Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Ir M
Ir M ssbauer spectroscopic parameters of Vaska's complexes and their oxidative adducts
ssbauer spectroscopic parameters of Vaska's complexes and their oxidative adductsKaneko, Masashi; Nakashima, Satoru*
Inorganic Chemistry, 60(17), p.12740 - 12752, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.69(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)In the present study, density functional theory (DFT) calculation was applied to Vaska's complexes of formula 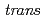 -[IrCl(CO)(PPh
-[IrCl(CO)(PPh )
) ], and their oxidative adducts with small molecules (YZ) including H
], and their oxidative adducts with small molecules (YZ) including H , i.e.,
, i.e., 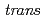 -[IrCl(YZ)(CO))(PPh
-[IrCl(YZ)(CO))(PPh )
) ], to successfully correlate the electronic states of the complexes with the corresponding
], to successfully correlate the electronic states of the complexes with the corresponding  Ir M
Ir M ssbauer spectroscopic parameters. After confirming the reproducibility of the DFT methods for elucidating the equilibrium structures and
ssbauer spectroscopic parameters. After confirming the reproducibility of the DFT methods for elucidating the equilibrium structures and 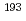 Ir M
Ir M ssbauer isomer shifts of the octahedral Ir complexes, the isomer shifts and quadrupole splitting values of Vaska's complexes and their oxidative adducts were calculated. A bond critical point analysis revealed that the tendency in the isomer shifts was correlated with the strength of the covalent interaction in the coordination bonds. In an electric field gradient (EFG) analysis of the oxidative adducts, the sign of the principal axis was found to be positive for the complex with YZ = Cl
ssbauer isomer shifts of the octahedral Ir complexes, the isomer shifts and quadrupole splitting values of Vaska's complexes and their oxidative adducts were calculated. A bond critical point analysis revealed that the tendency in the isomer shifts was correlated with the strength of the covalent interaction in the coordination bonds. In an electric field gradient (EFG) analysis of the oxidative adducts, the sign of the principal axis was found to be positive for the complex with YZ = Cl and negative for the complex with YZ = H
and negative for the complex with YZ = H . This reversal of the sign of the EFG principal axis was caused by the difference in the electron density distribution for the coordination bonds between Ir and YZ, according to a density of states analysis.
. This reversal of the sign of the EFG principal axis was caused by the difference in the electron density distribution for the coordination bonds between Ir and YZ, according to a density of states analysis.
 Ru M
Ru M ssbauer parameters of ruthenium-nitrosyl complexes
ssbauer parameters of ruthenium-nitrosyl complexesKaneko, Masashi; Kato, Akane*; Nakashima, Satoru*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Inorganic Chemistry, 58(20), p.14024 - 14033, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:62.43(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We applied density functional theory calculations to ruthenium-nitrosyl complexes, which are known to exist in high-level radioactive waste, to give a theoretical correlation between  Ru M
Ru M ssbauer spectroscopic parameters (
ssbauer spectroscopic parameters ( and
and 
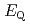 ) and ligand field strength (
) and ligand field strength (
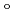 ) for the first time. The structures of the series of complexes, [Ru(NO)L
) for the first time. The structures of the series of complexes, [Ru(NO)L ] (L = Br
] (L = Br , Cl
, Cl , NH
, NH , CN
, CN ), were modeled based on the corresponding single-crystal X-ray coordinates. The comparisons of the geometries and total energies between the different spin states suggested that the singlet spin state of [Ru(II)(NO
), were modeled based on the corresponding single-crystal X-ray coordinates. The comparisons of the geometries and total energies between the different spin states suggested that the singlet spin state of [Ru(II)(NO )L
)L ] complexes were the most stable. The calculated results of both the
] complexes were the most stable. The calculated results of both the  and
and 
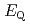 values reproduced the experimental results by reported previously and increased in the order of L = Br
values reproduced the experimental results by reported previously and increased in the order of L = Br , Cl
, Cl , NH
, NH , CN
, CN . Finally, we estimated the ligand field strength (
. Finally, we estimated the ligand field strength (
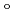 ) based on molecular orbitals, assuming C
) based on molecular orbitals, assuming C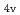 symmetry and showed the increase of
symmetry and showed the increase of 
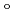 values in that order, being consistent with well-known spectrochemical series of ligands. The increase attributes to the strengthening of the abilities of
values in that order, being consistent with well-known spectrochemical series of ligands. The increase attributes to the strengthening of the abilities of  -donor and
-donor and  -acceptor of the L-ligands to the Ru atom, resulting in the increase of the
-acceptor of the L-ligands to the Ru atom, resulting in the increase of the  values.
values.
 NbO
NbO (0.5≦x≦2)
(0.5≦x≦2)Nakamura, Akio; ; Nakada, Masami; Saeki, Masakatsu; *; Akimitsu, Jun*
Ceramic Transactions, 71, p.295 - 306, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
 -iron telluride(Fe
-iron telluride(Fe Te) by Moessbauer spectroscopy
Te) by Moessbauer spectroscopy; Tsuji, Toshihide*; *
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 203, p.179 - 185, 1993/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:38.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Fe-atoms after EC-decay of
Fe-atoms after EC-decay of  Co-labelled Co(BrO
Co-labelled Co(BrO )
)
 6H
6H O studied by coincidence Moessbauer spectroscopy
O studied by coincidence Moessbauer spectroscopyNakada, Masami; *; Nakahara, Hiromichi*; *
Hyperfine Interactions, 70, p.1241 - 1244, 1992/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.67(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)no abstracts in English
 ssbauer spectroscopic parameters
ssbauer spectroscopic parametersKaneko, Masashi
no journal, ,
This study aims to perform the optimization of density functional methods using experimental data of M ssbauer isomer shifts and apply these methods to d, f-block coordination chemistry. In the d-block complexes, the validity for the spin-crossover (SCO) switching behavior of iron(II) assembled complexes was confirmed. The application of this method indicated that whether SCO occurs or not depends on the dihedral angle between iron atom and pyridine plane. In the f-block complexes, the benchmarking of computational method was performed using
ssbauer isomer shifts and apply these methods to d, f-block coordination chemistry. In the d-block complexes, the validity for the spin-crossover (SCO) switching behavior of iron(II) assembled complexes was confirmed. The application of this method indicated that whether SCO occurs or not depends on the dihedral angle between iron atom and pyridine plane. In the f-block complexes, the benchmarking of computational method was performed using  Eu and
Eu and  Np M
Np M ssbauer isomer shifts. The optimized method reproduced the separation behavior of Am(III) ion from Eu(III) ion and implied that the difference in the bonding contribution between 5f(Am) and 4f(Eu) attributes to the selectivity of Am(III) compared with Eu(III).
ssbauer isomer shifts. The optimized method reproduced the separation behavior of Am(III) ion from Eu(III) ion and implied that the difference in the bonding contribution between 5f(Am) and 4f(Eu) attributes to the selectivity of Am(III) compared with Eu(III).
 ssbauer isomer shift values for heavy metal complexes
ssbauer isomer shift values for heavy metal complexesKaneko, Masashi; Watanabe, Masayuki
no journal, ,
A linear relationship between M ssbauer isomer shift values and electron densities at nucleus position assures the quantitative evaluation of the covelant interaction between a M
ssbauer isomer shift values and electron densities at nucleus position assures the quantitative evaluation of the covelant interaction between a M ssbauer element and the surroundings. The evaluation of the linearity between experimental isomer shift values and estimated electron densities via quantum chemical calculation helps us to validate the computational method for estimating the bonding property. Our recent studies have demonstrated the benchmarking with the linear relationship using density functional calculations for heavy metal complexes, including
ssbauer element and the surroundings. The evaluation of the linearity between experimental isomer shift values and estimated electron densities via quantum chemical calculation helps us to validate the computational method for estimating the bonding property. Our recent studies have demonstrated the benchmarking with the linear relationship using density functional calculations for heavy metal complexes, including  Ru,
Ru,  Eu,
Eu, 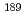 Os and
Os and  Np M
Np M ssbauer nuclides. The linearity was obtained with high correlation coefficient by mixing exact exchange potential into density functional. We will also present the bonding properties for the heavy metal complexes, as well as the application possibility of the computational method to the field of minor actinide partitioning.
ssbauer nuclides. The linearity was obtained with high correlation coefficient by mixing exact exchange potential into density functional. We will also present the bonding properties for the heavy metal complexes, as well as the application possibility of the computational method to the field of minor actinide partitioning.
 ssbauer isomer shift and the application to f-block metal coordination chemistry
ssbauer isomer shift and the application to f-block metal coordination chemistryKaneko, Masashi; Watanabe, Masayuki
no journal, ,
M ssbauer isomer shift obtained by measuring M
ssbauer isomer shift obtained by measuring M ssbauer spectroscopy has first-order linear responsibility to electron density at nucleus and varies based on the covalent interaction between an element and the surroundings. It assures the quantitative evaluation of the covalent interaction by comparing the linearity. This help us to validate the computational method for estimating the bonding property. We have presented the benchmarking of exchange-correlation functional of density functional theory using M
ssbauer spectroscopy has first-order linear responsibility to electron density at nucleus and varies based on the covalent interaction between an element and the surroundings. It assures the quantitative evaluation of the covalent interaction by comparing the linearity. This help us to validate the computational method for estimating the bonding property. We have presented the benchmarking of exchange-correlation functional of density functional theory using M ssbauer isomer shifts of Ru, Os, Eu and Np nuclides. We have indicated that the reproducibility of M
ssbauer isomer shifts of Ru, Os, Eu and Np nuclides. We have indicated that the reproducibility of M ssbauer isomer shift can be correlated to the mixing degree of exact Hartree-Fock exchange admixture in the functional. We will present the applications of the density functional theory to f-block coordination compounds to elucidate their structures and stabilities.
ssbauer isomer shift can be correlated to the mixing degree of exact Hartree-Fock exchange admixture in the functional. We will present the applications of the density functional theory to f-block coordination compounds to elucidate their structures and stabilities.
 and stainless steel
and stainless steelKumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Kirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Taishi*
no journal, ,
Fuel debris generated due to nuclear severe accidents is expected to contain a wide variety of uranium compounds. In this project, we have investigated chemical stability of simulated fuel debris containing elements from stainless steel (Fe, Cr, and Ni) against exposure to water. The simulated debris was prepared from the powders of UO and SUS304 by heating the mixed powder at 1200
and SUS304 by heating the mixed powder at 1200  C for 1 h under continuous gas flow of 2% O
C for 1 h under continuous gas flow of 2% O in Ar. The produced powder was characterized by XRD, SEM-EDX, Raman micro-spectroscopy, and M
in Ar. The produced powder was characterized by XRD, SEM-EDX, Raman micro-spectroscopy, and M ssbauer spectroscopy. The series of characterization revealed that the simulated debris comprised U(Fe,Cr)O
ssbauer spectroscopy. The series of characterization revealed that the simulated debris comprised U(Fe,Cr)O , U
, U O
O , and Fe(III) oxides. Then, the simulated debris was exposed to pure water for 30 days. The same leaching test of U
, and Fe(III) oxides. Then, the simulated debris was exposed to pure water for 30 days. The same leaching test of U O
O was performed for comparison. The chemical analysis of leached metals demonstrated that the U elution from the simulated debris was significantly lower than that from U
was performed for comparison. The chemical analysis of leached metals demonstrated that the U elution from the simulated debris was significantly lower than that from U O
O . In addition, Fe, Cr, and Ni were under quantitation limit as well. The Raman spectra showed that the exposure to water induced insignificant change in the spectra of the simulated debris, while the Raman band structure of U
. In addition, Fe, Cr, and Ni were under quantitation limit as well. The Raman spectra showed that the exposure to water induced insignificant change in the spectra of the simulated debris, while the Raman band structure of U O
O seemed to become slightly unclear after 30 days immersion.
seemed to become slightly unclear after 30 days immersion.
Kumagai, Yuta; Watanabe, Masayuki; Kusaka, Ryoji; Nakada, Masami; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Sasaki, Takayuki*
no journal, ,
Fuel debris generated in the accident at 1F NPS has been exposed to coolant water and the condition will change once the retrieval operation starts. In this situation, long-term chemical degradation is implied from previous studies on spent nuclear fuel. In this study, we have investigated chemical stability of simulated fuel debris containing elements from stainless steel (Fe, Cr, and Ni) against exposure to water. The simulated debris was prepared from the powders of UO and SUS304 by heating the mixed powder at 1200 or 1600
and SUS304 by heating the mixed powder at 1200 or 1600  C for 1 h under continuous gas flow of 2% O
C for 1 h under continuous gas flow of 2% O in Ar. The simulated debris was exposed to pure water for 30 days. The chemical analysis of leached metals demonstrated that the U elution from the simulated debris was significantly lower than that from U
in Ar. The simulated debris was exposed to pure water for 30 days. The chemical analysis of leached metals demonstrated that the U elution from the simulated debris was significantly lower than that from U O
O . In addition, Fe, Cr, and Ni were under quantitation limit. The Raman spectra showed that the exposure to water induced insignificant change in the spectra of the simulated debris.
. In addition, Fe, Cr, and Ni were under quantitation limit. The Raman spectra showed that the exposure to water induced insignificant change in the spectra of the simulated debris.
 ssbauer spectroscopic study
ssbauer spectroscopic studyKumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Kirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Sasaki, Takayuki*
no journal, ,
 -emitting nuclides analysis of the stagnant water including sediments in Fukushima Daiichi NPS, 4; Fe analysis of particulate solids in the contaminated water at Fukushima Daiichi NPS by M
-emitting nuclides analysis of the stagnant water including sediments in Fukushima Daiichi NPS, 4; Fe analysis of particulate solids in the contaminated water at Fukushima Daiichi NPS by M ssbauer spectroscopy
ssbauer spectroscopyOuchi, Kazuki; Nakada, Masami; Yomogida, Takumi; Oka, Toshitaka; Koma, Yoshikazu; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
In order to understand the chemical form of particulate solids contained in the retained water at three locations of Fukushima Daiichi NPS, the chemical species of Fe which is the main constituent element of solids were analyzed with M ssbauer spectroscopy. Most Fe was found to be
ssbauer spectroscopy. Most Fe was found to be  -form Fe(III) oxyhydroxide. Small amounts of Fe(II) hydroxide and magnetic substance were also detected in the torus and tank samples, respectively.
-form Fe(III) oxyhydroxide. Small amounts of Fe(II) hydroxide and magnetic substance were also detected in the torus and tank samples, respectively.