Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Moribayashi, Kengo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamashita, Shinichi; Katsumura, Yosuke; Maeyama, Takuya*; Meesungnoen, J.*; Jay-Gerin, J.-P.*; Baldacchino, G.*; Murakami, Takeshi*
no journal, ,
Although water is one of the most ubiquitous molecules as well as a main component of human body, understanding of water radiolysis is not always sufficient. Among many types of ionizing radiations, heavy ions deposit their energies very densely, resulting in distinctive following processes. Comprehension of water radiolysis itself is essential to consider indirect actions of ionizing radiations. Moreover, energy deposition distributions in water is related to that in/on biomolecules including DNA, proteins, and so on, and spatial distributions and temporal behaviors of water radicals give a clue to think over the fate of DNA damage produced within several nanoseconds. In this presentation, yields of water decomposition products which have been measured at HIMAC will be introduced in comparison to one of the most advanced Monte-Carlo simulation.
Muto, Yasuko; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yokoya, Akinari; Shikazono, Naoya; Fujii, Kentaro
no journal, ,
In many studies, base lesions are visualized as additional DNA strand breaks by the enzymatic glycosylase activity. However, these studies do have some limitations of detecting plural base lesions in a clustered base lesion site because the complex damage may retard the enzymatic activity to remove the base lesions. In order to determine the yield of base lesions constituting the clustered lesion site, we have developed a novel technique by which irradiated DNA is analyzed after a denaturation-annealing treatment. The DNA including a clustered base lesion site is denatured to a single strand molecule, and then annealed with a new complementary strand. In the obtained double strand molecule, the clustered base lesion site would be resolved to isolated lesions which are able to be processed by enzymes. We will report the optimal condition of the denaturation-annealing treatment and present a result of preliminary experiment using X-irradiated DNA.
Shiina, Takuya; Sugaya, Yuki; Shiraishi, Iyo; Watanabe, Ritsuko; Yokoya, Akinari
no journal, ,
Many studies using synthetic AP clusters reported that AP clusters retard base excision repair processes. Sutherland et al. (2002) showed that AP clusters are induced efficiently in human cells by low LET X-irradiation with the similar yields with those for the pyrimidine or purine base lesion clusters. There, however, has been very little knowledge of AP sites and AP clusters induced by high LET radiation. In order to clarify the relation between track structure of C ions or X-rays and the induction processes of an AP or AP clusters, we measure the yield of AP sites visualized by the treatment of irradiated pUC18 plasmid DNA with the AP endoclease (Nfo), which converts an AP site to detectable single strand break. Several scavenging capacities of the samples are tested to estimate the effect of indirect action of diffusible OH radicals. These experimental data will be discussed with theoretical radiation track structure in the respect of repair susceptibility of the AP cluster.
Hase, Yoshihiro; Yoshihara, Ryohei; Nozawa, Shigeki; Tamaoki, Masanori*; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Urushibara, Ayumi; Kodama, Seiji*; Yokoya, Akinari
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ouchi, Noriyuki
no journal, ,
Radiation dose, frequency of DNA strand breaks and frequency of chromosomal aberrations are commonly used for the measure of radiation effects. As we know, dose, DNA strand breaks and chromosomal aberrations are successive events, there are no common understandings for these relations. We are modeling chromosome using a kind of "toy-model", and extensively studied many dynamical features. Here, we will report on the physical properties of dynamics of chromosome, for example elastic movement, arising from computer simulation of our mathematical model.
Watanabe, Ritsuko; Yokoya, Akinari; Suzuki, Masao*; Tsuruoka, Chizuru*; Hirayama, Ryoichi*; Furusawa, Yoshiya*
no journal, ,
In general, survival curves of mammalian cells can be fit by linear-quadratic model. However, it is still open question that what is the lethal damage and what kind of condition can be related to the linear and quadratic terms of the lethal damage. The purpose of this study is to elucidate and modeling the relationship between initial DNA damage and cell lethality. Here, the yield of lethal damage is estimated from experimentally obtained survival curves using linear-quadratic model. The estimated yields are compared with the simulated DNA spectrum and the spatial distribution such as the distance between damages in cell nucleus. From the comparison, the condition of initial damage related to the cell lethality is examined. In particular, LET and cell cycle dependent of survival curves are discussed relating to the initial DNA damage pattern and repair pathways, respectively.
 model
modelTakahashi, Momoko; Noguchi, Miho; Hirakawa, Hirokazu*; Okayasu, Ryuichi*
no journal, ,
Ionizing radiation has been widely used as a tool for tumor treatment. However, there are still difficulties to treat the solid tumor with only irradiation. Several studies have been shown that the combination therapy using both X-irradiation and antitumor drug is more effective to tumor compared with X-irradiation only. Previously Noguchi et al. showed the Hsp90 inhibitor 17AAG induced tumor cell death effectively with X-irradiation. Hsp90 is the enzymes activated by cellular stress and activates several tumor-related genes. To clarify whether or not the combination therapy of carbon ion beam and 17AAG is effective to solid tumors, we tested the growth of solid tumor with the combination of X-irradiation and 17AAG  and compared the results from
and compared the results from  study.
study.
Noguchi, Miho; Urushibara, Ayumi; Yokoya, Akinari; Shikazono, Naoya
no journal, ,
In this study, we used plasmid based assay in  to measure the mutation frequency of clustered damage site containing 8-oxoG. Briefly, we constructed clustered damage sites carrying an SSB and 8-oxoG. 8-oxoG was placed within the recognition site of a restriction enzyme (
to measure the mutation frequency of clustered damage site containing 8-oxoG. Briefly, we constructed clustered damage sites carrying an SSB and 8-oxoG. 8-oxoG was placed within the recognition site of a restriction enzyme ( I). Damaged DNA was transfected into
I). Damaged DNA was transfected into  . The plasmids were extracted and the mutation frequency was assessed by the inability to cut by the restriction enzyme. The nature of mutation was determined by sequence analysis. The results suggested that an SSB on the same strand lowers, whereas an SSB on the opposite strand enhances the mutagenic potential of 8-oxoG. Sequence analyses of mutations revealed that the majority of the mutations were derived from 8-oxoG. Our study demonstrates that the mutagenic potential of clustered damage is influenced by the presence of an SSB and that there is a hierarchy of repair of lesions in a clustered damage site.
. The plasmids were extracted and the mutation frequency was assessed by the inability to cut by the restriction enzyme. The nature of mutation was determined by sequence analysis. The results suggested that an SSB on the same strand lowers, whereas an SSB on the opposite strand enhances the mutagenic potential of 8-oxoG. Sequence analyses of mutations revealed that the majority of the mutations were derived from 8-oxoG. Our study demonstrates that the mutagenic potential of clustered damage is influenced by the presence of an SSB and that there is a hierarchy of repair of lesions in a clustered damage site.
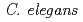 and its time course
and its time courseSuzuki, Michiyo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Hattori, Yuya; Tsuji, Toshio*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Akamatsu, Ken; Shikazono, Naoya
no journal, ,
Clustered damage site, that is a DNA region with multiple lesions within a few helical turns, is believed to hardly be repaired. This type of damage is considered to be induced around high-LET radiation tracks and at track-end of secondary electron. However, details of the clustered damage sites are not known. We have developed an analytical method for measuring the degree of dispersion of distances between DNA lesions using fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET). Complementary two single-strand DNA with an AP (apurinic/apyrimidinic)-site at each center nucleotide were synthesized. As a result, FRET occurred by anealing these strands. D-A distance calculated from the FRET efficiency was 4 nm, which was reasonable with the estimated one taking the diameter of B-form DNA duplex and length of each probe into account. Now we have tried to apply the FRET method to plasmid DNA irradiated with some radiation qualities. The results and the perspective will be discussed.
Yokota, Yuichiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Muto, Yasuko; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
Heavy-ion-induced DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) have been focused to reveal the underlying mechanism of the well-known findings that relative biological effectiveness is greater in high-LET heavy ions than in low-LET radiation. Since 1990s, DSBs have been quantified with pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) technology. In conventional studies, DNA preparation from irradiated cells was performed in agarose plugs for avoiding excess DNA fragmentation during experimental procedures. However, we have found here that DNA fragments are partly lost from the agarose plug during DNA preparation. This makes difficult to reveal the total DSB yield in irradiated cells.
Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
To carry out further analysis of mechanisms of heavy-ion radiation action, we developed a new heavy-ion focusing microbeam system, which can focus heavy-ion beam to minimum one micrometer in vacuum. To irradiate this finer beam to the specific region of individual cells, a cell targeting system was designed and installed under the beam extraction window. Using the system, irradiation of HeLa cells was carried out. The cells were stained with fluorescent dye and inoculated on a film of ion track detector, and their positions were extracted by image analysis code. The cells were, thereafter, targeted and irradiated with focusing Ne ion beam. After irradiation, the tracks of traversed ion were visualized and hit positions on the target samples were confirmed. The ions were well focused and hit on cells precisely. Therefore, we concluded that our system can target and irradiate individual cultured cells by focusing heavy-ion beam.
 -ray irradiation to dilute aqueous solution of plasmid DNA; Chemical repair of radiation-induced lesions on DNA by antioxidant edaravone
-ray irradiation to dilute aqueous solution of plasmid DNA; Chemical repair of radiation-induced lesions on DNA by antioxidant edaravoneHata, Kuniki; Urushibara, Ayumi; Yamashita, Shinichi; Shikazono, Naoya; Yokoya, Akinari; Katsumura, Yosuke*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oka, Toshitaka; Yamashita, Shinichi; Saiki, Seiichi; Yokoya, Akinari; Katsumura, Yosuke*; Kamibayashi, Masato*
no journal, ,
The reactive oxygen species play crucial roles in biological oxidative damage. In order to clarify the behaviour of hydroxyl and superoxide radicals closely related to the indirect effect of radiation damage of living body and DNA, detection and quantification of these radicals are essential. These radicals are easily produced by radiolysis of water but short lived. In the previous work we reported the rate constants of the reaction of a novel spin trap CYPMPO (5-(2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propoxy cyclophosphoryl)-5-methyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide) towards water decomposed species, e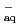 and
and  OH In the present study we have detected these radicals as spin adducts of CYPMPO by ESR and stability of these spin adducts, especially under the acid condition, have been evaluated.
OH In the present study we have detected these radicals as spin adducts of CYPMPO by ESR and stability of these spin adducts, especially under the acid condition, have been evaluated.
 ray irradiation at base pair level
ray irradiation at base pair levelSakamoto, Fuminori; Igarashi, Shosuke*; Onuki, Toshihiko
no journal, ,
It is known that DNA is damaged by the radiation, and many researchers studied the type of DNA damage, the DNA repair mechanism, and so on. However, identification of scission site and specificity of scission site have not been studied in detail up to now. We, therefore, cleaved DNA by irradiation of  Co
Co  ray, and specified the scission sites at one base pair level by using the technique that we developed. We considered the relationship between the scission sites and the type of base as well as DNA secondary structure.
ray, and specified the scission sites at one base pair level by using the technique that we developed. We considered the relationship between the scission sites and the type of base as well as DNA secondary structure.

Yoshihara, Ryohei; Takimoto, Koichi*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Nozawa, Shigeki; Sakamoto, Ayako; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
We constructed a mutation detection system by integrating a linearized plasmid DNA that has 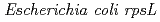 gene into the chromosomal DNA of
gene into the chromosomal DNA of  . We first analyzed the UV-induced mutation spectrum. The frequency of G to A transitions was increased after the exposure to UV light. To evaluate the effects of photorepair activity for CPDs in maintaining genomic integrity, we constructed RNAi plants in which the expression of CPD photolyase was suppressed. The mutation spectrum analysis in the RNAi plants showed that the frequency of frameshift mutations was increased together with that of G to A transitions. This suggests that the suppression of CPD photorepair not only increase the typical base substitutions but also other kinds of mutations. We next analyzed the mutation spectrum induced by
. We first analyzed the UV-induced mutation spectrum. The frequency of G to A transitions was increased after the exposure to UV light. To evaluate the effects of photorepair activity for CPDs in maintaining genomic integrity, we constructed RNAi plants in which the expression of CPD photolyase was suppressed. The mutation spectrum analysis in the RNAi plants showed that the frequency of frameshift mutations was increased together with that of G to A transitions. This suggests that the suppression of CPD photorepair not only increase the typical base substitutions but also other kinds of mutations. We next analyzed the mutation spectrum induced by  rays and carbon-ion beams (LET 121.5 keV/
rays and carbon-ion beams (LET 121.5 keV/ m). The results showed that
m). The results showed that  rays tended to induce shorter size of deletions than the carbon ions.
rays tended to induce shorter size of deletions than the carbon ions.
Sakashita, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
Systems biology is a new research field of basic biology to reveal the meaning of complicated life systems. Recently, groups of Europe and USA applied the system biology to the radiation biology. Here, p53-MDM2 feedback loop is presented as a example of systems radiation biology. Finally, a future of systems radiation biology is discussed.