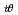 ) at failure significantly decreased in the case of 5.0 and 10.0 kN tests, compared with the case of 0 kN tests. It is considered that the data obtained in this study can be used as a fundamental basis for quantifying the failure criteria of fuel cladding under a biaxial stress state.
) at failure significantly decreased in the case of 5.0 and 10.0 kN tests, compared with the case of 0 kN tests. It is considered that the data obtained in this study can be used as a fundamental basis for quantifying the failure criteria of fuel cladding under a biaxial stress state.