Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
町田 昌彦; 山田 進; Kim, M.; 奥村 雅彦; 宮村 浩子; 志風 義明; 佐藤 朋樹*; 沼田 良明*; 飛田 康弘*; 山口 隆司; et al.
RIST News, (69), p.2 - 18, 2023/09
福島第一原子力発電所(1F)建屋内には、原子炉内から漏洩した放射性物質の汚染により高い放射線量を示す地点が多数存在し、廃炉作業を円滑に進める上での大きな障害の一つとなっている。この課題解決に資するため、日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)は、経済産業省の廃炉・汚染水対策事業費補助金「原子炉建屋内の環境改善のための技術の開発(被ばく低減のための環境・線源分布のデジタル化技術の開発)」を受託し、令和3年度より2年間に渡り、放射線源の逆推定と推定線源に対する対策を仮想空間で実施可能とするためのデジタル技術の研究開発を実施してきた。本記事では、上記プロジェクトの成果(以下、前期プロジェクトと呼び、その2年間の研究開発の成果)を紹介する他、令和5年度4月より、新たに開始した継続プロジェクト(以下、後期プロジェクトと呼ぶ)の計画についても報告する。前期プロジェクトにて当初予定していた機械学習技術(LASSO)については、建屋内の複雑な構造情報と汚染源の性質を反映した一つの派生版手法へと結実させた成果を報告する他、実際の原子炉施設での検証結果を示す。更に、開発技術を集約したプラットフォームとしての機能を持つソフトウエア:3D-ADRES-Indoorを紹介し、継続して実施する予定の後期プロジェクトの研究開発計画も紹介する。
河 侑成; 飛田 徹; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 145(2), p.021501_1 - 021501_9, 2023/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:59.37(Engineering, Mechanical)The fracture toughness in the heat-affected zone (HAZ), which is located under the weld overlay cladding on the inner surface of the reactor pressure vessel (RPV), was evaluated by considering the inhomogeneous microstructures of the HAZ. In this regard, 0.4T-C(T) specimens and Mini-C(T) specimens were manufactured to clarify the effect of the HAZ on fracture toughness. First, the fracture toughness was evaluated using 0.4T-C(T) specimens targeted on microstructural distribution due to the cladding bead location. The reference temperature (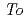 ) of HAZ at middle region of cladding bead was 12
) of HAZ at middle region of cladding bead was 12 C higher than that at overlap cladding beads. Second, the fracture toughness was evaluated using Mini-C(T) specimens focused on the microstructural difference with distance from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal. The
C higher than that at overlap cladding beads. Second, the fracture toughness was evaluated using Mini-C(T) specimens focused on the microstructural difference with distance from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal. The 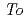 value of the central position located at 3 mm to 7 mm from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal was higher than those of the other positions in HAZ. However, the
value of the central position located at 3 mm to 7 mm from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal was higher than those of the other positions in HAZ. However, the 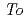 values of HAZ for both 0.4T-C(T) and Mini-C(T) specimens were significantly lower than that of the base metal at a quarter thickness by 40
values of HAZ for both 0.4T-C(T) and Mini-C(T) specimens were significantly lower than that of the base metal at a quarter thickness by 40 C
C 60
60 C. Compared with the literature data that indicated fracture toughness at the inner surface without overlay cladding and the base metal at a quarter thickness, this study concluded that the HAZ under the overlay cladding showed no detrimental effect on the conservatism of the structural integrity assessment of RPV steel.
C. Compared with the literature data that indicated fracture toughness at the inner surface without overlay cladding and the base metal at a quarter thickness, this study concluded that the HAZ under the overlay cladding showed no detrimental effect on the conservatism of the structural integrity assessment of RPV steel.
下平 昌樹; 飛田 徹; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; 塙 悟史
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(1), p.011304_1 - 011304_7, 2022/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Engineering, Mechanical)JEAC4206-2016における原子炉圧力容器の構造健全性評価では、材料の破壊靭性が、想定欠陥であるクラッド下半楕円亀裂の先端における応力拡大係数よりも高いことが求められている。しかしながら、破壊靭性試験片と想定亀裂の亀裂深さやクラッドの有無といった違いにより、塑性拘束状態や破壊靭性評価に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。本研究では、クラッド下亀裂が破壊靭性評価に及ぼす影響を調べるため、3点曲げ破壊靭性試験及び有限要素解析を実施した。その結果、クラッド下亀裂の塑性拘束が表面亀裂のそれに比べて弱いことを解析によって示した。さらに、クラッド下亀裂の弱い塑性拘束の影響により、クラッド下亀裂の破壊靭性が表面亀裂よりも見かけ上高くなることを実験及びローカルアプローチによって明らかにした。
河 侑成; 下平 昌樹; 高見澤 悠; 飛田 徹; 勝山 仁哉; 西山 裕孝
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2021/07
The semi-elliptical crack sized 10 mm in depth  60 mm in length shall be postulated near the inner surface of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) in pressurized thermal shock events. We investigated the fracture toughness distribution in the postulated crack area under the PTS events of unirradiated and highly-neutron irradiated RPV steels. Vickers hardness in heat-affected zone (HAZ) due to stainless overlay cladding and 10 mm from the cladding were higher than that of a quarter thickness position, where the surveillance specimens are machined, for both unirradiated (E1) and irradiated (up to 1
60 mm in length shall be postulated near the inner surface of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) in pressurized thermal shock events. We investigated the fracture toughness distribution in the postulated crack area under the PTS events of unirradiated and highly-neutron irradiated RPV steels. Vickers hardness in heat-affected zone (HAZ) due to stainless overlay cladding and 10 mm from the cladding were higher than that of a quarter thickness position, where the surveillance specimens are machined, for both unirradiated (E1) and irradiated (up to 1  10
10 n/cm
n/cm , WIM) materials. Fracture toughness of HAZ and 10 mm from the cladding was higher for the above highly-neutron irradiated material. The same result was obtained in the unirradiated material. Therefore, it was confirmed that fracture toughness obtained from surveillance specimens can provide conservative assessment of structural integrity of RPV.
, WIM) materials. Fracture toughness of HAZ and 10 mm from the cladding was higher for the above highly-neutron irradiated material. The same result was obtained in the unirradiated material. Therefore, it was confirmed that fracture toughness obtained from surveillance specimens can provide conservative assessment of structural integrity of RPV.
岩田 景子; 端 邦樹; 飛田 徹; 廣田 貴俊*; 高見澤 悠; 知見 康弘; 西山 裕孝
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2021/07
The crack arrest fracture toughness, K , values for highly-irradiated reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels are estimated according to a linear relationship between crack arrest toughness reference temperature, T
, values for highly-irradiated reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels are estimated according to a linear relationship between crack arrest toughness reference temperature, T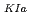 , and the temperature corresponding to a fixed arrest load, equal to 4 kN, T
, and the temperature corresponding to a fixed arrest load, equal to 4 kN, T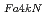 , obtained by instrumented Charpy impact test. The relationship between T
, obtained by instrumented Charpy impact test. The relationship between T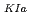 derived from the instrumented Chrapy impact test and fracture toughness reference temperature, T
derived from the instrumented Chrapy impact test and fracture toughness reference temperature, T , was expressed as an equation proposed in a previous report. The coefficients in the equation could be fine-tuned to obtain a better fitting curve using the present experimental data and previous K
, was expressed as an equation proposed in a previous report. The coefficients in the equation could be fine-tuned to obtain a better fitting curve using the present experimental data and previous K data. The K
data. The K curve for RPV;A533B class1 steels irradiated up to 1.3
curve for RPV;A533B class1 steels irradiated up to 1.3 10
10 n/cm
n/cm (E
(E  1 MeV) was compared with a K
1 MeV) was compared with a K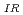 curve defined in JEAC4206-2016. It was shown that the K
curve defined in JEAC4206-2016. It was shown that the K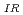 curve was always lower than the 1%ile curve of K
curve was always lower than the 1%ile curve of K for these irradiated RPV steels. This result indicates that the conservativeness of the method defined in JEAC4206-2016 to evaluate K
for these irradiated RPV steels. This result indicates that the conservativeness of the method defined in JEAC4206-2016 to evaluate K using K
using K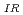 curve is confirmed for highly-irradiated RPV steels.
curve is confirmed for highly-irradiated RPV steels.
下平 昌樹; 飛田 徹; 名越 康人*; Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2021/07
JEAC4206-2016における原子炉圧力容器の構造健全性評価では、材料の破壊靭性が、想定欠陥であるクラッド下半楕円亀裂の先端における応力拡大係数よりも高いことが求められている。しかしながら、破壊靭性試験片と想定亀裂の亀裂深さやクラッドの有無といった違いにより、塑性拘束状態や破壊靭性評価に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。本研究では、半楕円亀裂に対する拘束効果やクラッドが破壊靭性評価に及ぼす影響を調べるため、4点曲げ破壊靭性試験及び有限要素解析を実施した。その結果、半楕円亀裂最深点における見かけの破壊靭性がマスターカーブ法に基づく5%信頼下限を上回り、現行評価手法が保守性を有することを確認した。半楕円亀裂における破壊の起点は亀裂最深点だけでなく試験体表面近傍にも観察された。有限要素解析の結果、半楕円亀裂における塑性拘束は亀裂最深点に比べて表面近傍で弱くなっていることが分かった。また、表面亀裂の場合に比べてクラッド下亀裂の場合には塑性拘束が弱められ、その弱い拘束の影響によりクラッド下亀裂の見かけの破壊靭性が表面亀裂のそれよりも高くなることがローカルアプローチによって示唆された。
下平 昌樹; 飛田 徹; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; 塙 悟史
Proceedings of ASME 2020 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2020) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2020/08
JEAC4206「原子炉圧力容器に対する供用期間中の破壊靭性の確認方法」では、加圧熱衝撃事象時の原子炉圧力容器(RPV)の健全性評価において、原子炉圧力容器内面のステンレスオーバーレイクラッド(クラッド)下亀裂(UCC)を想定し、亀裂先端の応力拡大係数がRPV鋼の破壊靭性値を上回らないことを定めている。本研究では、クラッドの存在が破壊靭性値に与える影響を評価することを目的に、UCCまたは表面亀裂を有する試験体を用いた3点曲げ破壊靭性試験と有限要素解析(FEA)を行い、UCCに対する塑性拘束効果の影響を調べた。その結果、UCCの破壊靭性値が表面亀裂に比べて高いことを実験的に示した。また、有限要素解析により、クラッドの存在によりUCCの塑性拘束効果が弱められることを示した。
近藤 悟; 飛田 吉春
JAEA-Research 2019-009, 382 Pages, 2020/03
日本原子力研究開発機構(旧動力炉・核燃料開発事業団)が開発したSIMMER-IIIは、2次元・多速度場・多成分流体力学を空間・時間依存の核動特性モデルと結合した計算コードであり、液体金属高速炉の炉心崩壊事故の解析に広く利用されている。コードの開発と並行して、包括的なコード検証プログラムを、第1期(流体力学個別モデルのverification)及び第2期(炉心崩壊事故における複雑かつ重要な現象についてのvalidation)の2段階に分けて実施してきた。SIMMER-III検証プログラムには欧州の研究開発機関が参加し、第1期の成果は1996年に総合的にとりまとめられた。本報告書は元の1996年の非公式の文書を再生・改訂することにより、第1期検証の研究成果を再編集したものである。第1期検証プログラムでは、流体対流、境界面積及び運動量交換、熱伝達、溶融・固化、蒸発・凝縮の分野で計34のテスト問題の解析が参加機関により分担して実施された。第1期プログラムで明らかとなった課題についてはその後のモデル開発・改良及び第2期プログラムに反映した。本報告書は新たに得られた研究知見に基づいて改訂しているが、参加者による元の解析結果と結論は、批判的な内容を含めて、そのまま記載している。
河 侑成; 下平 昌樹; 飛田 徹; 塙 悟史; 山崎 翔太*; 宇野 定則*
2018年度量子科学技術研究開発機構施設共用実施報告書(インターネット), 3 Pages, 2019/09
原子炉圧力容器の母材の内表面から約10mm深さの範囲に生じるステンレスオーバーレイクラッド下溶接熱影響部の照射脆化感受性を調査するための電子線照射試験の準備として、原子炉圧力容器鋼の実機環境相当である290 Cを目標とした照射温度の制御実験を実施した。冷却装置や試料固定治具の製作等を行い、電子線照射時の電流値による試料の発熱と熱伝導による冷却のバランスを調整し、照射温度を290
Cを目標とした照射温度の制御実験を実施した。冷却装置や試料固定治具の製作等を行い、電子線照射時の電流値による試料の発熱と熱伝導による冷却のバランスを調整し、照射温度を290 Cに制御する条件を調べた。その結果、適切な厚さのステンレススペーサーの使用により、290.6
Cに制御する条件を調べた。その結果、適切な厚さのステンレススペーサーの使用により、290.6 C
C 4.7
4.7 C範囲で照射温度を制御できることを確認した。
C範囲で照射温度を制御できることを確認した。
高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; 河 侑成; 飛田 徹; 西山 裕孝; 鬼沢 邦雄
Proceedings of 2019 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2019) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2019/07
原子炉圧力容器鋼の溶接熱影響部(HAZ)について、実際の原子炉圧力容器を模擬した継手溶接材(継手HAZ)及びHAZの代表的な組織を再現した熱処理材を作製し、JRR-3を用いた中性子照射試験及び照射後試験を実施し、照射前後の微細組織変化及び機械的特性変化を調べた。未照射材において、継手HAZ及び細粒HAZの破壊靭性が母材よりも低く、その要因が島状マルテンサイトやフェライト相の存在に因ることを明らかにした。また、粗粒HAZの中性子照射脆化感受性は母材よりも小さい値を示し、継手HAZ及び細粒HAZは母材と同等であることを明らかにした。
飛田 徹; 西山 裕孝; 鬼沢 邦雄
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-013, 60 Pages, 2018/11
原子炉圧力容器の健全性を判断する上で、破壊靱性をはじめとする材料の機械的特性は重要な情報となる。本レポートは、日本原子力研究開発機構が取得した中性子照射材を含む原子炉圧力容器鋼材の機械的特性、具体的には引張試験, シャルピー衝撃試験, 落重試験及び破壊靱性試験の公開データをまとめたものである。対象とした材料は、初期プラントから最新プラント相当の不純物含有量及び靱性レベルで製造されたJIS SQV2A(ASTM A533B Class1)相当の5種類の原子炉圧力容器鋼である。また母材に加え、原子炉圧力容器の内張りとして用いられている2種類のステンレスオーバーレイクラッド材の機械的特性データについても記載した。これらの機械的特性データは、材料ごとにグラフで整理するとともに今後のデータの活用しやすさを考慮して表形式でリスト化した。
河 侑成; 飛田 徹; 大津 拓与; 高見澤 悠; 西山 裕孝
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 140(5), p.051402_1 - 051402_6, 2018/10
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:32.89(Engineering, Mechanical)The applicability of miniature compact tension (Mini-C(T)) specimens to fracture toughness evaluation of neutron-irradiated reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels was investigated. Three types of RPV steels neutron-irradiated to a high-fluence region were prepared and manufactured as Mini-C(T) specimens according to Japan Electric Association Code (JEAC) 4216-2015. Through careful selection of the test temperature by considering previously obtained mechanical properties data, valid fracture toughness, and reference temperature T was obtained with a relatively small number of specimens. Comparing the fracture toughness and T
was obtained with a relatively small number of specimens. Comparing the fracture toughness and T values determined using other larger specimens with those determined using the Mini-C(T) specimens, T
values determined using other larger specimens with those determined using the Mini-C(T) specimens, T values of both unirradiated and irradiated Mini-C(T) specimens were found to be the acceptable margin of error. The scatter of 1T-equivalent fracture toughness values of both unirradiated and irradiated materials obtained using Mini-C(T) specimens did not differ significantly from the values obtained using larger specimens. The correlation between the Charpy 41J transition temperature (T
values of both unirradiated and irradiated Mini-C(T) specimens were found to be the acceptable margin of error. The scatter of 1T-equivalent fracture toughness values of both unirradiated and irradiated materials obtained using Mini-C(T) specimens did not differ significantly from the values obtained using larger specimens. The correlation between the Charpy 41J transition temperature (T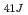 ) and the T
) and the T values agreed very well with that of the data in the literature, regardless of specimen size and fracture toughness of the materials before irradiation. Based on these findings, it was concluded that Mini-C(T) specimens can be applied to fracture toughness evaluation of neutron-irradiated materials without significant specimen size dependence.
values agreed very well with that of the data in the literature, regardless of specimen size and fracture toughness of the materials before irradiation. Based on these findings, it was concluded that Mini-C(T) specimens can be applied to fracture toughness evaluation of neutron-irradiated materials without significant specimen size dependence.
河 侑成; 飛田 徹; 高見澤 悠; 塙 悟史; 西山 裕孝
Proceedings of 2018 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2018), 6 Pages, 2018/07
An evaluation of the fracture toughness of the heat-affected zone (HAZ), which is located under the weld overlay cladding of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV), was performed. Considering inhomogeneous microstructures of the HAZ, 0.4T-C(T) specimens were manufactured from the cladding strips locations, and Mini-C(T) specimens were fabricated from the distanced location as well as under the cladding. The reference temperature (T ) values of HAZ for both 0.4T-C(T) and Mini-C(T) specimens were significantly lower than that of the base metal at a quarter thickness by 40
) values of HAZ for both 0.4T-C(T) and Mini-C(T) specimens were significantly lower than that of the base metal at a quarter thickness by 40 C
C 60
60 C. Compared to the literature data that indicated fracture toughness at the surface without overlay cladding and base metal of a quarter thickness in a pressure vessel plate, this study concluded that the welding thermal history showed no significant effect on the fracture toughness of the inner surface of RPV steel.
C. Compared to the literature data that indicated fracture toughness at the surface without overlay cladding and base metal of a quarter thickness in a pressure vessel plate, this study concluded that the welding thermal history showed no significant effect on the fracture toughness of the inner surface of RPV steel.
知見 康弘; 岩田 景子; 飛田 徹; 大津 拓与; 高見澤 悠; 吉本 賢太郎*; 村上 毅*; 塙 悟史; 西山 裕孝
JAEA-Research 2017-018, 122 Pages, 2018/03
原子炉圧力容器の加圧熱衝撃(Pressurized Thermal Shock: PTS)事象に対する構造健全性評価に与える影響項目の一つである高温予荷重(Warm Pre-stress: WPS)効果は、高温時に予め荷重を受けた場合に、冷却中の荷重減少過程では破壊が生じず、低温での再負荷時の破壊靱性が見かけ上増加する現象である。WPS効果については、主として弾性データによって再負荷時の見かけの破壊靱性を予測するための工学的評価モデルが提案されているが、試験片の寸法効果や表面亀裂に対して必要となる弾塑性評価は考慮されていない。本研究では、実機におけるPTS時の過渡事象を模擬した荷重-温度履歴を与える試験(WPS効果確認試験)を行い、WPS効果に対する試験片寸法や荷重-温度履歴の影響を確認するとともに、工学的評価モデルの検証を行った。再負荷時の見かけの破壊靭性について、予荷重時の塑性の程度が高くなると試験結果は工学的評価モデルによる予測結果を下回る傾向が見られた。比較的高い予荷重条件に対しては、塑性成分等を考慮することにより工学的評価モデルの高精度化が可能となる見通しが得られた。
Shamsuzzaman, M.*; 堀江 達郎*; 浮池 亮太*; 神山 基紀*; 森岡 徹*; 松元 達也*; 守田 幸路*; 田上 浩孝; 鈴木 徹*; 飛田 吉春
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 111, p.474 - 486, 2018/01
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:85.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)Particle bed characteristics are experimentally investigated for the sedimentation and subsequent bed formation of solid particles, related to the coolability aspects in core-disruptive accidents. Presently a series of experiments with gravity driven discharge of solid particles into a quiescent water pool was performed to evaluate bed formation characteristic in the course of particle sedimentation. We evaluated the effects of the crucial factors: nozzle diameter, particle density, particle diameter and nozzle height on four key quantitative parameters of bed shape: mound dimple area, mound dimple volume, repose angle and mound height to illustrate the role of the crucial factors on forming the particle bed shape. The investigated crucial factors exhibit a significant role that diversifies the particle bed formation process. Based on the data obtained in the experimental observations, we developed an empirical correlation to compare the predicted results with the experimental bed heights. The proposed empirical correlation can reasonably demonstrate the general trend of the experimental bed height. This correlation could be useful to assess the particle bed elevation, and to identify the governing parameters.
河 侑成; 飛田 徹; 高見澤 悠; 西山 裕孝
Proceedings of 2017 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2017) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2017/07
圧力容器鋼の破壊靱性評価へのミニチュアC(T)試験片の適用性を調べるため、中性子照射された圧力容器鋼材のシャルピー試験片からミニチュアC(T)試験片を加工するとともに破壊靱性試験に供し、参照温度 を評価した。その結果、ミニチュアC(T)試験片で得られる
を評価した。その結果、ミニチュアC(T)試験片で得られる は疲労予亀裂入りシャルピー型破壊靭性試験片から得られる値とよく一致すること、ミニチュアC(T)試験片から得られる1T-C(T)相当の破壊靱性値のばらつきは疲労予亀裂入りシャルピー型破壊靭性試験片等から得られるものと大差が無いこと、参照温度
は疲労予亀裂入りシャルピー型破壊靭性試験片から得られる値とよく一致すること、ミニチュアC(T)試験片から得られる1T-C(T)相当の破壊靱性値のばらつきは疲労予亀裂入りシャルピー型破壊靭性試験片等から得られるものと大差が無いこと、参照温度 とシャルピー吸収エネルギー41Jレベルの延性脆性遷移温度の関係は、米国データのばらつきの範囲内にあることが明らかになった。
とシャルピー吸収エネルギー41Jレベルの延性脆性遷移温度の関係は、米国データのばらつきの範囲内にあることが明らかになった。
小野田 雄一; 松場 賢一; 飛田 吉春; 鈴木 徹
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 4(3), p.16-00597_1 - 16-00597_14, 2017/06
For the prototype sodium-cooled fast reactor, MONJU, the mechanical energy and structural response under energetics caused by neutronic power excursion during Unprotected Loss of Flow accident (ULOF) were preliminarily analyzed. The objective of this study is to demonstrate the integrity of the reactor vessel against the mechanical load induced by the energetics. Conservative energy production was assumed in order to confirm the robustness of the safety design of MONJU. Mechanical energy was evaluated with the code in which mechanistic modelling of core expansion was implemented. The mechanical energy, which were obtained by analyzing the expanding behavior of core materials after energetics, were about one order of magnitude below the thermodynamic work potential calculated by assuming isentropic expansion of the fuel vapor to one atmosphere, which was often used as an indicator to express the severity of the energetics. Structural integrity was then evaluated with coupled fluid-structure dynamics code using the obtained mechanical energy. No or very small circumferential residual strain of the reactor vessel was evaluated in most analytical cases, and even in the most conservative energy production case, the residual strain was only 0.008 % so that the integrity of the reactor vessel is maintained. The result obtained in the present study shows that MONJU has enough robustness against the mechanical load under energetics.
曽我部 丞司; 鈴木 徹; 和田 雄作; 飛田 吉春
日本機械学会論文集(インターネット), 83(848), p.16-00393_1 - 16-00393_10, 2017/04
高速炉の代表的な炉停止失敗事象である冷却材流量喪失時炉停止失敗事象(ULOF: Unprotected Loss of Flow)の熱的影響を評価するためには、事故が核的に終息した後の再配置/冷却過程において、損傷炉心物質が炉容器内のどこに再配置し、それぞれの場所で長期にわたって安定冷却できるかを示す必要がある。本報では、IVR(In-Vessel Retention)成立性に関する見通しを得るために実施した低圧プレナム移行燃料及び炉心残留燃料の安定冷却性評価について報告する。
鈴木 徹; 曽我部 丞司; 飛田 吉春; 堺 公明*; 中井 良大
日本機械学会論文集(インターネット), 83(848), p.16-00395_1 - 16-00395_9, 2017/04
高速炉の炉停止失敗事象(ATWS: Anticipated Transient without Scram)に対して、原子炉容器内での事象終息(IVR: In-Vessel Retention)の成立性を検討した。検討においては、確率論的評価に基づいて冷却材流量喪失時炉停止失敗事象(ULOF: Unprotected Loss of Flow)をATWSの代表事象に選定した上で、総合的安全解析コードや個別物理モデルを活用して炉心損傷時の事象進展を解析し、事故の機械的影響と熱的影響を評価した。本検討の結果から、原子炉容器は機械的にも熱的にも損傷することはなく、IVRが成立する見通しを得ることができた。
曽我部 丞司; 鈴木 徹; 和田 雄作; 飛田 吉春
Proceedings of 10th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-10) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2016/11
The achievement of in-vessel retention (IVR) of accident consequences in an unprotected loss of flow (ULOF), which is one of the technically inconceivable events postulated beyond design basis, is an effective and rational approach to enhancing the safety characteristics of the sodium-cooled fast reactor. The objective of the present study is to show that the decay heat generated from the relocated fuels would be stably removed in post-accident-material-relocation/post-accident-heat-removal (PAMR/PAHR) phase, where the relocated fuels mean fuel discharged from the core into low-pressure plenum through control-rod guide tubes, and fuel remnant in the disrupted core region (non-discharged fuel). As a result of the assessment, it can be concluded that the stable cooling of the relocated fuels was confirmed and the prospect of IVR was obtained.