Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 is characterized as Type II bacterial topoisomerase and its activity is differentially regulated by PprA in vitro
is characterized as Type II bacterial topoisomerase and its activity is differentially regulated by PprA in vitroKota, S.*; Rajpurohit, Y. S.*; Charaka, V. K.*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*; Misra, H, S.*
Extremophiles, 20(2), p.195 - 205, 2016/03
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:40.92(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)The multipartite genome of  forms toroidal structure. It encodes topoisomerase IB and both the subunits of DNA gyrase (DrGyr) while lacks other bacterial topoisomerases. Recently, PprA a pleiotropic protein involved in radiation resistance in
forms toroidal structure. It encodes topoisomerase IB and both the subunits of DNA gyrase (DrGyr) while lacks other bacterial topoisomerases. Recently, PprA a pleiotropic protein involved in radiation resistance in  has been suggested for having roles in cell division and genome maintenance. In vivo interaction of PprA with topoisomerases has also been shown. DrGyr constituted from recombinant gyrase A and gyrase B subunits showed decatenation, relaxation and supercoiling activities. Wild type PprA stimulated DNA relaxation activity while inhibited supercoiling activity of DrGyr. Thus, we showed that DrGyr confers all three activities of bacterial type IIA family DNA topoisomerases, which are differentially regulated by PprA, highlighting the significant role of PprA in DrGyr activity regulation and genome maintenance in
has been suggested for having roles in cell division and genome maintenance. In vivo interaction of PprA with topoisomerases has also been shown. DrGyr constituted from recombinant gyrase A and gyrase B subunits showed decatenation, relaxation and supercoiling activities. Wild type PprA stimulated DNA relaxation activity while inhibited supercoiling activity of DrGyr. Thus, we showed that DrGyr confers all three activities of bacterial type IIA family DNA topoisomerases, which are differentially regulated by PprA, highlighting the significant role of PprA in DrGyr activity regulation and genome maintenance in  .
.
 by ion beam breeding technology
by ion beam breeding technology佐藤 勝也; 上田 涼史郎*; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成*; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 100, 2016/02
Bioremediation uses biological organisms to solve an environmental problem. However, microorganisms are sometimes not enough effective to achieve efficient recovery. Therefore, enhancing the functionality of microorganisms is needed to promote the active use of bioremediation. This study began with the purpose of development of Cs-accumulating bacteria by ion beam breeding technology. Previously, we suggested that  is the most suitable species for the development of high Cs-accumulating bacteria by ion beam breeding technology. Candidates of Cs-accumulating mutant were screened from the mutagenized cells by ion beam breeding technology on the basis of the luminescent intensity and the cell area as indicators of intracellular Cs level and cell growth, respectively. As a result, we obtained 33 candidates, whose Cs-accumulating abilities were over 2-fold higher than that of the wild-type, from the population of mutagenized cells.
is the most suitable species for the development of high Cs-accumulating bacteria by ion beam breeding technology. Candidates of Cs-accumulating mutant were screened from the mutagenized cells by ion beam breeding technology on the basis of the luminescent intensity and the cell area as indicators of intracellular Cs level and cell growth, respectively. As a result, we obtained 33 candidates, whose Cs-accumulating abilities were over 2-fold higher than that of the wild-type, from the population of mutagenized cells.

上田 涼史郎*; 佐藤 勝也; 林 秀謙*; 鳴海 一成*; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 101, 2016/02
It is suggesting a possibility that the polyphosphate granules in cells could accumulate harmful metal ions such as radiocesium to protect the cells from cytotoxicity. In this study, we investigated the accumulation of cesium and its association with intracellular polyphosphate in  using the gene disruptant and overexpressing strains. The cesium accumulation level in the disruptant and overexpressing strains was compared with that of the wild-type strain. The cesium accumulations in the
using the gene disruptant and overexpressing strains. The cesium accumulation level in the disruptant and overexpressing strains was compared with that of the wild-type strain. The cesium accumulations in the 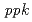 disruptant and overexpressing strains were slightly decreased and almost same, respectively. Like the intracellular polyphosphate level, the cesium accumulation level was significantly increased in the
disruptant and overexpressing strains were slightly decreased and almost same, respectively. Like the intracellular polyphosphate level, the cesium accumulation level was significantly increased in the 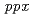 disruptant strain. These results suggested that the intracellular polyphosphate level was positively correlated with the cesium accumulation level in
disruptant strain. These results suggested that the intracellular polyphosphate level was positively correlated with the cesium accumulation level in  .
.
 mutant
mutant北村 智; 大野 豊; 鳴海 一成*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 64, 2016/02
イオンビームは新しい変異体を誘発するのに効果的である。既存のイオンビーム変異体に対するイオンビーム再照射は、イオンビームがゲノムの一部のみを改変する特徴を活かした変異誘発法で、植物の形質を一歩ずつ改変していくのに有効である。今回、シロイヌナズナにおいてイオンビーム照射法を適用し、従来法では得られないような色素蓄積変異体の選抜を行った。
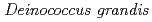 , isolated from freshwater fish in Japan
, isolated from freshwater fish in Japan佐藤 勝也; 小野寺 威文*; 面曽 宏太*; 武田-矢野 喜代子*; 片山 豪*; 大野 豊; 鳴海 一成*
Genome Announcements (Internet), 4(1), p.e01631-15_1 - e01631-15_2, 2016/01
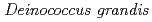 was isolated as a gram-negative, red-pigmented, radioresistant, rod-shaped bacterium from freshwater fish. The draft genome sequence of
was isolated as a gram-negative, red-pigmented, radioresistant, rod-shaped bacterium from freshwater fish. The draft genome sequence of 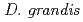 ATCC 43672 was 4,092,497 bp, with an average G+C content of 67.5% and comprised of 4 circular contigs and 3 linear contigs that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/Genbank under the accession number BCMS00000000. The draft genome sequence indicates that
ATCC 43672 was 4,092,497 bp, with an average G+C content of 67.5% and comprised of 4 circular contigs and 3 linear contigs that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/Genbank under the accession number BCMS00000000. The draft genome sequence indicates that 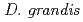 possesses a DNA damage response regulator (encoded by
possesses a DNA damage response regulator (encoded by  homolog) and radiation-desiccation response regulons (
homolog) and radiation-desiccation response regulons ( ,
, 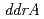 ,
, 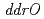 ,
,  and
and 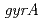 homologs etc.), which are involved in the unique radiation-desiccation response system in
homologs etc.), which are involved in the unique radiation-desiccation response system in  . As it is for
. As it is for  ,
, 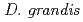 seems to employ the same radioresistant mechanisms. In future, the draft genome sequence of
seems to employ the same radioresistant mechanisms. In future, the draft genome sequence of 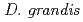 will be useful for elucidating the common principles of the radioresistance based on the extremely efficient DNA repair mechanisms in Deinococcus species by the comparative analysis of genomic sequences.
will be useful for elucidating the common principles of the radioresistance based on the extremely efficient DNA repair mechanisms in Deinococcus species by the comparative analysis of genomic sequences.
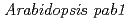 , a mutant with reduced anthocyanins in immature seeds from
, a mutant with reduced anthocyanins in immature seeds from 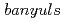 , harbors a mutation in the MATE transporter
, harbors a mutation in the MATE transporter 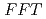
北村 智; 大野 豊; 鳴海 一成*
Plant Molecular Biology, 90(1-2), p.7 - 18, 2016/01
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:65.13(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)種皮にプロアントシアニジンに代わってアントシアニンを蓄積するシロイヌナズナ変異体banを用いて、イオンビームによる変異誘発を実施し、未熟種子におけるアントシアニン量の変化した変異体選抜を行うことで新規変異体pab1を得た。pab1はアントシアニン量が低下しているもののその合成酵素遺伝子の発現は正常であることがわかった。map-based cloningによってpab1変異体ではMATE型輸送体であるFFT遺伝子に変異が生じていることが明らかとなった。pab1変異体にFFT遺伝子を導入するとアントシアニン量が復帰したこと、FFT遺伝子が種皮のフラボノイド蓄積細胞層で発現していること、FFTタンパク質が液胞の膜に局在することから、FFTはアントシアニンの液胞蓄積のために液胞膜で機能していると考えられた。今回実施した変異体選抜を用いると、従来の変異体選抜では見つからないようなアントシアニン関連変異体が得られる可能性が示唆された。
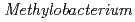 sp. ME121, isolated from soil as a mixed single colony with
sp. ME121, isolated from soil as a mixed single colony with 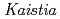 sp. 32K
sp. 32K藤浪 俊*; 武田 喜代子*; 小野寺 威文*; 佐藤 勝也; 清水 哲*; 若林 佑*; 鳴海 一成*; 中村 顕*; 伊藤 政博*
Genome Announcements (Internet), 3(5), p.e01005-15_1 - e01005-15_2, 2015/09
 sp. ME121 was isolated from soil as a mixed single colony with
sp. ME121 was isolated from soil as a mixed single colony with  sp. 32K during our screening of L-glucose-utilizing microorganisms, and its growth was enhanced by coculture. It was expected that genomic analysis of this bacterium would provide novel information on coculture-dependent growth enhancement. The genomic information of symbiotic bacteria could be of use for studying the molecular mechanisms underlying microbial symbiosis. The draft genome sequence of
sp. 32K during our screening of L-glucose-utilizing microorganisms, and its growth was enhanced by coculture. It was expected that genomic analysis of this bacterium would provide novel information on coculture-dependent growth enhancement. The genomic information of symbiotic bacteria could be of use for studying the molecular mechanisms underlying microbial symbiosis. The draft genome sequence of  sp. ME121 is 7,096,979 bp in total length and comprises 197 large contigs (
sp. ME121 is 7,096,979 bp in total length and comprises 197 large contigs ( 500 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank under the accession number BBUX00000000. The draft genome sequence shows that
500 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank under the accession number BBUX00000000. The draft genome sequence shows that  sp. ME121 has some genes that encode putative methanol/ethanol family PQQ-dependent dehydrogenases involved in methylotrophy. Some unknown factor provided by the coculture may contribute to increase the growth of
sp. ME121 has some genes that encode putative methanol/ethanol family PQQ-dependent dehydrogenases involved in methylotrophy. Some unknown factor provided by the coculture may contribute to increase the growth of 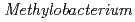 sp. ME121.
sp. ME121.
大野 豊; 長谷 純宏; 佐藤 勝也; 野澤 樹; 鳴海 一成*
放射線と産業, (138), p.17 - 20, 2015/06
イオンビーム育種技術は、近年植物や微生物の改変に活発に利用され、有用品種の作出に成果をあげている。東京電力福島第一原子力発電所の事故対応のためにイオンビーム育種でなにができるのか。日本原子力研究開発機構量子ビーム応用センターでは、高崎量子応用研究所のサイクロトロンを利用し、セシウム高・低吸収植物やセシウム高濃縮菌の開発に取り組み、変異体の候補を得ることに成功した。
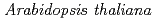 exhibiting different anthocyanin accumulation patterns
exhibiting different anthocyanin accumulation patterns北村 智; 大野 豊; 鳴海 一成*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 72, 2015/03
イオンビームは新しい変異体を誘発するのに効果的である。既存のイオンビーム変異体に対するイオンビーム再照射は、イオンビームがゲノムの一部のみを改変する特徴を活かした変異誘発法で、植物の形質を一歩ずつ改変していくのに有効である。今回、シロイヌナズナにおいてイオンビーム照射法を適用し、従来法では得られないような色素蓄積変異体の選抜を行った。
佐藤 勝也; 上田 涼史郎; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成*; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 117, 2015/03
Bioremediation uses biological organisms to solve an environmental problem. However, microorganisms are sometimes not enough effective to achieve efficient recovery. Therefore, enhancing the functionality of microorganisms is needed to promote the active use of bioremediation. This study began with the purpose of development of Cs-accumulating bacteria by ion beam breeding technology. We investigated which members are better suited for Cs-accumulation in the genus  (
( ,
, 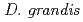 ,
, 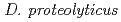 ,
,  ,
,  and
and  ) exhibit extraordinary radioresistant. The Cs concentration in the
) exhibit extraordinary radioresistant. The Cs concentration in the  cells exhibited over 4-fold compared with that of the
cells exhibited over 4-fold compared with that of the  by atomic absorption spectrometer analysis. This result suggested that
by atomic absorption spectrometer analysis. This result suggested that  and
and  are best two suitable species for the development of high Cs-accumulating bacteria by ion beam breeding technology.
are best two suitable species for the development of high Cs-accumulating bacteria by ion beam breeding technology.

上田 涼史郎; 佐藤 勝也; 林 秀謙*; 鳴海 一成*; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 118, 2015/03
It is suggesting a possibility that the polyphosphate granules in cells could accumulate harmful metal ions such as radiocesium to protect the cells from cytotoxicity.  has been considered as a microorganism for bioremediation under highly radioactive contaminated environments. We generated the polyphosphate biosynthesis-related genes (
has been considered as a microorganism for bioremediation under highly radioactive contaminated environments. We generated the polyphosphate biosynthesis-related genes ( and
and 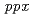 ) disruptant strains and characterized their disruption effect to clarify the role of polyphosphate for the accumulation of cesium in
) disruptant strains and characterized their disruption effect to clarify the role of polyphosphate for the accumulation of cesium in  . The intracellular levels of polyphosphates in the
. The intracellular levels of polyphosphates in the 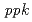 disruptant and overexpressing strains were almost same and slightly increased, respectively. On other hand, the intracellular level of polyphosphates significantly increased in the
disruptant and overexpressing strains were almost same and slightly increased, respectively. On other hand, the intracellular level of polyphosphates significantly increased in the 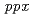 disruptant strains, suggesting that the
disruptant strains, suggesting that the 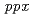 gene plays an important role in the accumulation of polyphosphate in
gene plays an important role in the accumulation of polyphosphate in  .
.
 USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation
USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation武田 喜代子*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*; 大野 豊; 大津 直子*; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 120, 2015/03
Major constraint of biofertilizer utilization in agricultural practice is a viability loss of beneficial microorganisms in biofertilizers by high temperature stress during both storage and transportation. Therefore, we have tried to improve high temperature tolerance of  USDA110 using carbon-ion beams accelerated by an AVF cyclotron at TIARA. Consequently, we have obtained a high temperature tolerant mutant that can maintain a high survival rate at 42
USDA110 using carbon-ion beams accelerated by an AVF cyclotron at TIARA. Consequently, we have obtained a high temperature tolerant mutant that can maintain a high survival rate at 42  C for at least 7 days in yeast-mannitol broth medium, and named it as M14. The genome sequence of M14 was determined by a whole-genome shotgun strategy. The acquirement of high temperature tolerance in M14 could be attributed to 18 base mutations and/or a large-scale inversion (1.27 Mb). In the future, we will conduct further analysis on these mutations in order to decipher the molecular mechanisms of high temperature tolerance of M14.
C for at least 7 days in yeast-mannitol broth medium, and named it as M14. The genome sequence of M14 was determined by a whole-genome shotgun strategy. The acquirement of high temperature tolerance in M14 could be attributed to 18 base mutations and/or a large-scale inversion (1.27 Mb). In the future, we will conduct further analysis on these mutations in order to decipher the molecular mechanisms of high temperature tolerance of M14.
 ray-induced mutagenesis
ray-induced mutagenesis西東 力*; Fitriana, Y.*; 佐藤 勝也; 大野 豊; 鳴海 一成*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 121, 2015/03
Entomopathogenic fungi, such as  , are economically important agents for integrated pest management programmes of insect pests. However, negative effects of temperature, such as heat stress that exceeds 35
, are economically important agents for integrated pest management programmes of insect pests. However, negative effects of temperature, such as heat stress that exceeds 35  C, can have serious deleterious effects on conidial germination and persistence, vegetative growth, sporulation, and/or the infection process in these entomopathogenic fungi. In this study, we attempted to enhance thermotolerance in a model entomopathogenic fungus,
C, can have serious deleterious effects on conidial germination and persistence, vegetative growth, sporulation, and/or the infection process in these entomopathogenic fungi. In this study, we attempted to enhance thermotolerance in a model entomopathogenic fungus,  , by mutagenesis using ion beams or
, by mutagenesis using ion beams or  rays and evaluated the relative virulence of the resulting mutants compared with the wild-type isolates. In conclusion, ion beams and
rays and evaluated the relative virulence of the resulting mutants compared with the wild-type isolates. In conclusion, ion beams and  rays are useful tools for improving biological characteristics, such as thermotolerance and fungicide-tolerance, in entomopathogenic fungi, but the mutants obtained in this study must be carefully evaluated for unpredictable negative side effects.
rays are useful tools for improving biological characteristics, such as thermotolerance and fungicide-tolerance, in entomopathogenic fungi, but the mutants obtained in this study must be carefully evaluated for unpredictable negative side effects.

布柴 達男*; 山内 理子*; 岩田 梨佳*; 佐藤 勝也; 大野 豊; 鳴海 一成*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 124, 2015/03
The LOH (loss of heterozygosity) induction by various ion beam radiations was investigated in diploid  . The ion beams
. The ion beams  C
C ,
,  C
C ,
,  He
He and
and  Ar
Ar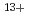 at the lowest dose of 37.5 Gy, which had
at the lowest dose of 37.5 Gy, which had  10% lethality, induced LOH with
10% lethality, induced LOH with  5
5 90%) resulted from homologous recombination. Pol
90%) resulted from homologous recombination. Pol may be involved in the induction of LOH by ion beam radiations, because in the strain lacking Rev3, only slight induction of LOH was observed, whereas no remarkable effect of deletion for Pol
may be involved in the induction of LOH by ion beam radiations, because in the strain lacking Rev3, only slight induction of LOH was observed, whereas no remarkable effect of deletion for Pol was observed on ion beam induced LOH. In addition, the effects of
was observed on ion beam induced LOH. In addition, the effects of 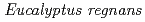 extracts were examined on iron-beam radiation induced LOH, and ethanol extract of
extracts were examined on iron-beam radiation induced LOH, and ethanol extract of 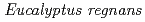 possessed inhibitory effect on LOH induced by
possessed inhibitory effect on LOH induced by  C
C ,
,  He
He and
and  Ar
Ar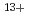 ion-beam radiation.
ion-beam radiation.
 (Hypocreales: Clavicipitaceae) mutants induced by ion beams
(Hypocreales: Clavicipitaceae) mutants induced by ion beamsFitriana, Y.*; 篠原 忍*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*; 西東 力*
Applied Entomology and Zoology, 50(1), p.123 - 129, 2015/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:1.75(Chemistry, Physical)Fungicides targeted at phytopathogens can be harmful to entomopathogenic fungi. The purpose of this study was to use ion-beam irradiation technology to produce benomyl-resistant mutants of the entomopathogenic fungus  . After irradiation of conidia at 150 Gy, two mutant isolates, BB22 and BB24, were selected on media containing the fungicide. In an assay of vegetative growth, BB22 and BB24 were over 500 and 800 times more tolerant to benomyl, respectively, compared with the wild isolate. A mutation was found at position 198 of the
. After irradiation of conidia at 150 Gy, two mutant isolates, BB22 and BB24, were selected on media containing the fungicide. In an assay of vegetative growth, BB22 and BB24 were over 500 and 800 times more tolerant to benomyl, respectively, compared with the wild isolate. A mutation was found at position 198 of the  -tubulin gene in the mutant isolates, with a substitution of glutamate for alanine (E198A). Ion beams have great potential as a tool to improve the traits of entomopathogenic fungi such as increasing tolerance to fungicides. Fungicide-resistant mutants produced in this way could be useful agents for biological control within IPM programmes where fungicides are also used.
-tubulin gene in the mutant isolates, with a substitution of glutamate for alanine (E198A). Ion beams have great potential as a tool to improve the traits of entomopathogenic fungi such as increasing tolerance to fungicides. Fungicide-resistant mutants produced in this way could be useful agents for biological control within IPM programmes where fungicides are also used.
 L. irradiated by
L. irradiated by  rays
rays北野 沙也佳*; 宮城 敦子*; 大野 豊; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成*; 山口 雅利*; 内宮 博文*; 川合 真紀*
Metabolomics, 11(1), p.134 - 142, 2015/02
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:25.41(Endocrinology & Metabolism)We investigated on the metabolic effectiveness of  ray irradiation to seeds of
ray irradiation to seeds of  , which are known to accumulate high level of soluble oxalate, to lower oxalate accumulation in leaves. Reduced rate of germination, discoloration of cotyledons, and deformed true leaves were observed by elevated irradiation. Metabolome analysis of primary metabolites using capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry showed a decrease in oxalate contents in the leaves of plants from
, which are known to accumulate high level of soluble oxalate, to lower oxalate accumulation in leaves. Reduced rate of germination, discoloration of cotyledons, and deformed true leaves were observed by elevated irradiation. Metabolome analysis of primary metabolites using capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry showed a decrease in oxalate contents in the leaves of plants from  ray-irradiated seeds. Moreover, organic acids such as malate and 2-oxoglutarate also decreased, whereas amino acids such as glutamate and glutamine increased. These results indicated that seed irradiation by
ray-irradiated seeds. Moreover, organic acids such as malate and 2-oxoglutarate also decreased, whereas amino acids such as glutamate and glutamine increased. These results indicated that seed irradiation by  rays leads to dynamic changes in metabolic pathways as well as plant growth/development.
rays leads to dynamic changes in metabolic pathways as well as plant growth/development.
川崎 通夫*; 桔梗 翔梧*; 野澤 樹; 秋田 祐介*; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成*
日本作物学会東北支部会報, (57), p.61 - 62, 2014/12
毛豆は青森県在来のエダマメ・ダイズであり、津軽地方を中心に古くから栽培されている。現在、青森県内では毛豆を地域資源として利活用し、地域振興に役立てる活動が行われている。毛豆のエダマメとしての収穫時期は9月中旬であることから、国内のエダマメ需要最盛期である8月上 中旬に出荷できない。
中旬に出荷できない。 線を用いた突然変異育種により早生化したエダマメ品種が育成されている例があるように、毛豆由来の新たな有用品種を育成することは青森県の地域振興に資すると考えられる。近年、イオンビームが様々な植物種に適応されているが、エダマメ・ダイズについては知見が少ない。そこで、炭素イオンビーム照射が毛豆の形質に及ぼす影響について検討した。種子に320MeV炭素イオンビームを0
線を用いた突然変異育種により早生化したエダマメ品種が育成されている例があるように、毛豆由来の新たな有用品種を育成することは青森県の地域振興に資すると考えられる。近年、イオンビームが様々な植物種に適応されているが、エダマメ・ダイズについては知見が少ない。そこで、炭素イオンビーム照射が毛豆の形質に及ぼす影響について検討した。種子に320MeV炭素イオンビームを0 16Gy照射した。発芽率、生存率及び草丈は照射線量に応じて低下した。形態異常を示す個体の出現率は照射線量に応じて増加した。形態異常の1つとして、ねじれた葉柄の横断切片を観察した結果、髄部中央に間隙が発達して歪みが生じていることが確認された。
16Gy照射した。発芽率、生存率及び草丈は照射線量に応じて低下した。形態異常を示す個体の出現率は照射線量に応じて増加した。形態異常の1つとして、ねじれた葉柄の横断切片を観察した結果、髄部中央に間隙が発達して歪みが生じていることが確認された。
 AV1934, a classic alkaliphile isolated from human feces in 1934
AV1934, a classic alkaliphile isolated from human feces in 1934Attie, O.*; Jayaprakash, A.*; Shah, H.*; Paulsen, I. T.*; 守野 正人*; 高橋 優嘉*; 鳴海 一成*; Sachidanandam, R.*; 佐藤 勝也; 伊藤 政博*; et al.
Genome Announcements (Internet), 2(6), p.e01175-14_1 - e01175-14_2, 2014/11
The alkaliphilic bacterium  AV1934, isolated from human feces, recent has indicated novel potassium ion coupling to motility in this extremophile. We report draft sequences that will facilitate an examination of whether that coupling is part of a larger cycle of potassium ion-coupled transporters. This draft genome has 4,095 predicted genes and 4,063 predicted proteins. The whole-genome shotgun project has been deposited in Genbank under the accession no. ALPT02000000. In addition to the
AV1934, isolated from human feces, recent has indicated novel potassium ion coupling to motility in this extremophile. We report draft sequences that will facilitate an examination of whether that coupling is part of a larger cycle of potassium ion-coupled transporters. This draft genome has 4,095 predicted genes and 4,063 predicted proteins. The whole-genome shotgun project has been deposited in Genbank under the accession no. ALPT02000000. In addition to the  genes encoding the MotPS channel that uses either potassium or sodium coupling, two loci encoding multisubunit Mrp-type antiporters, were found. The
genes encoding the MotPS channel that uses either potassium or sodium coupling, two loci encoding multisubunit Mrp-type antiporters, were found. The  AV1934 genome reveals no tripartite ATP-independent (TRAP-T family) uptake systems, a major sodium-coupled complement in the other two alkaliphiles. The
AV1934 genome reveals no tripartite ATP-independent (TRAP-T family) uptake systems, a major sodium-coupled complement in the other two alkaliphiles. The  AV1934 genomic data will enable us to test the hypothesis of a major role of potassium in ion coupling in this extremophile.
AV1934 genomic data will enable us to test the hypothesis of a major role of potassium in ion coupling in this extremophile.

安達 基泰; 平山 裕士; 清水 瑠美; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*; 黒木 良太
Protein Science, 23(10), p.1349 - 1358, 2014/10
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:25.51(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)DNAの修復に関与する多機能なPprAは、デイノコッカスラジオデュランスの高度な放射線耐性を促進する重要なタンパク質である。PprAによる放射線耐性機構を解明するために、大腸菌で発現した組換え型PprAと2本鎖DNAとの相互作用解析を実施した。ゲルシフトアッセイにより、PprAとスーパーコイル型のpUC19 DNAとの複合体のゲルシフトが2極性であり、それが1mMのMg, Ca, Srイオンで促進されることが示された。シフトしたバンドの相対的な割合からPprAとスーパーコイル型のpUC19 DNAとの複合体形成のヒル係数および解離定数を計算したところ、1mM Mgイオンの存在下で、それぞれ3.3と0.6 Mであった。このことは、PprAがスーパーコイル型のpUC19 DNAに少なくとも281分子結合していることを示しており、ゲル濾過での分離後にUV吸収で見積もられた値と一致した。この結果は、PprAが2本鎖DNAに沿って、直鎖状に重合して結合していることを示唆している。一方で、直鎖状の2本鎖DNAとニックがある環状DNAのバンドシフトに関しては、飽和が見られず、1.3
Mであった。このことは、PprAがスーパーコイル型のpUC19 DNAに少なくとも281分子結合していることを示しており、ゲル濾過での分離後にUV吸収で見積もられた値と一致した。この結果は、PprAが2本鎖DNAに沿って、直鎖状に重合して結合していることを示唆している。一方で、直鎖状の2本鎖DNAとニックがある環状DNAのバンドシフトに関しては、飽和が見られず、1.3 M以上のPprA濃度の時、さらに大きな複合体の形成が確認された。この結果は、DNAに結合したPprAが、ダメージを受けたDNAの末端の会合を濃度依存的に促進していることを示している。
M以上のPprA濃度の時、さらに大きな複合体の形成が確認された。この結果は、DNAに結合したPprAが、ダメージを受けたDNAの末端の会合を濃度依存的に促進していることを示している。
 sp. strain TCA20, isolated from a hot spring containing a high concentration of calcium ions
sp. strain TCA20, isolated from a hot spring containing a high concentration of calcium ions藤浪 俊*; 武田 喜代子*; 小野寺 威文*; 佐藤 勝也; 佐野 元彦*; 高橋 優嘉*; 鳴海 一成*; 伊藤 政博*
Genome Announcements (Internet), 2(5), p.e00866-14_1 - e00866-14_2, 2014/09
Calcium-dependent  sp. strain TCA20 was isolated from a water sample of a hot spring containing a high concentration of calcium ions. Here, we report the draft genome sequence of this bacterium, which may be the basis for the research of calcium ion homeostasis. The draft genome sequence of
sp. strain TCA20 was isolated from a water sample of a hot spring containing a high concentration of calcium ions. Here, we report the draft genome sequence of this bacterium, which may be the basis for the research of calcium ion homeostasis. The draft genome sequence of  sp. strain TCA20 totals 5,631,463 bp in length and is composed of 33 large contigs (
sp. strain TCA20 totals 5,631,463 bp in length and is composed of 33 large contigs ( 500 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/Genbank under the accession no. BBIW00000000. The annotation of the draft genome sequence shows that
500 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/Genbank under the accession no. BBIW00000000. The annotation of the draft genome sequence shows that  sp. strain TCA20 has a calcium-specific calcium/proton antiporter, ChaA, and a P-type calcium-transporting ATPase, YloB, was identified as calcium transporters. These transporters may also be important for the growth of
sp. strain TCA20 has a calcium-specific calcium/proton antiporter, ChaA, and a P-type calcium-transporting ATPase, YloB, was identified as calcium transporters. These transporters may also be important for the growth of  sp. strain TCA20 under the high concentration of calcium ions.
sp. strain TCA20 under the high concentration of calcium ions.