Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Saha, P. K.; Takeda, Osamu*; Saeki, Riuji*; Muto, Masayoshi*
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.937 - 941, 2023/11
In the J-PARC 3GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS), the 400MeV H beam is changed to H+ beam by a charge exchange foil and accelerated to 3GeV. So far, RCS had used two types of charge exchange foil. One is the HBC (Hybrid Boron mixed Carbon) foil and the other is the Kaneka GTF (Graphene Thin Film). HBC foil is a patented deposition method developed at KEK for the stable production of thick carbon foil. Initially, the RCS used HBC foil produced atKEK. However, in 2017, JAEA had started HBC foil production and has been using it since then. Recently, we have succeeded in depositing thick pure carbon foil, which had been considered difficult to produce by the arc deposition method. As a new challenge, this pure carbon foil was used in the user operation from March 2023. As a result, Pure carbon foils showed less deformation and more stable charge exchange performance than HBC and GTF.
beam is changed to H+ beam by a charge exchange foil and accelerated to 3GeV. So far, RCS had used two types of charge exchange foil. One is the HBC (Hybrid Boron mixed Carbon) foil and the other is the Kaneka GTF (Graphene Thin Film). HBC foil is a patented deposition method developed at KEK for the stable production of thick carbon foil. Initially, the RCS used HBC foil produced atKEK. However, in 2017, JAEA had started HBC foil production and has been using it since then. Recently, we have succeeded in depositing thick pure carbon foil, which had been considered difficult to produce by the arc deposition method. As a new challenge, this pure carbon foil was used in the user operation from March 2023. As a result, Pure carbon foils showed less deformation and more stable charge exchange performance than HBC and GTF.
Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Saha, P. K.; Takeda, Osamu*; Saeki, Riuji*; Muto, Masayoshi*
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.629 - 633, 2023/01
In the J-PARC 3-GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS), a 400 MeV H- beam injected from the linac is exchange to an H+ beam by a charge exchange foil and accelerated to 3 GeV. The charge exchange foils mainly used in the RCS are HBC foil (Hybrid Boron mixed Carbon stripper foil), which are made by adding a small amount of boron to carbon rods and using them as electrodes by the arc deposition method. Since 2018, foils produced by JAEA have been used for user operation. So far, no major problems have occurred due to the foils. Meanwhile, the beam power of the RCS has been gradually increased from 500 kW to 830 kW since 2018. As beam power increases, the foil issues were identified to achieve the RCS design power of 1 MW. In this paper, we will report on the recent foil usage status and issue in the user operation.
Takei, Hayanori
Isotope News, (779), p.11 - 15, 2022/02
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has designed a Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P) as an experimental facility in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The TEF-P is a critical assembly driven by a low-power proton beam, a maximum of 10 W, which is extracted from a high-power beam source, such as 250 kW of 400 MeV proton beam of the J-PARC Linac. To extract such a low-power proton beam from the high-power proton beam, we developed a laser charge exchange (LCE) device and employed its technique, which is one of the non-contact beam extraction techniques. For the proof of performance of the LCE device to the TEF-P, a low-power proton beam was extracted using a negative-hydrogen Linac having an energy of 3 MeV, and a bright laser. This paper summarizes the experimental results.
Takei, Hayanori; Tsutsumi, Kazuyoshi*; Meigo, Shinichiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(5), p.588 - 603, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has designed a Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P) as an experimental facility in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The TEF-P is a critical assembly driven by a low-power proton beam, a maximum of 10 W, which is extracted from a high-power beam source, such as 250 kW of 400 MeV proton beam of the J-PARC Linac. To extract such a low-power proton beam from the high-power proton beam, we developed a laser charge exchange (LCE) device and employed its technique, which is one of the non-contact beam extraction techniques. For the proof of performance of the LCE device to the TEF-P, a low-power proton beam was extracted using a negative-hydrogen (H ) Linac having an energy of 3 MeV, and a bright continuous laser. Proton beam with the power of 0.57 mW was successfully extracted with a laser stripping efficiency of
) Linac having an energy of 3 MeV, and a bright continuous laser. Proton beam with the power of 0.57 mW was successfully extracted with a laser stripping efficiency of 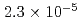 . These experimental values are in good agreement with the estimated ones.
. These experimental values are in good agreement with the estimated ones.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Kinsho, Michikazu
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011026_1 - 011026_6, 2021/03
The charge-exchange multi-turn injection by using a carbon stripper foil is adopted in high-intensity proton ring accelerators worldwide. It is a beneficial method to compress the pulsed proton beam with high intensity but there are serious issues for high intensity. First issue is a short lifetime of the foil by deformation or breaking itself. Another issue is high radiation dose corresponding to the scattered particles on the foil. Therefore, a non-destructive stripping injection method is required for higher intensity proton beam. We newly propose a non-destructive method of H stripping by using only laser. The new method is called "laser stripping injection". To establish our method, we are preparing for a POP (Proof-of-Principle) experiment of 400 MeV H- stripping to proton at J-PARC. In our presentation we will present the current status of laser system development for laser stripping injection at J-PARC.
stripping by using only laser. The new method is called "laser stripping injection". To establish our method, we are preparing for a POP (Proof-of-Principle) experiment of 400 MeV H- stripping to proton at J-PARC. In our presentation we will present the current status of laser system development for laser stripping injection at J-PARC.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Saha, P. K.; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Okazaki, Hiroyuki*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Yamada, Naoto*; Yamagata, Ryohei*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011019_1 - 011019_7, 2021/03
The multi-turn charge-exchange H beam injection scheme with stripper foils is one of the key techniques to achieve a MW-class high power proton beam. The J-PARC RCS adopts Hybrid type Boron-doped Carbon (HBC) stripper foil, which was developed in KEK to improve the lifetime. Indeed, the RCS user operation confirmed that HBC foil has the great advantage of a longer lifetime against high beam irradiation. To examine characteristics of the HBC foils, various beam studies were performed, such as the stripping efficiency measurement and long-term observation with an H
beam injection scheme with stripper foils is one of the key techniques to achieve a MW-class high power proton beam. The J-PARC RCS adopts Hybrid type Boron-doped Carbon (HBC) stripper foil, which was developed in KEK to improve the lifetime. Indeed, the RCS user operation confirmed that HBC foil has the great advantage of a longer lifetime against high beam irradiation. To examine characteristics of the HBC foils, various beam studies were performed, such as the stripping efficiency measurement and long-term observation with an H beam in the J-PARC RCS, foil analysis using RBS, EDR and PIXE methods, and SEM and TEM observation after the ion beam irradiation in Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application (TIARA) on National Institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology (QST). Recently, the deposition apparatus for the HBC foils from the KEK Tsukuba-site was relocated to the JAEA Tokai-site, and we started fabrication of new HBC foil in 2017. (The new one fabricated in JAEA we call J-HBC foil.) And, we continue investigations in TIARA with the J-HBC foils. Furthermore, in-depth researches by changing the process parameters of the foil deposition are carried on. Recent results suggest that the amount of the boron doped in the foil is more important parameter than the ratio of the discharge amount of carbon from cathode and anode electrodes. In this presentation, we will report the details of recent analysis of the J-HBC foil.
beam in the J-PARC RCS, foil analysis using RBS, EDR and PIXE methods, and SEM and TEM observation after the ion beam irradiation in Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application (TIARA) on National Institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology (QST). Recently, the deposition apparatus for the HBC foils from the KEK Tsukuba-site was relocated to the JAEA Tokai-site, and we started fabrication of new HBC foil in 2017. (The new one fabricated in JAEA we call J-HBC foil.) And, we continue investigations in TIARA with the J-HBC foils. Furthermore, in-depth researches by changing the process parameters of the foil deposition are carried on. Recent results suggest that the amount of the boron doped in the foil is more important parameter than the ratio of the discharge amount of carbon from cathode and anode electrodes. In this presentation, we will report the details of recent analysis of the J-HBC foil.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 17th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.441 - 445, 2020/09
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme is destructive-type method by using the foil and can accumulate high intensity proton beam. However, the uncontrolled beam losses by scattering at the foil and the foil breaking by the beam collision are a key issue of high-intensity proton accelerator. In order to realize higher intensity, new injection scheme of non-destructive type is needed instead of the foil. We newly propose laser stripping injection scheme by using laser pulse. We plan proof of principle experiment at J-PARC and are developing the laser system. In my presentation, we introduce the overview of laser stripping injection scheme and report the status of laser development.
 beam by electron beam
beam by electron beamOkabe, Kota
Proceedings of 17th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.446 - 448, 2020/09
One of the important research themes for further enhancement of the proton accelerator is the advancement of the charge exchange injection method. At present, the charge exchange injection method in the high-intensity proton accelerator facility currently in operation mainly uses the charge exchange foil. However, this method has a problem in that activation of the around the charge exchange injection point due to beam scattering by the foil and neutrons generated from the foil. In order to solve this problem, new charge exchange injection methods such as laser charge exchange method are being researched in accelerator facilities around the world. In this research, we focus on the charge exchange method using electron beams and proceed with the basic experiments. In this presentation, we will report the progress of the charge exchange efficiency measurement of negative hydrogen ion beam using electron beam.
Takei, Hayanori; Hirano, Koichiro; Meigo, Shinichiro; Tsutsumi, Kazuyoshi*
Proceedings of 8th International Beam Instrumentation Conference (IBIC 2019) (Internet), p.595 - 599, 2020/06
Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) has a plan to build the Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P), in which a 400-MeV proton beam will be delivered from negative hydrogen (H ) accelerated by the linac. Since the TEF-P requires a stable proton beam with a power of less than 10 W, a steady and meticulous beam extraction method is required to extract a small amount of the proton beam from the high power beam using 250 kW. To fulfill this requirement, we have developed beam extraction based on the Laser Charge Exchange (LCE) method. For the demonstration present beam extraction technique, an experiment was conducted using H
) accelerated by the linac. Since the TEF-P requires a stable proton beam with a power of less than 10 W, a steady and meticulous beam extraction method is required to extract a small amount of the proton beam from the high power beam using 250 kW. To fulfill this requirement, we have developed beam extraction based on the Laser Charge Exchange (LCE) method. For the demonstration present beam extraction technique, an experiment was conducted using H beam accelerated by the 3-MeV linac at RFQ test-stand in J-PARC. As a result of the experiment with continuous wave (CW) of the Laser, a charge-exchanged long-pulsed H
beam accelerated by the 3-MeV linac at RFQ test-stand in J-PARC. As a result of the experiment with continuous wave (CW) of the Laser, a charge-exchanged long-pulsed H beam with a power of about 0.70 W equivalent was successfully obtained under the TEF-P beam condition.
beam with a power of about 0.70 W equivalent was successfully obtained under the TEF-P beam condition.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Saha, P. K.; Kinsho, Michikazu
EPJ Web of Conferences, 229, p.01001_1 - 01001_7, 2020/02
In the 3-GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), we adopted thick Hybrid type Boron-doped Carbon (HBC) stripper foil for the multi-turn H charge-exchange injection. The HBC stripper foil developed at KEK has been successfully demonstrated to improve the foil lifetime significantly. Early manufacturing process of the stripper foil in the J-PARC had been carried out in following two steps: foil fabrication in KEK Tsukuba-site and foil preparation in JAEA Tokai-site. However, to proceed with the foil manufacturing in a same place efficiently, the carbon discharge arc-evaporation system for HBC stripper foil was removed from the Tsukuba-site and relocated in the Tokai-site. After reassembling of the carbon discharge arc-evaporation system, performance evaluation tests of new HBC foil which are produced at the JAEA Tokai site (J-HBC) are implemented at the TIARA facility of QST-Takasaki. As results of argon beam irradiation for lifetime evaluation, components analysis with RBS method, and impurity evaluation with micro-PIXE method, we can verify that the J-HBC foil performs pretty much equally to the original HBC foil. After the irradiation test by using 400MeV H
charge-exchange injection. The HBC stripper foil developed at KEK has been successfully demonstrated to improve the foil lifetime significantly. Early manufacturing process of the stripper foil in the J-PARC had been carried out in following two steps: foil fabrication in KEK Tsukuba-site and foil preparation in JAEA Tokai-site. However, to proceed with the foil manufacturing in a same place efficiently, the carbon discharge arc-evaporation system for HBC stripper foil was removed from the Tsukuba-site and relocated in the Tokai-site. After reassembling of the carbon discharge arc-evaporation system, performance evaluation tests of new HBC foil which are produced at the JAEA Tokai site (J-HBC) are implemented at the TIARA facility of QST-Takasaki. As results of argon beam irradiation for lifetime evaluation, components analysis with RBS method, and impurity evaluation with micro-PIXE method, we can verify that the J-HBC foil performs pretty much equally to the original HBC foil. After the irradiation test by using 400MeV H beam in the J-PARC RCS, user operation by using the J-HBC foil was successfully demonstrated for 10 days.
beam in the J-PARC RCS, user operation by using the J-HBC foil was successfully demonstrated for 10 days.
Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Takeda, Osamu*; Saeki, Riuji*; Muto, Masayoshi*
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.545 - 549, 2019/07
In the 3 GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research complex (J-PARC), we adopted the carbon stripper foil for the multi-turn H- charge exchange injection. The charge exchange foil which use in RCS is fabricated by the arc discharge method with the boron doped carbon electrode. The foil fabricated this method is called HBC foil (Hybrid Boron mixed Carbon stripper foil). HBC foil had been developed at KEK. It has high durability for the beam irradiation damage. In past days, the foil fabrication process was conducted in KEK Tsukuba-site and the foil preparation process was conducted in JAEA Tokai-site. In 2017, the foil deposition apparatus has been relocated from KEK to JAEA, and we started both processes in Tokai-site. We carried out the offline beam irradiation test for the new HBC foil which fabricated in JAEA, and we confirmed that its performance is equivalent to the original HBC foil. Next we tested a new HBC foil with actual beam in RCS and we confirmed it could withstand 1 week beam irradiation. After that, we started user operation with the new HBC foil in 2018. So far we accomplished stable user operation for one year by using the new HBC foil only.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Inoue, Shunsuke*; Sato, Atsushi*; Suganuma, Kazuaki; Yamane, Isao*; Kinsho, Michikazu; Irie, Yoshiro*
Proceedings of 15th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.811 - 815, 2018/08
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme can realize high intensity proton beam but the uncontrolled beam losses occur by scattering at the foil. Additionally, the beam collision at the foil may cause the break itself. Therefore, a new injection scheme for higher intensity is needed as an alternative to the foil. We newly propose and develop a laser stripping injection scheme. At the first step, we propose a proof-of-principle (POP) experiment of the scheme in J-PARC and develop a laser system. In this presentation, we will introduce the laser stripping injection scheme and describe an overview of a POP experiment. We will report a current status of the laser system.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Matsuda, Hiroki; Takei, Hayanori
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1021(1), p.012072_1 - 012072_4, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Takei, Hayanori; Hirano, Koichiro; Tsutsumi, Kazuyoshi; Meigo, Shinichiro
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 13(Sp.1), p.2406012_1 - 2406012_6, 2018/03
The Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) has a plan to build the Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P), in which a 400-MeV negative proton (H ) beam will be delivered from the J-PARC linac. Since the TEF-P requires a stable proton beam with a power of less than 10 W, a stable and meticulous beam extraction method is required to extract a small amount of the proton beam from the high power beam using 250 kW. To fulfil this requirement, the Laser Charge Exchange (LCE) method has been developed. To demonstrate the charge exchange of the H
) beam will be delivered from the J-PARC linac. Since the TEF-P requires a stable proton beam with a power of less than 10 W, a stable and meticulous beam extraction method is required to extract a small amount of the proton beam from the high power beam using 250 kW. To fulfil this requirement, the Laser Charge Exchange (LCE) method has been developed. To demonstrate the charge exchange of the H , a preliminary LCE experiment was conducted using a linac with energy of 3 MeV in J-PARC. As a result of the experiment, a charge-exchanged H
, a preliminary LCE experiment was conducted using a linac with energy of 3 MeV in J-PARC. As a result of the experiment, a charge-exchanged H beam with a power of about 8 W equivalent and an accuracy of about 2% was obtained under the J-PARC linac beam condition.
beam with a power of about 8 W equivalent and an accuracy of about 2% was obtained under the J-PARC linac beam condition.
Takei, Hayanori; Hirano, Koichiro; Meigo, Shinichiro; Tsutsumi, Kazuyoshi*
Proceedings of 6th International Beam Instrumentation Conference (IBIC 2017) (Internet), p.435 - 439, 2018/03
The Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) has a plan to build the Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P), in which a 400-MeV negative proton (H ) beam will be delivered from the J-PARC linac. Since the TEF-P requires a stable proton beam with a power of less than 10 W, a stable and meticulous beam extraction method is required to extract a small amount of the proton beam from the high power beam using 250 kW. To fulfil this requirement, the Laser Charge Exchange (LCE) method has been developed. To demonstrate the charge exchange of the H
) beam will be delivered from the J-PARC linac. Since the TEF-P requires a stable proton beam with a power of less than 10 W, a stable and meticulous beam extraction method is required to extract a small amount of the proton beam from the high power beam using 250 kW. To fulfil this requirement, the Laser Charge Exchange (LCE) method has been developed. To demonstrate the charge exchange of the H , a preliminary LCE experiment was conducted using a linac with energy of 3 MeV in J-PARC. As a result of the experiment, a charge-exchanged H
, a preliminary LCE experiment was conducted using a linac with energy of 3 MeV in J-PARC. As a result of the experiment, a charge-exchanged H beam with a power of about 8 W equivalent and an accuracy of about 2% was obtained under the J-PARC linac beam condition.
beam with a power of about 8 W equivalent and an accuracy of about 2% was obtained under the J-PARC linac beam condition.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Yamane, Isao*; Saha, P. K.; Suganuma, Kazuaki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Irie, Yoshiro*; Kato, Shinichi
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.684 - 688, 2017/12
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme can realize high intensity proton beam but the uncontrolled beam losses are caused by scattering between beams and the foil. Additionally, the collision may occur the foil beak. Therefore, a new injection scheme for higher intensity is needed as an alternative to the foil. In the J-PARC 3GeV RCS, we newly propose and develop a laser stripping injection scheme. However, it is necessary that laser power is two order higher than latest laser one. To realize this big issue, we develop the laser storage ring, which can provide laser pulse of high repetition rate by recycling one. In this presentation, we will introduce the laser stripping injection scheme and describe the concept of the laser storage ring with high repetition rate and report the current status.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Kato, Shinichi; Okabe, Kota; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.877 - 881, 2017/12
It is key issue to reduce the level of the radio-activation of the devices in high power proton accelerator, to achieve MW class high power beam operation. The 3 GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) adopted a beam collimation system which aims to localize the beam loss at the collimators and to reduce the level of residual doses at the other devices. However, relatively high residual doses are detected in not only the beam collimator area but also a vicinity of the stripper foil. The results of previous work, measurements of the detailed residual dose distribution and simulations of the radio-activation by the PHITS, indicate that the high level residual dose around the stripper foil is caused by secondary particles due to nuclear reaction at the foil. In order to suppress the secondary particles from foil, we try hard to reduce the number of foil hitting particles during the beam injection period. As a result, the level of the radio-activation around the foil can be decreased. At the same time, new beam loss monitor to detect the secondary particles from the foil is developed. In this presentation, we report the secondary particles detections and estimations of number of the foil hitting particles. In addition, we discuss the reduction of the radio-activation.
Takei, Hayanori; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Meigo, Shinichiro; Miura, Akihiko; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Tsutsumi, Kazuyoshi
Proceedings of 5th International Beam Instrumentation Conference (IBIC 2016) (Internet), p.736 - 739, 2017/03
The Accelerator-driven System (ADS) is one of the candidates for transmuting long-lived nuclides, such as minor actinide (MA), produced by nuclear reactors. For efficient transmutation of the MA, a precise pre-diction of neutronics of ADS is required. In order to obtain the neutronics data for the ADS, the Japan Pro-ton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) has a plan to build the Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P), in which a 400-MeV negative proton (H ) beam will be delivered from the J-PARC linac. Since the TEF-P requires a stable proton beam with a power of less than 10W, a stable and meticulous beam extraction method is required to extract a small amount of the proton beam from the high power beam using 250kW. To fulfil this requirement, the Laser Charge Exchange (LCE) method has been developed. The LCE strips the electron of the H
) beam will be delivered from the J-PARC linac. Since the TEF-P requires a stable proton beam with a power of less than 10W, a stable and meticulous beam extraction method is required to extract a small amount of the proton beam from the high power beam using 250kW. To fulfil this requirement, the Laser Charge Exchange (LCE) method has been developed. The LCE strips the electron of the H beam and neutral protons will separate at the bending magnet in the proton beam transport. To demonstrate the charge exchange of the H
beam and neutral protons will separate at the bending magnet in the proton beam transport. To demonstrate the charge exchange of the H , a preliminary LCE experiment was conducted using a linac with energy of 3MeV in J-PARC. As a result of the experiment, a charge-exchanged H
, a preliminary LCE experiment was conducted using a linac with energy of 3MeV in J-PARC. As a result of the experiment, a charge-exchanged H beam with a power of about 5W equivalent was obtained under the J-PARC linac beam condition, and this value almost satisfied the power requirement of the proton beam for the TEF-P.
beam with a power of about 5W equivalent was obtained under the J-PARC linac beam condition, and this value almost satisfied the power requirement of the proton beam for the TEF-P.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yamane, Isao*; Kato, Shinichi; Kinsho, Michikazu; Irie, Yoshiro*
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.983 - 986, 2016/11
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme can realize high intensity proton beam but the uncontrolled beam losses are caused by scattering between beams and the foil. Additionally, the collision may occur the foil beak. Therefore, a new injection scheme for higher intensity is needed as an alternative to the foil. In the J-PARC 3GeV RCS, we newly propose and develop a laser stripping injection scheme However, it is necessary that laser power is two order higher than latest laser one. To realize this big issue, we develop the laser storage ring, which can provide laser pulse of high repetition rate by recycling one. In this presentation, we will introduce the laser stripping injection scheme and describe the concept of the laser storage ring with high repetition rate.
Takei, Hayanori; Hirano, Koichiro; Tsutsumi, Kazuyoshi; Chishiro, Etsuji; Miura, Akihiko; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Meigo, Shinichiro
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.987 - 991, 2016/11
Accelerator-driven system (ADS) is one of candidates to transmute long-lived nuclides such as minor actinide (MA) produced at nuclear reactor. For efficient transmutation of the MA, precise prediction of neutronics of ADS is indispensable. In order to obtain the neutronics data for the ADS, J-PARC has a plan to build the Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P). Since the TEF-P requires stable power of the beam and will operate with thermal power less than 500 W and the proton beam power of 10 W so that a stable and meticulous beam extraction method is required to extract small amount of the beam from the high power LINAC beam with 250 kW. To fulfill requirement, Laser charge exchange method (LCE) has been developed for delivery of 400-MeV proton beam with 25Hz to the TEF-P. The LCE strips the electron of H beam and H
beam and H will separate at the bending magnet at the proton beam transport. The LCE device consists of YAG-laser with high power as 1.6 J/shot and 25 Hz and transport control system with high accuracy of the beam position. For the demonstration of the charge exchange of the H
will separate at the bending magnet at the proton beam transport. The LCE device consists of YAG-laser with high power as 1.6 J/shot and 25 Hz and transport control system with high accuracy of the beam position. For the demonstration of the charge exchange of the H , the further LCE tests is conducted using H
, the further LCE tests is conducted using H beam with energy of 3-MeV at RFQ test stand in J-PARC. In this paper, present status of LCE tests is presented.
beam with energy of 3-MeV at RFQ test stand in J-PARC. In this paper, present status of LCE tests is presented.