Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishii, Mamoru*; Shiota, Daiko*; Tao, Chihiro*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Fujiwara, Hitoshi*; Ishii, Takako*; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi*; Kataoka, Ryuho*; Koga, Kiyokazu*; Kubo, Yuki*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.108_1 - 108_20, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:59.6(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)We surveyed the relationship between the scale of space weather events and their occurrence rate in Japan and we discussed the social impact of these phenomena during the Project for Solar-Terrestrial Environment Prediction (PSTEP). The information was compiled for domestic users of space weather forecasts for appropriate preparedness against space weather disasters. This paper gives a comprehensive summary of the survey, focusing on the fields of electricity, satellite operations, communication and broadcasting, satellite positioning usage, aviation, human space activity, and daily life on the Earth's surface, using the cutting-edge knowledge of space weather. Quantitative estimations of the economic impact of space weather events on electricity and aviation are also given.
Kusano, Kanya*; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi*; Ishii, Mamoru*; Miyoshi, Yoshizumi*; Yoden, Shigeo*; Akiyoshi, Hideharu*; Asai, Ayumi*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Fujiwara, Hitoshi*; Goto, Tadanori*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.159_1 - 159_29, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:47.66(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The PSTEP is a nationwide research collaboration in Japan and was conducted from April 2015 to March 2020, supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. It has made a significant progress in space weather research and operational forecasts, publishing over 500 refereed journal papers and organizing four international symposiums, various workshops and seminars, and summer school for graduate students at Rikubetsu in 2017. This paper is a summary report of the PSTEP and describes the major research achievements it produced.
 Sb
Sb uncovered by soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
uncovered by soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroismSaito, Yuji; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Yasui, Akira*; Kadono, Toshiharu*; Sugawara, Hitoshi*; Kikuchi, Daisuke*; Sato, Hideyuki*; Suga, Shigemasa*; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Sekiyama, Akira*; et al.
Physical Review B, 102(16), p.165152_1 - 165152_8, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.7(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) VAl probed by soft X-ray spectroscopies
VAl probed by soft X-ray spectroscopiesNagai, Kodai*; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; Fujioka, Shuhei*; Yomosa, Hiroshi*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Kiss, Takayuki*; Sekiyama, Akira*; Kuroda, Fumiaki*; Fujii, Hitoshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 97(3), p.035143_1 - 035143_8, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:70.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have studied the electronic structure of ferrimagnetic Mn VAl single crystals by means of soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), X-ray absorption magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), and resonant soft X-ray inelastic scattering (RIXS). We have successfully observed the XMCD signals for all the constituent elements. The Mn L
VAl single crystals by means of soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), X-ray absorption magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), and resonant soft X-ray inelastic scattering (RIXS). We have successfully observed the XMCD signals for all the constituent elements. The Mn L XAS and XMCD spectra are reproduced by spectral simulations based on density-functional theory, indicating the itinerant character of the Mn 3
XAS and XMCD spectra are reproduced by spectral simulations based on density-functional theory, indicating the itinerant character of the Mn 3 states. On the other hand, the V 3
states. On the other hand, the V 3 electrons are rather localized since the ionic model can qualitatively explain the V L
electrons are rather localized since the ionic model can qualitatively explain the V L XAS and XMCD spectra. This picture is consistent with local
XAS and XMCD spectra. This picture is consistent with local 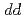 excitations revealed by the V L
excitations revealed by the V L RIXS.
RIXS.
Yang, B.*; Onda, Yuichi*; Omori, Yoshihiro*; Sekimoto, Hitoshi*; Fujiwara, Toru*; Wakiyama, Yoshifumi*; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Takahashi, Junko*; Sun, X.*
Science of the Total Environment, 603-604, p.49 - 56, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.75(Environmental Sciences)Uesaka, Mitsuru*; Kobayashi, Hitoshi*; Kureta, Masatoshi; Nakatsuka, Shigehiro*; Nishimura, Kazuya*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Hori, Junichi*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Tagi, Kazuhiro*; Seki, Toshichika*; et al.
Reviews of Accelerator Science and Technology, 8, p.181 - 207, 2015/00
We choose nuclear data and nuclear material inspection for energy application and nondestructive testing of explosive and hidden nuclear materials for security application. 90 keV electrostatic accelerators of deuterium are commercially available for nondestructive testing. For nuclear data measurement, electrostatic ion accelerators and L-band and S-band electron linear accelerators (linac) are used for the neutron source. Compact or mobile X-band electron linac neutron sources are under development. Compact proton linac neutron source is used for nondestructive testing especially water in solids. Several efforts for more neutron intensity using proton and deuteron accelerators are also introduced.
Fujiwara, Satoru; Matsumoto, Fumiko; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Endo, Hitoshi*; Oda, Toshiro*
no journal, ,
A variety of functions of F-actin related to cell motility arises from flexibility of F-actin that makes interactions with various actin-binding proteins possible. To understand flexibility of F-actin and thereby its multiple functions, it is important to understand dynamic properties of F-actin. As one of the ongoing projects towards this ultimate purpose, we employed neutron spin-echo (NSE) spectroscopy to investigate the motions of F-actin on pico-to-nanosecond timescales and nm spatial scales. We carried out the NSE experiments of F-actin and G-actin with the instrument, iNSE, run by the Institute for Solid State Physics, the University of Tokyo. It was shown that the motions of F-actin and G-actin on nano-scales were described by single relaxation processes, and the motions of F-actin were slower than those of G-actin. Diffusion constants obtained suggested the effects of internal motions of the actin-protomers.
Masui, Tomomi; Fujiwara, Satoru; Endo, Hitoshi; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Kataoka, Mikio
no journal, ,
Water is essential for organisms and desiccation damages the cells severely, and causes death of most organisms. Some organisms, however, known to survive under such arid conditions. This desiccation tolerance has been known to be related to the production of sugars in these organisms. One property which is important for the desiccation tolerance is stabilization of the cell membranes in the fluid phase by limiting the dehydration-induced increase in the gel-fluid transition temperature of the membranes. The membranes not only act as a barrier within or around a cell, but also control transfer of substances across the membranes. Elucidating how sugars interact with the membranes is therefore important for understanding the molecular mechanism of the desiccation tolerance. We investigated the effects of the sugars on the structures and the dynamics of the lipid membranes by small- and wide-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS and WAXS), and neutron spin-echo (NSE), techniques.
Fujiwara, Satoru; Plazanet, M.*; Matsumoto, Fumiko; Endo, Hitoshi; Oda, Toshiro*
no journal, ,
Actin is one of the most abundant proteins in eukaryotic cells, and expresses a variety of functions related to cell motility. Actin monomers (G-actin) polymerize into the helical F-actin. It has been shown that the multiple functions of F-actin arise from flexibility of F-actin. For understanding flexibility of F-actin and thereby its multiple functions, it is important to understand dynamic properties of F-actin. We employed elastic incoherent and quasielastic neutron scattering, to characterize dynamic properties of F-actin and G-actin. We showed that the dynamics properties of F-actin and G-actin are different. Furthermore, neutron spin-echo experiments of F-actin and G-actin showed that the motions of F-actin and G-actin on nano-scales, described by single relaxation processes, are different. Diffusion constants obtained suggested the effects of internal motions of the actin-protomers.