Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
針井 一哉*; 埋田 真樹; 有沢 洋希*; 日置 友智*; 佐藤 奈々; 岡安 悟; 家田 淳一
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(7), p.073701_1 - 073701_4, 2023/07
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:61.99(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Magnetic property modification of an easy-plane magnetic insulator caused by an accumulation of nanocolumnar defects along the film normal was investigated by numerical simulations and heavy-ion beam irradiation experiments. Micromagnetic simulations suggest that depending on the density of the nonmagnetic nanocolumnar defects, the microstructure of the fragmented ferromagnetic domains is formed leading to magnetic coercivity enhancement as well as magnetization reduction. To prove this prediction, gold ions with 300 MeV were used for the irradiation to create amorphous nanocolumnar defects in crystalline bismuth-doped lutetium iron garnet (Bi:LuIG) films. As increasing the ion-irradiation dose, the modifications of the saturation magnetization and magnetic coercivity were observed in an uncorrelated manner; the enhancement of magnetic coercivity exhibits a fluence threshold whereas the decrease of saturation magnetization caused by ion-beam damage is monotonic with increasing beam fluence. These behaviors qualitatively agree with the numerical simulations and the models by continuum percolation theory. Because the irradiation effects are controlled by beam fluences, the present method has the potential to be a microstructuring technique for magnetic insulator.
 Fe
Fe O
O /Pt heterostructures
/Pt heterostructures家田 淳一; 岡安 悟; 針井 一哉*; 小畠 雅明; 吉井 賢資; 福田 竜生; 石田 真彦*; 齊藤 英治
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 58(8), p.1301106_1 - 1301106_6, 2022/08
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:22.45(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)スピンゼーベック効果(SSE)に基づくスピン駆動熱電(STE)デバイスと、熱源としての放射性同位元素の組み合わせは、宇宙探査機の電源などの応用における次世代の発電方法としての可能性を秘めている。しかし、スピン熱電デバイスの照射耐性を示す利用可能な知識は非常に限られている。重イオンビーム加速器と硬X線光電子分光法(HAXPES)測定を使用した分析を通じて、Y Fe
Fe O
O /Ptヘテロ構造に基づく典型的なSTEデバイスが高エネルギー重イオンビームの照射に対する耐性を持つことを検証する。使用済み核燃料の表面から放出される核分裂生成物による累積損傷をモデル化した320MeVの金イオンビームを使用し、線量レベルを変えることにより、SSE要素の熱電および磁気特性が
/Ptヘテロ構造に基づく典型的なSTEデバイスが高エネルギー重イオンビームの照射に対する耐性を持つことを検証する。使用済み核燃料の表面から放出される核分裂生成物による累積損傷をモデル化した320MeVの金イオンビームを使用し、線量レベルを変えることにより、SSE要素の熱電および磁気特性が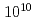 イオン/cm
イオン/cm フルエンスまでのイオン照射線量の影響を受けず、イオントラックがサンプル表面をほぼ完全に覆う約
フルエンスまでのイオン照射線量の影響を受けず、イオントラックがサンプル表面をほぼ完全に覆う約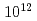 イオン/cm
イオン/cm でSSE信号が消滅することを確認した。さらに、HAXPES測定は、Y
でSSE信号が消滅することを確認した。さらに、HAXPES測定は、Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt界面への影響を理解するために実行した。HAXPES測定は、SSE信号を減少させる化学反応が照射線量の増加とともに強化されることを示唆している。過酷な環境使用に適用できるより優れたSTEデバイスを開発するために、Y
/Pt界面への影響を理解するために実行した。HAXPES測定は、SSE信号を減少させる化学反応が照射線量の増加とともに強化されることを示唆している。過酷な環境使用に適用できるより優れたSTEデバイスを開発するために、Y Fe
Fe O
O /Ptで損傷分析の現在の理解を共有したい。
/Ptで損傷分析の現在の理解を共有したい。
社本 真一*; 赤津 光洋*; 松浦 直人*; 河村 聖子; 針井 一哉*; 小野 正雄*; Chang, L.-J.*; 伊藤 孝; 根本 祐一*; 家田 淳一
Physical Review Research (Internet), 4(1), p.013245_1 - 013245_7, 2022/03
イットリウム鉄ガーネットの磁気ブラッグピークに対する超音波注入効果を、準弾性中性子散乱によって研究した。磁気ブラッグピークは、温度の低下とともに大幅に強化さる。エネルギー幅は、超音波注入によって引き起こされる試料温度上昇の平方根に比例して増加した。磁気ブラッグピークは格子振動によって増強されることから、この増強はスピン-格子結合と密接に関連していると予想される。縦波モードで100Kを超えると観測された急激な散乱信号の低下は、スピン-格子結合の劣化を示唆している。これは、温度が100Kを超えるとスピンゼーベック効果が低下することと一致しており、スピン-格子結合による劣化メカニズムに証明を与えている。
中堂 博之; 松尾 衛*; 針井 一哉*; 前川 禎通*; 齊藤 英治
Applied Physics Express, 13(10), p.109102_1 - 109102_2, 2020/10
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:52.38(Physics, Applied)バーネット効果とは物体を回転させるとその物体が磁化する現象である。これは磁気モーメントに対して回転座標系での慣性力として磁場が働くと解釈できる。その磁場をバーネット磁場と呼ぶ。バーネット磁場は慣性力であるために、高速で回転する物体と同じ速度で回転する測定系が必要である。我々は新規にコイル回転法を独自開発し、その共振回路を用いて核磁気共鳴法(NMR)測定を行ったところ、核磁気モーメントに働くバーネット磁場によってNMRの共鳴周波数が回転数に比例してシフトするという結果を得た。この成果は2014年にApplied Physics Expressに掲載されたが、2018年の夏、Jean Jeener人物から、我々が測定したものはバーネット磁場ではなく、コイルを回転させた事による人為的な効果であるとの批判が出た。本論文はこれに対する我々の返答である。
岡安 悟; 針井 一哉*; 小畠 雅明; 吉井 賢資; 福田 竜生; 石田 真彦*; 家田 淳一; 齊藤 英治
Journal of Applied Physics, 128(8), p.083902_1 - 083902_7, 2020/08
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:19.49(Physics, Applied)The ion-irradiation tolerance of thermoelectric devices based on the spin Seebeck effect (SSE) was investigated by using 320 MeV gold ion (Au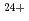 ) beams modeling cumulative damages due to fission products emitted from the surface of spent nuclear fuels. For this purpose, prototypical Pt/Y
) beams modeling cumulative damages due to fission products emitted from the surface of spent nuclear fuels. For this purpose, prototypical Pt/Y Fe
Fe O
O /Gd
/Gd Ga
Ga O
O SSE elements were irradiated with varying the dose level at room temperature and measured the SSE voltage of them. We confirmed that the thermoelectric and magnetic properties of the SSE elements are not affected by the ion-irradiation up to
SSE elements were irradiated with varying the dose level at room temperature and measured the SSE voltage of them. We confirmed that the thermoelectric and magnetic properties of the SSE elements are not affected by the ion-irradiation up to 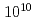 ions/cm
ions/cm fluence and that the SSE signal is extinguished around
fluence and that the SSE signal is extinguished around 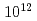 ions/cm
ions/cm , in which the ion tracks almost fully cover the sample surface. We also performed the hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HAXPES) measurements to understand the effects at the interface of Pt/Y
, in which the ion tracks almost fully cover the sample surface. We also performed the hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HAXPES) measurements to understand the effects at the interface of Pt/Y Fe
Fe O
O . The HAXPES measurements suggest that the chemical reaction that diminishes the SSE signals is enhanced with the increase of the irradiation dose. The present study demonstrates that SSE-based devices are applicable to thermoelectric generation even in harsh environments for a long time period.
. The HAXPES measurements suggest that the chemical reaction that diminishes the SSE signals is enhanced with the increase of the irradiation dose. The present study demonstrates that SSE-based devices are applicable to thermoelectric generation even in harsh environments for a long time period.
高橋 遼*; 中堂 博之; 松尾 衛; 針井 一哉*; 大沼 悠一*; 前川 禎通; 齊藤 英治
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.3009_1 - 3009_6, 2020/06
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:80.01(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Hydrodynamic motion can generate a flux of electron-spin's angular momentum via the coupling between fluid rotation and electron spins. Such hydrodynamic generation, called spin hydrodynamic generation (SHDG), has recently attracted attention in a wide range of fields, especially in spintronics. Spintronics deals with spin-mediated interconversion taking place on a micro or nano scale because of the spin-diffusion length scale. To be fully incorporated into the interconversion, SHDG physics should also be established in such a minute scale, where most fluids exhibit a laminar flow. Here, we report electric voltage generation due to the SHDG in a laminar flow of a liquid-metal mercury. The experimental results show a scaling rule unique to the laminar-flow SHDG. Furthermore, its energy con- version efficiency turns out to be about 105 greater than of the turbulent one. Our findings reveal that the laminar-flow SHDG is suitable to downsizing and to extend the coverage of fluid spintronics.
 Fe
Fe O
O
小畠 雅明; 吉井 賢資; 福田 竜生; 川崎 郁斗; 岡根 哲夫; 山上 浩志; 矢板 毅; 針井 一哉; 家田 淳一; 岡安 悟; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 30, p.011192_1 - 011192_6, 2020/03
スピンゼーベック効果を示す系として注目されているPt/Y Fe
Fe O
O (YIG)系に対し、放射光を用いた硬X線光電子分光(HAXPES)により表面及び界面の電子状態測定を行った。本系ではスピンゼーベック効果のほかに特異な性質を示すことが報告されている。例えば、外部磁場が存在しない状況でもホール効果を発現する。この起源として、YIG中のFe
(YIG)系に対し、放射光を用いた硬X線光電子分光(HAXPES)により表面及び界面の電子状態測定を行った。本系ではスピンゼーベック効果のほかに特異な性質を示すことが報告されている。例えば、外部磁場が存在しない状況でもホール効果を発現する。この起源として、YIG中のFe イオンがPt膜に染み出し、磁性を持つ金属間化合物を生成している可能性が提案されている。そこでHAXPESの分析深さを利用し、界面近傍の鉄イオン等の電子状態を測定した。Ptの厚みが2nm, 5nm, 8nm, 10nmの試料を測定したところ、2nmと5nmの試料において鉄イオンの分析を行うことができた。Fe 1s光電子スペクトルからは、鉄イオンが3+のものと金属的な0価に近い2つの状態が存在することが判明し、上記の可能性を支持する結果が得られた。Pt 4fやO 1sスペクトルなども測定しており、詳しい結果は当日報告する。
イオンがPt膜に染み出し、磁性を持つ金属間化合物を生成している可能性が提案されている。そこでHAXPESの分析深さを利用し、界面近傍の鉄イオン等の電子状態を測定した。Ptの厚みが2nm, 5nm, 8nm, 10nmの試料を測定したところ、2nmと5nmの試料において鉄イオンの分析を行うことができた。Fe 1s光電子スペクトルからは、鉄イオンが3+のものと金属的な0価に近い2つの状態が存在することが判明し、上記の可能性を支持する結果が得られた。Pt 4fやO 1sスペクトルなども測定しており、詳しい結果は当日報告する。
針井 一哉; Seo, Y.-J.*; 堤 康雅*; 中堂 博之; 大柳 洸一*; 松尾 衛; 塩見 雄毅*; 小野 崇人*; 前川 禎通; 齊藤 英治
Nature Communications (Internet), 10, p.2616_1 - 2616_5, 2019/06
被引用回数:28 パーセンタイル:81.46(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Electric current has been used to send electricity to far distant places. On the other hand, spin current, a flow of electron spin, can in principle also send angular momentum to distant places. In a magnet, there is a universal spin carrier called a spin wave, a wave-type excitation of magnetization. Since spin waves exhibit a long propagation length, it should be able to send angular momentum that can generate torque and force at a distant place: a new function of magnets. Here we observe mechanical angular momentum transmission and force generation due to spin waves injected into Y Fe
Fe O
O by the spin-Seebeck effect. The spin-wave current, transmitted through a Y
by the spin-Seebeck effect. The spin-wave current, transmitted through a Y Fe
Fe O
O micro cantilever, was found to create a mechanical force on the cantilever as a non-local reaction of the spin-Seebeck effect. Spin-wave current can be generated remotely even in open circuits, and it can be used to drive micro mechanical devices.
micro cantilever, was found to create a mechanical force on the cantilever as a non-local reaction of the spin-Seebeck effect. Spin-wave current can be generated remotely even in open circuits, and it can be used to drive micro mechanical devices.
 Dy
Dy Fe
Fe O
O detected by the Barnett effect
detected by the Barnett effect今井 正樹; 中堂 博之; 小野 正雄; 針井 一哉; 松尾 衛; 大沼 悠一*; 前川 禎通; 齊藤 英治
Applied Physics Letters, 114(16), p.162402_1 - 162402_4, 2019/04
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:73.01(Physics, Applied)We demonstrate that the angular momentum compensation temperature 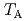 , at which the net angular momentum in the sample disappears, can be controlled in Ho
, at which the net angular momentum in the sample disappears, can be controlled in Ho Fe
Fe O
O by partially substituting Dy for Ho. The
by partially substituting Dy for Ho. The 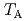 can be detected using the Barnett effect, by which mechanical rotation magnetizes an object due to spin-rotation coupling. We found that
can be detected using the Barnett effect, by which mechanical rotation magnetizes an object due to spin-rotation coupling. We found that 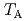 increases with the Dy content and clarified that the
increases with the Dy content and clarified that the 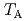 of Ho
of Ho Dy
Dy Fe
Fe O
O coincides with room temperature. The Barnett effect enables us to explore materials applicable to magnetic devices utilizing the angular momentum compensation only by rotating the powder sample at room temperature.
coincides with room temperature. The Barnett effect enables us to explore materials applicable to magnetic devices utilizing the angular momentum compensation only by rotating the powder sample at room temperature.
 Fe
Fe O
O micro bridge
micro bridge有沢 洋希*; 大門 俊介*; 追川 康之*; Seo, Y.-J.*; 針井 一哉; 大柳 洸一*; 齊藤 英治
Applied Physics Letters, 114(12), p.122402_1 - 122402_5, 2019/03
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:27.67(Physics, Applied)We have investigated magnetic field effects on mechanical vibration of a magnetic microbridge made of ferrimagnetic insulator Y Fe
Fe O
O at room temperature. The mechanical resonance frequency of the bridge exhibits a steep change at the saturation magnetic field of the microbridge. The steep change was shown to originate from magnetoelastic coupling combined with shape magnetic anisotropy. The competition between shape magnetic anisotropy and the external magnetic field can drive a delta-E effect, the modulation of Young modulus via the magnetoelastic coupling, in a narrow field range, which results in the observed steep change in the mechanical property.
at room temperature. The mechanical resonance frequency of the bridge exhibits a steep change at the saturation magnetic field of the microbridge. The steep change was shown to originate from magnetoelastic coupling combined with shape magnetic anisotropy. The competition between shape magnetic anisotropy and the external magnetic field can drive a delta-E effect, the modulation of Young modulus via the magnetoelastic coupling, in a narrow field range, which results in the observed steep change in the mechanical property.
今井 正樹; 緒方 裕大*; 中堂 博之; 小野 正雄; 針井 一哉; 松尾 衛*; 大沼 悠一*; 前川 禎通; 齊藤 英治
Applied Physics Letters, 113(5), p.052402_1 - 052402_3, 2018/07
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:65.6(Physics, Applied)We report direct observation of gyromagnetic reversal, which is the sign change of gyromagnetic ratio in a ferrimagnet Ho Fe
Fe O
O , by using the Barnett effect measurement technique at low temperatures. The Barnett effect is a phenomenon in which magnetization is induced by mechanical rotation through the coupling between rotation and total angular momentum
, by using the Barnett effect measurement technique at low temperatures. The Barnett effect is a phenomenon in which magnetization is induced by mechanical rotation through the coupling between rotation and total angular momentum  of electrons. The magnetization of Ho
of electrons. The magnetization of Ho Fe
Fe O
O induced by mechanical rotation disappears at 135 K and 240 K. The temperatures correspond to the magnetization compensation temperature
induced by mechanical rotation disappears at 135 K and 240 K. The temperatures correspond to the magnetization compensation temperature 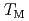 and the angular momentum compensation temperature
and the angular momentum compensation temperature 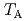 , respectively. Between
, respectively. Between 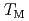 and
and 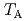 , the magnetization flips over to be parallel against the angular momentum due to the sign change of gyromagnetic ratio. This study provides an unprecedented technique to explore the gyromagnetic properties.
, the magnetization flips over to be parallel against the angular momentum due to the sign change of gyromagnetic ratio. This study provides an unprecedented technique to explore the gyromagnetic properties.
緒方 裕大; 中堂 博之; Gu, B.; 小林 伸聖*; 小野 正雄; 針井 一哉; 松尾 衛; 齊藤 英治; 前川 禎通
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 442, p.329 - 331, 2017/11
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:66.67(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The gyroscopic g factor, 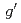 , of FeCo nanogranules embedded in a matrix of MgF
, of FeCo nanogranules embedded in a matrix of MgF (FeCo-MgF
(FeCo-MgF ) was determined by measuring the magnetic-field generation from a rotating sample due to the Barnett effect. The
) was determined by measuring the magnetic-field generation from a rotating sample due to the Barnett effect. The 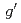 value of the FeCo-MgF
value of the FeCo-MgF is estimated to be 1.76
is estimated to be 1.76  0.11. The orbital contribution to the magnetic moment in the FeCo nanogranules was found to be quite large compared with that in bulk FeCo, being consistent with a density-functional-theory calculation that shows that the orbital magnetic moment may increase at the FeCo/MgF
0.11. The orbital contribution to the magnetic moment in the FeCo nanogranules was found to be quite large compared with that in bulk FeCo, being consistent with a density-functional-theory calculation that shows that the orbital magnetic moment may increase at the FeCo/MgF interfaces. The result suggests that the orbital magnetic moment is enhanced by symmetry breaking at the surface of the FeCo nanogranules.
interfaces. The result suggests that the orbital magnetic moment is enhanced by symmetry breaking at the surface of the FeCo nanogranules.
 Fe
Fe O
O cantilevers
cantileversSeo, Y.-J.*; 針井 一哉; 高橋 遼*; 中堂 博之; 大柳 洸一*; Qiu, Z.*; 小野 崇人*; 塩見 雄毅*; 齊藤 英治
Applied Physics Letters, 110(13), p.132409_1 - 132409_4, 2017/03
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:50.89(Physics, Applied)フェリ磁性体であるY Fe
Fe O
O を用いたサブミクロンカンチレバーを収束イオンビーム法によって作成し、その振動特性を磁場によって制御した。カンチレバーは縦横2つの振動モードを示し、それぞれのモードは外部磁場の印加によって共鳴周波数が減少、増大した。この結果は磁気力の磁場変化を取り扱った数値シミュレーションでよく再現された。周波数変化は数%に及ぶことから、磁場による高効率な振動制御が行われたと結論できる。
を用いたサブミクロンカンチレバーを収束イオンビーム法によって作成し、その振動特性を磁場によって制御した。カンチレバーは縦横2つの振動モードを示し、それぞれのモードは外部磁場の印加によって共鳴周波数が減少、増大した。この結果は磁気力の磁場変化を取り扱った数値シミュレーションでよく再現された。周波数変化は数%に及ぶことから、磁場による高効率な振動制御が行われたと結論できる。
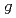 factor of rare earth metals
factor of rare earth metals緒方 裕大; 中堂 博之; 小野 正雄; 針井 一哉; 松尾 衛; 前川 禎通; 齊藤 英治
Applied Physics Letters, 110(7), p.072409_1 - 072409_4, 2017/02
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:65.79(Physics, Applied)We develop the 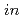
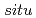 magnetization measurement apparatus for observing the Barnett effect consisting of a fluxgate sensor, high speed rotor with frequencies of up to 1.5 kHz, and magnetic shield at room temperature. The effective magnetic field (Barnett field) in a sample arising from rotation magnetizes the sample and is proportional to the rotational frequency. The gyroscopic
magnetization measurement apparatus for observing the Barnett effect consisting of a fluxgate sensor, high speed rotor with frequencies of up to 1.5 kHz, and magnetic shield at room temperature. The effective magnetic field (Barnett field) in a sample arising from rotation magnetizes the sample and is proportional to the rotational frequency. The gyroscopic 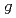 factor,
factor, 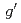 , of rare earth metals, in particular, Gd, Tb and Dy were estimated to be 2.00
, of rare earth metals, in particular, Gd, Tb and Dy were estimated to be 2.00 0.08, 1.53
0.08, 1.53 0.17, and 1.15
0.17, and 1.15 0.32, respectively, from the slopes of the rotation dependence of the Barnett field. This study provides a technique to determine the
0.32, respectively, from the slopes of the rotation dependence of the Barnett field. This study provides a technique to determine the 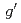 factor even in samples where the spectroscopic method may not be available.
factor even in samples where the spectroscopic method may not be available.
高橋 遼*; 松尾 衛; 小野 正雄; 針井 一哉; 中堂 博之; 岡安 悟; 家田 淳一; 高橋 三郎*; 前川 禎通; 齊藤 英治
Nature Physics, 12, p.52 - 56, 2016/01
被引用回数:108 パーセンタイル:96.36(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Magnetohydrodynamic generation is the conversion of fluid kinetic energy into electricity. Such conversion, which has been applied to various types of electric power generation, is driven by the Lorentz force acting on charged particles and thus a magnetic field is necessary. On the other hand, recent studies of spintronics have revealed the similarity between the function of a magnetic field and that of spin-orbit interactions in condensed matter. This suggests the existence of an undiscovered route to realize the conversion of fluid dynamics into electricity without using magnetic fields. Here we show electric voltage generation from fluid dynamics free from magnetic fields; we excited liquid-metal flows in a narrow channel and observed longitudinal voltage generation in the liquid. This voltage has nothing to do with electrification or thermoelectric effects, but turned out to follow a universal scaling rule based on a spin-mediated scenario. The result shows that the observed voltage is caused by spin-current generation from a fluid motion: spin hydrodynamic generation. The observed phenomenon allows us to make mechanical spin-current and electric generators, opening a door to fluid spintronics.
小野 正雄; 中堂 博之; 針井 一哉; 岡安 悟; 松尾 衛; 家田 淳一; 高橋 遼*; 前川 禎通; 齊藤 英治
Physical Review B, 92(17), p.174424_1 - 174424_4, 2015/11
被引用回数:29 パーセンタイル:74.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report the observation of the Barnett effect in paramagnetic states by mechanically rotating gadolinium (Gd) metal with a rotational frequency of up to 1.5 kHz above the Curie temperature. An in situ magnetic measurement setup comprising a high-speed rotational system and a fluxgate magnetic sensor was developed for the measurement. Temperature dependence of the observed magnetization follows that of paramagnetic susceptibility, indicating that any emergent magnetic field is proportional to the rotational frequency and is independent of temperature. From the proportionality constant of the emergent field, the gyromagnetic ratio of Gd is calculated to be -29  5 GHz/T. This study revisits the primordial issue of magnetism with modern technologies to shed new light on the fundamental spin-rotation coupling.
5 GHz/T. This study revisits the primordial issue of magnetism with modern technologies to shed new light on the fundamental spin-rotation coupling.
針井 一哉; 中堂 博之; 小野 正雄; 松尾 衛; 家田 淳一; 岡安 悟; 前川 禎通; 齊藤 英治
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 54(5), p.050302_1 - 050302_3, 2015/05
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:49.9(Physics, Applied)Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements for a nuclear spin 1/2 system in an external magnet field and mechanical rotation in kHz range are reported. NMR signals are measured by the synchronous rotation of a sample and a detector coil under the condition that the rotation axis is perpendicular to the external field. NMR line splits into two despite the system having a single Zeeman level separation. We analytically show that the splitting originates in the nuclear spin motion under mechanical rotation, and is determined by only the angular velocity of the rotation without any material parameters.
中堂 博之; 針井 一哉; 松尾 衛; 家田 淳一; 小野 正雄; 前川 禎通; 齊藤 英治
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(4), p.043601_1 - 043601_4, 2015/04
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:72.24(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report the observation of the rotational Doppler effect using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). We have developed a coil-spinning technique that enables measurements by rotating a detector and fixing a sample. We found that the rotational Doppler effect gives rise to NMR frequency shifts equal to the rotation frequency. We formulate the rotational Doppler effect and the Barnett field using a vector model for the nuclear magnetic moment. This formulation reveals that, with just the sample rotating, both effects cancel each other, thereby explaining the absence of an NMR frequency shift in conventional sample-spinning NMR measurements.
中堂 博之; 小野 正雄; 針井 一哉; 松尾 衛; 家田 淳一; 春木 理恵*; 岡安 悟; 前川 禎通; 安岡 弘志; 齊藤 英治
Applied Physics Express, 7(6), p.063004_1 - 063004_4, 2014/06
被引用回数:44 パーセンタイル:84.37(Physics, Applied)電気的に中性な物体であっても、回転する物体中の粒子には磁場が生じることが予言されている。この磁場をバーネット磁場という。我々は核磁気共鳴法が固体中に生じたバーネット磁場を測定できることを示す。我々は試料とNMR検出コイルを同じ早さで回転させると核磁気モーメントの符号を反映したNMRシフトが生じることを見いだした。この結果はバーネット磁場の直接的証拠である。NMRを用いたバーネット磁場の測定は未知の核磁気モーメントの符号を決定できる。
安 東秀*; Vasyuchka, V. I.*; 内田 健一*; Chumak, A. V.*; 山口 和也*; 針井 一哉; 大江 純一郎*; Jungfleisch, M. B.*; 梶原 瑛祐*; 安立 裕人; et al.
Nature Materials, 12(6), p.549 - 553, 2013/06
被引用回数:126 パーセンタイル:96.33(Chemistry, Physical)In this paper, we show a magnetically controllable heat flow caused by a spin-wave current. The direction of the flow can be switched by applying a magnetic field. When microwave energy is applied to a region of ferrimagnetic Y Fe
Fe O
O , an end of the magnet far from this region is found to be heated in a controlled manner and a negative temperature gradient towards it is formed. This is due to unidirectional energy transfer by the excitation of spin-wave modes without time-reversal symmetry and to the conversion of spin waves into heat. The magnetically controlled remote heating we observe is directly applicable to the fabrication of a heat-flow controller.
, an end of the magnet far from this region is found to be heated in a controlled manner and a negative temperature gradient towards it is formed. This is due to unidirectional energy transfer by the excitation of spin-wave modes without time-reversal symmetry and to the conversion of spin waves into heat. The magnetically controlled remote heating we observe is directly applicable to the fabrication of a heat-flow controller.