Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 by ion beam breeding technology
by ion beam breeding technology佐藤 勝也; 上田 涼史郎*; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成*; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 100, 2016/02
Bioremediation uses biological organisms to solve an environmental problem. However, microorganisms are sometimes not enough effective to achieve efficient recovery. Therefore, enhancing the functionality of microorganisms is needed to promote the active use of bioremediation. This study began with the purpose of development of Cs-accumulating bacteria by ion beam breeding technology. Previously, we suggested that  is the most suitable species for the development of high Cs-accumulating bacteria by ion beam breeding technology. Candidates of Cs-accumulating mutant were screened from the mutagenized cells by ion beam breeding technology on the basis of the luminescent intensity and the cell area as indicators of intracellular Cs level and cell growth, respectively. As a result, we obtained 33 candidates, whose Cs-accumulating abilities were over 2-fold higher than that of the wild-type, from the population of mutagenized cells.
is the most suitable species for the development of high Cs-accumulating bacteria by ion beam breeding technology. Candidates of Cs-accumulating mutant were screened from the mutagenized cells by ion beam breeding technology on the basis of the luminescent intensity and the cell area as indicators of intracellular Cs level and cell growth, respectively. As a result, we obtained 33 candidates, whose Cs-accumulating abilities were over 2-fold higher than that of the wild-type, from the population of mutagenized cells.

上田 涼史郎*; 佐藤 勝也; 林 秀謙*; 鳴海 一成*; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 101, 2016/02
It is suggesting a possibility that the polyphosphate granules in cells could accumulate harmful metal ions such as radiocesium to protect the cells from cytotoxicity. In this study, we investigated the accumulation of cesium and its association with intracellular polyphosphate in  using the gene disruptant and overexpressing strains. The cesium accumulation level in the disruptant and overexpressing strains was compared with that of the wild-type strain. The cesium accumulations in the
using the gene disruptant and overexpressing strains. The cesium accumulation level in the disruptant and overexpressing strains was compared with that of the wild-type strain. The cesium accumulations in the 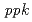 disruptant and overexpressing strains were slightly decreased and almost same, respectively. Like the intracellular polyphosphate level, the cesium accumulation level was significantly increased in the
disruptant and overexpressing strains were slightly decreased and almost same, respectively. Like the intracellular polyphosphate level, the cesium accumulation level was significantly increased in the 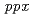 disruptant strain. These results suggested that the intracellular polyphosphate level was positively correlated with the cesium accumulation level in
disruptant strain. These results suggested that the intracellular polyphosphate level was positively correlated with the cesium accumulation level in  .
.
佐藤 勝也; 上田 涼史郎; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成*; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 117, 2015/03
Bioremediation uses biological organisms to solve an environmental problem. However, microorganisms are sometimes not enough effective to achieve efficient recovery. Therefore, enhancing the functionality of microorganisms is needed to promote the active use of bioremediation. This study began with the purpose of development of Cs-accumulating bacteria by ion beam breeding technology. We investigated which members are better suited for Cs-accumulation in the genus  (
( ,
, 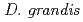 ,
, 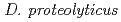 ,
, 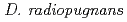 ,
,  and
and 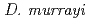 ) exhibit extraordinary radioresistant. The Cs concentration in the
) exhibit extraordinary radioresistant. The Cs concentration in the  cells exhibited over 4-fold compared with that of the
cells exhibited over 4-fold compared with that of the  by atomic absorption spectrometer analysis. This result suggested that
by atomic absorption spectrometer analysis. This result suggested that  and
and 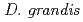 are best two suitable species for the development of high Cs-accumulating bacteria by ion beam breeding technology.
are best two suitable species for the development of high Cs-accumulating bacteria by ion beam breeding technology.

上田 涼史郎; 佐藤 勝也; 林 秀謙*; 鳴海 一成*; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 118, 2015/03
It is suggesting a possibility that the polyphosphate granules in cells could accumulate harmful metal ions such as radiocesium to protect the cells from cytotoxicity.  has been considered as a microorganism for bioremediation under highly radioactive contaminated environments. We generated the polyphosphate biosynthesis-related genes (
has been considered as a microorganism for bioremediation under highly radioactive contaminated environments. We generated the polyphosphate biosynthesis-related genes (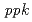 and
and 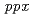 ) disruptant strains and characterized their disruption effect to clarify the role of polyphosphate for the accumulation of cesium in
) disruptant strains and characterized their disruption effect to clarify the role of polyphosphate for the accumulation of cesium in  . The intracellular levels of polyphosphates in the
. The intracellular levels of polyphosphates in the 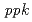 disruptant and overexpressing strains were almost same and slightly increased, respectively. On other hand, the intracellular level of polyphosphates significantly increased in the
disruptant and overexpressing strains were almost same and slightly increased, respectively. On other hand, the intracellular level of polyphosphates significantly increased in the 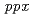 disruptant strains, suggesting that the
disruptant strains, suggesting that the 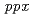 gene plays an important role in the accumulation of polyphosphate in
gene plays an important role in the accumulation of polyphosphate in  .
.
増渕 隆*; 日向 弘和*; 上田 涼史郎; 林 秀謙*; 池永 裕*; 佐藤 勝也; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 123, 2015/03
We analyzed genome sequence of the high ethyl caproate producing sake yeast mutant (No.227) generated by ion beam breeding in order to investigated factors contributing the reduced ability to alcohol fermentation. In the high ethyl caproate producing sake yeast, four pyruvate decarboxylase genes (PDC), six alcohol dehydrogenase genes (ADH), two biotin synthesis genes (BIO) and chitinase gene (CTS1) might be involved in the reduced ability to alcohol fermentation. The genome sequence of the strain No.227 was determined by a whole-genome shotgun strategy using pyrosequencing method and compared with the whole-genome sequence of the sake yeast strain Kyokai 7, which is characterized by the fermentation property, as a reference sequence. For the PDC, ADH, BIO and CTS1 loci, no mutation was found in the strain No.227, suggesting that these genes did not involved in the reduced ability to alcohol fermentation.
増淵 隆*; 上田 涼史郎; 上山 修*; 池永 裕*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 117, 2014/03
We have previously obtained high ethyl caproate producing Sake yeasts "No.227" and "No.1333" by ion beam breeding. The fatty acid synthase genes ( and
and 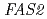 ) and the fatty acid esterase genes (
) and the fatty acid esterase genes ( and
and  ) might be involved in the higher production of ethyl caproate in the mutant strains. In this study, to identify the mutation sites of the mutant strains, each gene locus was sequenced. For the
) might be involved in the higher production of ethyl caproate in the mutant strains. In this study, to identify the mutation sites of the mutant strains, each gene locus was sequenced. For the  ,
,  and
and  loci, all the mutations found in mutant strains are nonsense mutations, suggesting that these mutations did not involved in the higher production of ethyl caproate. On the other hand, strains No.227 and No.1333 carried G/A and A/A mutations in
loci, all the mutations found in mutant strains are nonsense mutations, suggesting that these mutations did not involved in the higher production of ethyl caproate. On the other hand, strains No.227 and No.1333 carried G/A and A/A mutations in 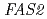 gene at nucleotide position 3,748 as heterozygous and homozygous states, respectively. This result strongly suggested that the higher production of ethyl caproate in strains No.227 and No.1333 is attributed to a dominant mutation in
gene at nucleotide position 3,748 as heterozygous and homozygous states, respectively. This result strongly suggested that the higher production of ethyl caproate in strains No.227 and No.1333 is attributed to a dominant mutation in 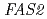 gene.
gene.
佐藤 勝也; 上田 涼史郎; 増淵 隆*; 上山 修*; 林 秀謙*; 池永 裕*; 鳴海 一成*; 田中 淳
no journal, ,
群馬県では、群馬産業技術センターが中心となり、特色ある吟醸酒の開発を目指して、清酒酵母の育種に取り組んでいる。これまでにイオンビームを用いた変異誘発処理により、吟醸酒の香気成分の一つであるカプロン酸エチルを高生産する変異株を取得し、群馬オリジナルの新しい清酒酵母として、希望する県内の酒造蔵に頒布している。このように、優良形質を持った清酒酵母が得られた一方で、優良な変異株を選抜するためには多大な労力を要するのが現状である。そこで、カプロン酸エチル生合成に関連する4つの遺伝子( ,
, 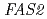 ,
,  及び
及び )について、イオンビーム育種により作出した優良清酒酵母のゲノムDNAの塩基配列を解析することでカプロン酸エチルを高生産する要因を明らかにするとともに、優良な変異株を早期選抜できるDNAマーカーの開発が可能か検討した。
)について、イオンビーム育種により作出した優良清酒酵母のゲノムDNAの塩基配列を解析することでカプロン酸エチルを高生産する要因を明らかにするとともに、優良な変異株を早期選抜できるDNAマーカーの開発が可能か検討した。
佐藤 勝也; 増淵 隆*; 上山 修*; 上田 涼史郎; 林 秀謙*; 池永 裕*; 鳴海 一成*
no journal, ,
清酒酵母は、地域産業振興の有力なツールであるが、年々その消費量は減少傾向にある。そこで、市場のニーズに迅速に対応すべく、新しいタイプの清酒酵母の育種が必要となっている。平成20年度より、原子力機構は、群馬県立群馬産業技術センターとの連携を密接に図りながら、特色ある吟醸酒の開発・実用化を目指し、イオンビーム育種技術を活用して、吟醸酒特有の香り成分の主成分の一つであるカプロン酸エチルを高生産する新たな吟醸用清酒酵母の育種に着手した。その結果、香気成分生成能・発酵力共に良好な吟醸酒製造に適した新たな清酒酵母の作出に成功した。さらに、新規清酒酵母を用いて醸造された吟醸酒の販売が平成25年4月より開始されている。また、新規清酒酵母におけるカプロン酸エチルを高生産する要因の一つとして、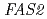 遺伝子内に点突然変異を有することを明らかにした。
遺伝子内に点突然変異を有することを明らかにした。
増淵 隆*; 上山 修*; 上田 涼史郎; 池永 裕*; 林 秀謙*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*
no journal, ,
群馬県では、群馬産業技術センターが中心となり、特色ある吟醸酒の開発を目指して、清酒酵母の育種に取り組んでいる。これまでにイオンビームを用いた変異誘発処理により、吟醸酒の香気成分の一つであるカプロン酸エチルを高生産する変異株を取得し、群馬オリジナルの新しい清酒酵母として、希望する県内の酒造蔵に頒布している。このように、優良形質を持った清酒酵母が得られた一方で、優良な変異株を選抜するためには多大な労力を要するのが現状である。そこで、カプロン酸エチル生合成に関連する4つの遺伝子( ,
, 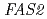 ,
,  及び
及び )について、イオンビーム育種により作出した優良清酒酵母のゲノムDNAの塩基配列を解析することでカプロン酸エチルを高生産する要因を明らかにするとともに、優良な変異株を早期選抜できるDNAマーカーの開発が可能か検討した。その結果、作出した優良清酒酵母は、変異型の
)について、イオンビーム育種により作出した優良清酒酵母のゲノムDNAの塩基配列を解析することでカプロン酸エチルを高生産する要因を明らかにするとともに、優良な変異株を早期選抜できるDNAマーカーの開発が可能か検討した。その結果、作出した優良清酒酵母は、変異型の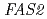 遺伝子を有することで、カプロン酸エチルを高生産することを明らかにした。
遺伝子を有することで、カプロン酸エチルを高生産することを明らかにした。
佐藤 勝也; 上田 涼史郎; 長谷 純宏; 大野 豊; 鳴海 一成*
no journal, ,
汚染環境の浄化技術として、微生物を活用したバイオレメディエーションは、物理的・化学的技術に比べ、環境負荷が小さいだけではなく、多様な汚染物質に対して適用可能であり、重要な技術として注目され、今後の利用拡大が期待されている。しかし、まだまだ微生物機能が低いという課題がある。そこで、資源確保や環境保全を踏まえた微生物の有効利用をさらに推進するためには、微生物の機能の向上が必要である。放射性セシウムの吸収・蓄積に微生物バイオレメディエーション技術を利用した場合、当然のことながら、微生物は被爆することから、期待される吸収・蓄積効果が見込めない可能性がある。そのため、放射能汚染環境下では、放射線に耐性を有する微生物の利用が適している。本研究では、デイノコッカス属細菌にイオンビーム誘発突然変異育種技術を活用し、遺伝子組換え技術に依存しない方法で、セシウム蓄積能の向上した突然変異体の創成を目的とした。
上田 涼史郎; 佐藤 勝也; 林 秀謙*; 鳴海 一成*; 大野 豊
no journal, ,
生体高分子であるポリリン酸は、リン酸が直鎖状に結合したポリマーであり、微生物の細胞内では負電荷を持つ形で蓄積されている。そのため、正電荷を持つ有害な金属イオンを捕捉し、細胞毒性の少ない形で蓄積されると考えられている。一方、放射線抵抗性細菌デイノコッカス・ラジオデュランスは、効率的なDNA修復能に起因する高い放射線耐性を有しており、放射能汚染環境下における微生物バイオレメディエーションへの利用が期待されている。東日本大震災の影響による東京電力福島第一原子力発電所の事故によって環境中に放出された放射性セシウムを回収・除去することは緊急の課題である。そこで本研究では、ラジオデュランスにおけるポリリン酸生合成関連遺伝子(polyphosphate kinaseをコードする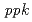 遺伝子及びexopolyphosphataseをコードする
遺伝子及びexopolyphosphataseをコードする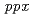 遺伝子)に着目し、これら遺伝子を破壊あるいは改変させることでポリリン酸蓄積への影響について解析した。
遺伝子)に着目し、これら遺伝子を破壊あるいは改変させることでポリリン酸蓄積への影響について解析した。
佐藤 勝也; 上田 涼史郎; 長谷 純宏; 大野 豊; 鳴海 一成*
no journal, ,
微生物によるバイオレメディエーションは、微生物の機能を活用して環境に有害な金属や汚染物質を除去することで、汚染環境の浄化・修復を図る技術である。しかし、目的の性能を十分に満たす微生物を得ることは困難である場合が多い。そこで、資源確保や環境保全を踏まえた微生物の有効利用を推進するためには、性能が向上した微生物を人為的に得る必要がある。また、微生物バイオレメディエーション技術を放射性物質の吸収・蓄積に利用しようとする場合は、細胞への放射線影響によって、期待される吸収・蓄積効果が見込めない可能性がある。デイノコッカス属細菌は、他の生物にとって致死的効果あるいは変異原性を示す放射線に対して極めて高い耐性を示すので、放射能汚染環境下でのバイオレメディエーションに適した微生物として有望視されている。本研究では、放射性セシウムの効率的な回収に資するため、デイノコッカス属細菌にイオンビーム誘発突然変異育種技術を適用することで、セシウム濃縮能が向上した突然変異体を創成することを目的とした。
上田 涼史郎; 佐藤 勝也; 林 秀謙*; 鳴海 一成*; 大野 豊
no journal, ,
生体高分子であるポリリン酸は、リン酸が直鎖状に結合したポリマーであり、微生物の細胞内では負電荷を持つ形で蓄積されている。そのため、正電荷を持つ有害な金属イオンを捕捉し、細胞毒性の少ない形で蓄積されると考えられている。一方、放射線抵抗性細菌デイノコッカス・ラジオデュランスは、突然変異及び致死効果のある放射線に対して非常に高い抵抗性を持つため、放射能汚染環境下における微生物バイオレメディエーションへの利用が期待できる。そこで、本研究では、ラジオデュランスにおけるポリリン酸生合成関連遺伝子(polyphosphate kinaseをコードする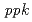 遺伝子及びexopolyphosphataseをコードする
遺伝子及びexopolyphosphataseをコードする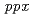 遺伝子)に着目し、これら遺伝子を破壊あるいは改変させることでポリリン酸蓄積への影響を明らかにし、セシウム濃縮菌の開発に向けた重要な知見を蓄積することを目的とした。
遺伝子)に着目し、これら遺伝子を破壊あるいは改変させることでポリリン酸蓄積への影響を明らかにし、セシウム濃縮菌の開発に向けた重要な知見を蓄積することを目的とした。
佐藤 勝也; 上田 涼史郎*; 長谷 純宏; 大野 豊; 鳴海 一成*
no journal, ,
放射性セシウムの効率的な回収に資するため、デイノコッカス・ラジオデュランスにイオンビーム誘発突然変異育種技術を活用し、遺伝子組換え技術に依存しない方法で、セシウム蓄積能の向上した突然変異体を創成することを目的とした。イオンビーム照射により作出した突然変異集団から、それぞれ菌体内セシウム蓄積と細胞増殖の指標として、セシウム蓄積変異株候補株を選抜した。その結果、突然変異集団から、野生株よりも2倍以上のセシウム蓄積能を有するセシウム蓄積変異株候補株を33株選抜した。選抜したセシウム蓄積変異株候補株について、さらに詳細なセシウム蓄積能及び 線に対する耐性を評価する必要があるが、イオンビーム照射技術によって作出したこれらの変異株は、バイオレメディエーションの供試菌としての利用が期待できる。
線に対する耐性を評価する必要があるが、イオンビーム照射技術によって作出したこれらの変異株は、バイオレメディエーションの供試菌としての利用が期待できる。
上田 涼史郎*; 佐藤 勝也; 大野 豊; 林 秀謙*; 鳴海 一成*
no journal, ,
放射線抵抗性細菌デイノコッカス・ラジオデュランスにおけるポリリン酸生合成関連遺伝子(polyphosphate kinaseをコードする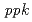 遺伝子及びexopolyphosphataseをコードする
遺伝子及びexopolyphosphataseをコードする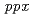 遺伝子)に着目し、これら遺伝子を破壊あるいは改変させることでポリリン酸蓄積への影響を明らかにし、セシウム蓄積との関連性について解析を行った。作製した遺伝子破壊株及び過剰発現株において、菌体内ポリリン酸蓄積量及びセシウム量を測定した。その結果、ポリリン酸蓄積量の増加に伴い、セシウム蓄積量が増加する傾向にあることから、ポリリン酸蓄積とセシウム蓄積に正の相関がある可能性が示唆された。さらに、ポリリン酸の高蓄積が
遺伝子)に着目し、これら遺伝子を破壊あるいは改変させることでポリリン酸蓄積への影響を明らかにし、セシウム蓄積との関連性について解析を行った。作製した遺伝子破壊株及び過剰発現株において、菌体内ポリリン酸蓄積量及びセシウム量を測定した。その結果、ポリリン酸蓄積量の増加に伴い、セシウム蓄積量が増加する傾向にあることから、ポリリン酸蓄積とセシウム蓄積に正の相関がある可能性が示唆された。さらに、ポリリン酸の高蓄積が 線耐性を低下させないことを明らかにした。
線耐性を低下させないことを明らかにした。