Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
丸山 結; 杉山 智之*; 島田 亜佐子; Lind, T.*; Bentaib, A.*; Sogalla, M.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Albright, L.*; Clayton, D.*
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.4782 - 4795, 2023/08
The Analysis of Information from Reactor Buildings and Containment Vessels of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) (ARC-F) project was initiated in January 2019 for three years with 22 signatories from 12 countries. Three main tasks were implemented in the ARC-F project, which were relevant to 1) refinement of analysis for accident scenarios and associated fission product (FP) transport and dispersion, 2) compilation and management of data and information, and 3) discussion for the next-phase project. Various activities were performed in Task 1, covering improvement of analysis for accident scenarios, and in-depth analyses for specific phenomena such as in-vessel melt progression, molten core/concrete interaction, FP transport and source term, hydrogen combustion and atmospheric dispersion of FPs. Through these studies, analyses for accident scenarios with severe accident codes were refined and important phenomena with large uncertainties were clarified. In order to share well selected and organized information from the FDNPS with the project partners, two databases, information source database and sample database, were built under Task 2. The analysis techniques including the separation of iodine species were developed also in Task 2 and applied to the analysis of FPs in several samples taken from the FDNPS. The next-phase project was discussed in Task 3, resulting in launching the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Information Collection and Evaluation (FACE) project. The FACE project officially started in July 2022 with the participation of 23 organizations from 12 countries and the European Commission.
南上 光太郎; 塩津 弘之; 丸山 結; 杉山 智之; 岡本 孝司*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(7), p.816 - 823, 2023/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)For proper source term evaluation, we constructed the theoretical model to estimate the mass transfer coefficient of gaseous iodine species under two-phase flow conditions, which complicates the direct experimental measurements. The mass transfer speed is determined by the product of the overall mass transfer coefficient and the interfacial area. By using the ratio of two gas components, the interfacial area, which is an important parameter that is difficult to measure, can be canceled out and the ratio of their overall mass transfer coefficients can be obtained. This ratio is expected to be equal to the ratio of their diffusion coefficients. Therefore, the unknown mass transfer coefficient such as iodine species can be estimated using the diffusion coefficients of two gas components and the reference mass transfer coefficient such as O . We carried out the experiments using the bubble column to confirm this relationship. From the results in this study, we confirmed that the ratio of the overall mass transfer coefficient was in good agreement with the ratio of diffusion coefficient under the bubbly flow conditions. Using this relationship confirmed in this study, we estimated the mass transfer coefficient of I
. We carried out the experiments using the bubble column to confirm this relationship. From the results in this study, we confirmed that the ratio of the overall mass transfer coefficient was in good agreement with the ratio of diffusion coefficient under the bubbly flow conditions. Using this relationship confirmed in this study, we estimated the mass transfer coefficient of I , one of the iodine species.
, one of the iodine species.
松本 俊慶; 川部 隆平*; 岩澤 譲; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 178, p.109348_1 - 109348_13, 2022/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)シビアアクシデント時の溶融物関連事象を評価するためにFCIコードであるJASMINEの機能拡張を行った。溶融物の冷却性評価ではキャビティ床面上における粒子状・アグロメレーション・ケーキ状デブリ質量割合や最終的な幾何形状の予測が必要である。アグロメレーションモデルでは、熱を保有した粒子同士のくっつきを考慮し、組み込んだ。もう一つのモデル改良は拡がりモデルの改良である。浅水方程式を導入し、拡がり先端部のクラスト成長に基づく拡がり停止条件を組み込んだ。調整係数の最適化のためにスウェーデンKTHにおいて実施されたDEFOR-A及びPULiMS実験を参照した。JASMINEコードによる実験解析では共通のパラメータセットで良い再現性が得られ、主要な現象は適切にモデル化されたことを示した。
Zheng, X.; 玉置 等史; 高原 省五; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Proceedings of Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management (PSAM16) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/09
Uncertainty gives rise to the risk. For nuclear power plants, probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) systematically concludes what people know to estimate the uncertainty in the form of, for example, risk triplet. Capable of developing a definite risk profile for decision-making under uncertainty, dynamic PRA widely applies explicit modeling techniques such as simulation to scenario generation as well as the estimation of likelihood/probability and consequences. When quantifying risk, however, epistemic uncertainties exist in both PRA and dynamic PRA, as a result of the lack of knowledge and model simplification. The paper aims to propose a practical approach for the treatment of uncertainty associated with dynamic PRA. The main idea is to perform the uncertainty analysis by using a two-stage nested Monte Carlo method, and to alleviate the computational burden of the nested Monte Carlo simulation, multi-fidelity models are introduced to the dynamic PRA. Multi-fidelity models include a mechanistic severe accident code MELCOR2.2 and machine learning models. A simplified station blackout (SBO) scenario was chosen as an example to show practicability of the proposed approach. As a result, while successfully calculating the probability of large early release, the analysis is also capable to provide uncertainty information in the form probability distributions. The approach can be expected to clarify questions such as how reliable are results of dynamic PRA.
Zheng, X.; 玉置 等史; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 223, p.108503_1 - 108503_12, 2022/07
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:91.89(Engineering, Industrial)Dynamic probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) more explicitly treats timing issues and stochastic elements of risk models. It extensively resorts to iterative simulations of accident progressions for the quantification of risk triplets including accident scenarios, probabilities and consequences. Dynamic PRA leverages the level of detail for risk modeling while intricately increases computational complexities, which result in heavy computational cost. This paper proposes to apply multi-fidelity simulations for a cost- effective dynamic PRA. It applies and improves the multi-fidelity importance sampling (MFIS) algorithm to generate cost-effective samples of nuclear reactor accident sequences. Sampled accident sequences are paralleled simulated by using mechanistic codes, which is treated as a high-fidelity model. Adaptively trained by using the high-fidelity data, low-fidelity model is used to predicting simulation results. Interested predictions with reactor core damages are sorted out to build the density function of the biased distribution for importance sampling. After when collect enough number of high-fidelity data, risk triplets can be estimated. By solving a demonstration problem and a practical PRA problem by using MELCOR 2.2, the approach has been proven to be effective for risk assessment. Comparing with previous studies, the proposed multi-fidelity approach provides comparative estimation of risk triplets, while significantly reduces computational cost.
大島 宏之; 森下 正樹*; 相澤 康介; 安藤 勝訓; 芦田 貴志; 近澤 佳隆; 堂田 哲広; 江沼 康弘; 江連 俊樹; 深野 義隆; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
ナトリウム冷却高速炉(SFR: Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor)の歴史や、利点、課題を踏まえた安全性、設計、運用、メンテナンスなどについて解説する。AIを利用した設計手法など、SFRの実用化に向けた設計や研究開発についても述べる。
島田 亜佐子; 谷口 良徳; 垣内 一雄; 大平 早希; 飯田 芳久; 杉山 智之; 天谷 政樹; 丸山 結
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12(1), p.2086_1 - 2086_11, 2022/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:31.61(Multidisciplinary Sciences)2011年3月12日に福島第一原子力発電所の1号機のベントが行われ、1・2号機共用スタックから放射性ガスが放出された。本研究ではこのベントにより放出された放射性核種の情報を有していると考えられる、1・2号機共用スタック基部のドレンピットから採取したドレン水の放射化学分析を実施した。揮発性の Iや
Iや Cs,
Cs,  Csだけでなく、
Csだけでなく、 Co,
Co,  Sr,
Sr,  Sb, 1号機由来安定Moが検出された。1号機由来安定Moの量はCsの量よりもはるかに少ないことから、事故時の炉内状況ではCs
Sb, 1号機由来安定Moが検出された。1号機由来安定Moの量はCsの量よりもはるかに少ないことから、事故時の炉内状況ではCs MoO
MoO の生成は抑制されたと考えられる。また、2020年10月時点では、約90%のIがI
の生成は抑制されたと考えられる。また、2020年10月時点では、約90%のIがI 、約10%がIO
、約10%がIO
 で存在した。
で存在した。 Csより多い
Csより多い Iが観測されたことから、事故時に
Iが観測されたことから、事故時に IはCsIというよりも分子状のヨウ素として放出されたことが示唆された。2011年3月11日に減衰補正した
IはCsIというよりも分子状のヨウ素として放出されたことが示唆された。2011年3月11日に減衰補正した Cs/
Cs/ Cs放射能比は0.86で、2号機や3号機由来と考えられる放射能比より低いことが示された。
Cs放射能比は0.86で、2号機や3号機由来と考えられる放射能比より低いことが示された。
丸山 智幸*; Baha Balantekin, A.*; Cheoun, M.-K.*; 梶野 敏貴*; 日下部 元彦*; Mathews, G. J.*
Physics Letters B, 824, p.136813_1 - 136813_8, 2022/01
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:52.69(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We study neutrino and antineutrino emission from the direct Urca process in neutron-star matter in the presence of strong magnetic fields. We calculate the neutrino emissivity of the direct Urca process, whereby a neutron converts to a proton, an electron and an antineutrino, or a proton-electron pair converts to a neutron-neutrino pair. We solve exact wave functions for protons and electrons in the states described with Landau levels. We find that the direct Urca process can satisfy the kinematic constraints even in density regions where this process could not normally occur in the absence of a magnetic field.
塩津 弘之; 伊藤 裕人*; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 163, p.108587_1 - 108587_9, 2021/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the late phase of severe accident in light water reactor nuclear power station, re-mobilization of fission products (FPs) has a significant impact on the source term because most portion of FPs is retained in reactor coolant system and/or containment vessel. Recently, VERDON-2 experiment showed noticeable re-vaporization, which was one of the re-mobilization phenomena, of iodine under air ingress condition, but this mechanism has not been identified yet. The present study numerically investigated the FPs behaviors in VERDON-2 experiment with the mechanistic FPs transport analysis code incorporating thermodynamic chemical equilibrium model in order to further understand nature for FPs behavior, especially iodine re-vaporization under air ingress condition. Consequently, this analysis reproduced the deposition profile of cesium, one of important FPs in the source term, along the thermal gradient tube (TGT) in the experiment, which revealed that cesium was transported as CsOH in early phase of FP release from fuel, and then formed Cs MoO
MoO and Cs
and Cs Te after the release of molybdenum and tellurium was activated. Regarding iodine as another important FP, formation of CsI was predicted in steam condition. The CsI was transported and partly deposited and condensed onto the TGTs and other components of the VERDON facility. Under the air ingress condition, the present analysis showed the agreement for iodine re-vaporization in the experiment and revealed its mechanism; the deposits of iodide were chemical re-vaporized as molecular iodine (I
Te after the release of molybdenum and tellurium was activated. Regarding iodine as another important FP, formation of CsI was predicted in steam condition. The CsI was transported and partly deposited and condensed onto the TGTs and other components of the VERDON facility. Under the air ingress condition, the present analysis showed the agreement for iodine re-vaporization in the experiment and revealed its mechanism; the deposits of iodide were chemical re-vaporized as molecular iodine (I ) gas by redox reaction with competitive elements such as molybdenum, chromium and tellurium.
) gas by redox reaction with competitive elements such as molybdenum, chromium and tellurium.
Trianti, N.; 茂木 孝介; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2020/08
The computational fluid dynamics (CFD) have been developed to analyze the correlation equation for laminar flame speed of hydrogen-air mixtures. This analysis was carried out on the combustion of hydrogen-air mixtures performed at the spherical bomb experiment facility consists of a spherical vessel equipped (563 mm internal diameter). The facility has been designed and built at CNRS-ICARE laboratory. The simulation was carried out using the reactingFoam solver, one of a transient chemical reaction solver in OpenFOAM 5.0. The LaunderSharmaKE model was applied for turbulent flow. The interaction of the chemical reaction with the turbulent flow was taken into account using PaSR (Partial Stirred Reactor) model with 19 elementary reactions for the hydrogen combustion. The initial condition of spherical flame analysis was set so as to be consistent with those of the experiment. The position of the flame front was detected by the steep drop of hydrogen mass fraction in the spherical radii, and the flame propagation velocity was estimated from the time-position relationship. The analysis result showed the characteristic of spherical flame acceleration was qualitatively reproduced even though it has a discrepancy with the experiment. After validating the calculation of spherical experiments, a laminar burning velocity correlation is presented using the same boundary conditions with the variation of hydrogen concentration, temperature, and pressure. The calculation of laminar flame speed of hydrogen-air mixtures by reactingFoam use reference temperature T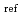 = 293 K and reference pressure P
= 293 K and reference pressure P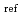 = 1 atm with validated in the range of hydrogen concentration 6-20%; range of temperature 293-493 K; and range of pressure 1-3 atm.
= 1 atm with validated in the range of hydrogen concentration 6-20%; range of temperature 293-493 K; and range of pressure 1-3 atm.
茂木 孝介; Trianti, N.; 松本 俊慶; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.4324 - 4335, 2019/08
Hydrogen managements under severe accidents are one of the most crucial problems and have attracted a great deal of attention after the occurrence of hydrogen explosions in the accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in March 2011. The primary purpose of our research is improvements in computational fluid dynamics techniques to simulate hydrogen combustion. Our target of analysis is ENACCEF2 hydrogen combustion benchmark test conducted in the framework of ETOSON-MITHYGENE project. Flame acceleration experiments of hydrogen premixed turbulent combustions were simulated by the Turbulent Flame Closure (TFC) model. We implemented several laminar flame speed correlations and turbulent flame speed models on XiFoam solver of OpenFOAM and compared the results to investigate the applicability of these correlation and model equations. We found that all the laminar flame speed correlations could predict qualitative behavior of the flame acceleration, but Ravi & Petersen laminar flame speed correlation that is originally implemented in OpenFOAM underestimated the maximum flame speed for the lean hydrogen concentration. Zimont model and G lder model of the turbulent flame speed could reasonably simulate the flame acceleration behavior and maximum pressure peaks. The flame velocities calculated with G
lder model of the turbulent flame speed could reasonably simulate the flame acceleration behavior and maximum pressure peaks. The flame velocities calculated with G lder model tend to be faster than that calculated with Zimont model.
lder model tend to be faster than that calculated with Zimont model.
玉置 等史; 石川 淳; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.72 - 82, 2019/08
原子力機構では、BSAF2計画に参加し、THALES2/KICHEコードを用いた福島第一原子力発電所の事故解析結果を提供した。THALES2/KICHEコードの重要な特徴の一つとして、液相における速度論に基づくヨウ素化学をモデル化している。本報告では、BSAF2計画における共通の境界条件や仮定に加え、格納容器の破損として、ベント弁が完全に閉まらなかったために引き起こされるベントラインからの継続的な漏洩をモデル化した1号機の3週間にわたる解析結果について紹介する。本仮定に基づく解析では、原子炉冷却系や格納容器の圧力履歴を再現できており、解析期間の3週間で環境に放出されたヨウ素及びセシウムの初期インベントリに対する割合は、各々約6%及び約1%であった。
玉置 等史; 石川 淳; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.100 - 111, 2019/08
JAEAでは、BSAF2計画に参加し、THALES2/KICHEコードを用いた福島第一原子力発電所の事故解析結果を提供した。THALES2/KICHEコードの重要な特徴の一つとして、液相における速度論に基づくヨウ素化学をモデル化している。本報告では、BSAF2計画における共通の境界条件や仮定に基づいた3週間にわたる2号機の解析結果、特にBSAF2計画では、2号機の事故進展に関し、3月14日の20時から15日2時の間に観測された3つの圧力容器内圧力ピークの生じた理由に着目しており、この時期の事故進展挙動を含め紹介する。また、本解析では、圧力抑制室の下部に破損を仮定し、水の漏洩を含め、格納容器圧力挙動を再現した。解析期間の3週間で環境に放出されたヨウ素及びセシウムの初期インベントリに対する割合は、各々約3%及び約0.1%であった。
石川 淳; 玉置 等史; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.536 - 547, 2019/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is pursuing the development and application of the integrated severe accident analysis code, THALES2/KICHE for analysis of severe accident progression and source term. The accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (NPS) from units 1 to 3 were analyzed using THALES2/KICHE code for better understanding of the accident in the OECD/NEA BSAF2 project. This paper describes three week analysis for the accident at unit 3. The leakage through the drywell head flange and an equipment hutch was assumed in order to reproduce the tendency of drywell pressure history in addition to the intermittent activation of the containment vessel venting system via the suppression chamber. As for the source term analysis, the dominant chemical forms for cesium and iodine were assumed to be cesium iodine (CsI) and cesium molibdate (Cs MoO
MoO ) based on the insights of the PHEBUS/FP experiments. The iodine chemical reaction kinetics in the containment aqueous phase, which were associated with the production of molecular iodine and organic iodide, were taken into consideration in the present analysis. The released iodine and cesium within three weeks after the earthquake were predicted to be approximately 3% and 6% of the initial inventory, respectively.
) based on the insights of the PHEBUS/FP experiments. The iodine chemical reaction kinetics in the containment aqueous phase, which were associated with the production of molecular iodine and organic iodide, were taken into consideration in the present analysis. The released iodine and cesium within three weeks after the earthquake were predicted to be approximately 3% and 6% of the initial inventory, respectively.
中塚 亨; 前田 敏克; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.1650 - 1656, 2019/08
経済協力開発機構原子力機関(OECD/NEA)は、「福島第一原子力発電所の原子炉建屋および格納容器内情報の分析(ARC-F)」プロジェクトを新たに開始した。本プロジェクトは、OECD/NEAで先行して実施された東京電力ホールディングス福島第一原子力発電所事故ベンチマーク解析(BSAF)プロジェクトの後継としての役割を担う。プロジェクトは、次の3つのタスクからなる。(1)事故進展解析及び核分裂生成物の移行と拡散やソースタームに関する解析の高度化(BSAF及びBSAF2プロジェクトのフォローアップ)、(2)得られたデータ・情報の集約管理、(3)将来の長期プロジェクトの検討。プロジェクトの運営は、原子力機構が行う。実施期間は、2019年1月から2021年12月までの3年間で、最終報告書は2022年に発行予定である。
岩澤 譲; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結; 金子 暁子*; 阿部 豊*
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2019/05
For evaluation of the debris coolability, agglomeration, which is merging of melt particles with the others and formation of massive debris, is critical in the severe accidents in light water reactors. We carried out small-scale experiments of agglomerated debris formation using metallic melt to establish a data base for modelling and validation. Molten metal of low melting point was ejected into a test section filled with water though a nozzle. A high-speed video camera recorded images of settlement of the melt particles generated form a melt jet onto a plate located in the test section. After the melt injection, we collected the debris and investigated detailed shapes of the debris. Based on the results, we assessed the feasibility of the experiments of agglomeration using the metallic melt.
横山 賢治; 杉野 和輝; 石川 眞; 丸山 修平; 長家 康展; 沼田 一幸*; 神 智之*
JAEA-Research 2018-011, 556 Pages, 2019/03
高速炉用統合炉定数ADJ2010の改良版となるADJ2017を作成した。統合炉定数は、核設計基本データベースに含まれる臨界実験解析等で得られるC/E値(解析/実験値)の情報を、炉定数調整法により実機の設計に反映するためのものであり、核データの不確かさ(共分散)、積分実験・解析の不確かさ、臨界実験に対する核データの感度等の情報と統合して炉定数を調整する。ADJ2017は、前バージョンのADJ2010と同様に、我が国の最新の核データライブラリJENDL-4.0をベースとしているが、マイナーアクチニド(MA)や高次化Puに関連する積分実験データを重点的に拡充した。ADJ2010では合計643個の積分実験データを解析評価し、最終的に488個の積分実験データを採用して統合炉定数を作成した。これに対して、ADJ2017では、合計719個の核特性の解析結果に対する総合評価を行い、最終的に620個の積分実験データを採用して統合炉定数を作成した。ADJ2017は、標準的なNa冷却MOX燃料高速炉の主要な核特性に対してADJ2010とほぼ同等の性能を発揮するとともに、MA・高次Pu関連の核特性に対しては、積分実験データのC/E値を改善する効果を持っており、核データに起因する不確かさを低減することができる。ADJ2017が今後、高速炉の解析・設計研究において広く利用されることを期待する。ADJ2017の作成に用いた積分実験データは、高速炉の炉心設計の基本データベースとして有効活用できると期待される。
塩津 弘之; 伊藤 裕人*; 石川 淳; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Proceedings of 11th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-11) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2018/11
The VERDON-2 experiment for FPs transport in steam environment was analyzed with the mechanistic FPs transport code incorporating thermodynamic chemical equilibrium model in order to assess its predictive capability for transport behavior of key FPs, especially for highly volatile FPs such as Cs and I. The present analysis reproduced well the Cs deposition profile obtained from the experiment, which revealed that Cs was transported as CsOH in early phase of FP release from fuel, and then formed Cs MoO
MoO after increasing Mo release. On the other hand, the deposition peak of I was predicted to appear at 720 K, which was significantly higher than the experimental result at 600 K. This discrepancy was potentially caused by the following two points: lack of the other stable species in thermodynamics database for thermodynamic chemical equilibrium model, or failure of chemical equilibrium assumption for iodide species.
after increasing Mo release. On the other hand, the deposition peak of I was predicted to appear at 720 K, which was significantly higher than the experimental result at 600 K. This discrepancy was potentially caused by the following two points: lack of the other stable species in thermodynamics database for thermodynamic chemical equilibrium model, or failure of chemical equilibrium assumption for iodide species.
Trianti, N.; 佐藤 允俊*; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Proceedings of 11th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-11) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2018/11
Simulation techniques have been developed to analyze the deflagration behavior of hydrogen generated during a hypothetical severe accident in nuclear power plants. The CFD analysis was carried out on the hydrogen deflagration experiment performed at the ENACCEF2 facility composed mainly of a vertical cylindrical tube filled with hydrogen-air mixture and nine annular obstacles were placed in the lower part of the tube. The simulation was carried out by the reactingFoam solver of OpenFOAM 3.0, an open source software for the CFD analysis. The RNG (Renormalization group) k- model was applied for turbulent flow. The interaction of the chemical reaction with the turbulent flow was considered using PaSR (Partial Stirred Reactor) model with 19 elementary reactions for the hydrogen combustion. The analysis result showed the characteristic of flame acceleration by the obstacle region was qualitatively reproduced even though has discrepancy with the experiment.
model was applied for turbulent flow. The interaction of the chemical reaction with the turbulent flow was considered using PaSR (Partial Stirred Reactor) model with 19 elementary reactions for the hydrogen combustion. The analysis result showed the characteristic of flame acceleration by the obstacle region was qualitatively reproduced even though has discrepancy with the experiment.
伊藤 裕人*; 塩津 弘之; 田中 洋一*; 西原 慧径*; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-012, 42 Pages, 2018/10
原子力施設事故時において施設内を移行する核分裂生成物(FP)の化学組成は、比較的遅い反応の影響を受けることにより化学平衡を仮定して評価した組成とは異なる場合が想定される。そのため、反応速度を考慮した化学組成評価が求められる。一方で、原子力施設事故時の複雑な反応に関する反応速度の知見は現状では限られており、実機解析に適用できるデータベースの構築に至っていない。そこで、FP化学組成評価における反応速度による不確かさの低減のため、化学平衡論及び反応速度論の部分混合モデルに基づく化学組成評価コードCHEMKEqを開発した。このモデルは、系全体の質量保存則の下、前駆平衡と見なせる化学種を化学平衡論モデルにより評価し、その後の比較的遅い反応を反応速度論モデルにより解くものである。さらにCHEMKEqは、本混合モデルに加え一般的な化学平衡論モデル及び反応速度論モデルが使用可能であり、かつ、それらモデル計算に必要なデータベースを外部ファイル形式とすることで汎用性の高い化学組成評価コードとなっている。本報は、CHEMKEqコードの使用手引書であり、モデル, 解法, コードの構成とその計算例を記す。また付録には、CHEMKEqコードを使用する上で必要な情報をまとめる。