Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Tetsuya; Nagame, Yuichiro*
Nihon Butsuri Gakkai-Shi, 78(2), p.64 - 72, 2023/02
The study of the chemistry of superheavy elements, which are located in the heavy extremes of the periodic table, has made considerable progress over the past 20 years, and new approaches based on various ideas have recently been developed. Research groups in Japan have also made significant contributions to the development of research on superheavy elements. Recently, notable results have been reported for the transactinide elements rutherfordium (element 104), dubnium (element 105), and seaborgium (element 106), and the heavy actinides with atomic numbers exceeding 100. The review will focus on the recent main results of these elements. This review outlines the main recent results and touches on future prospects.
Sato, Tetsuya
Kagaku To Kogyo, 72(10), P. 867, 2019/10
We conducted measurements of the first ionization potential (IP ) of the heavy actinide elements, lawrencium (Lr,
) of the heavy actinide elements, lawrencium (Lr, 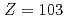 ), nobelium (No,
), nobelium (No,  ), mendelevium (Md,
), mendelevium (Md,  ) and fermium (Fm,
) and fermium (Fm,  ) by using a novel method based on a surface ionization process. The IP
) by using a novel method based on a surface ionization process. The IP measurements have been performed using the ISOL (Isotope Separator On-Line) system equipped with a surface ion-source with short-lived heavy actinide isotopes,
measurements have been performed using the ISOL (Isotope Separator On-Line) system equipped with a surface ion-source with short-lived heavy actinide isotopes,  Lr (
Lr (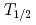 = 27s),
= 27s),  No (
No (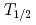 = 24.5s),
= 24.5s), 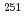 Md (
Md (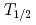 = 4.27 min), and
= 4.27 min), and  Fm (
Fm (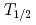 = 2.6 min). Our experimental results clearly showed that the IP
= 2.6 min). Our experimental results clearly showed that the IP of Lr is distinctly low among actinide elements. Moreover, No has the highest IP
of Lr is distinctly low among actinide elements. Moreover, No has the highest IP among them due to its full-filled 5f and 7s orbitals; the IP
among them due to its full-filled 5f and 7s orbitals; the IP value increased with an atomic number up to No and decreased dramatically at Lr, indicating the similar trend with that of heavy lanthanide elements. Therefore, we concluded Lr would be the last member of the actinide series.
value increased with an atomic number up to No and decreased dramatically at Lr, indicating the similar trend with that of heavy lanthanide elements. Therefore, we concluded Lr would be the last member of the actinide series.
Nagame, Yuichiro; Asai, Masato; Haba, Hiromitsu; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Goto, Shinichi; Sakama, Minoru; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Akiyama, Kazuhiko; Ichikawa, Shinichi
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences, 3(1), p.129 - 132, 2002/06
no abstracts in English
Sato, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
The experimental determination of the first ionization potential (IP) yields information on the electronic structure of the element. We successfully ionized and mass-separated  No and
No and  Lr with efficiencies (
Lr with efficiencies (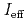 ) of (0.5
) of (0.5  0.1)% and (36
0.1)% and (36  7)% at 2800 K, respectively. From these
7)% at 2800 K, respectively. From these 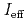 values, IP values of No and Lr were determined based on the relationship between
values, IP values of No and Lr were determined based on the relationship between 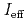 and IP. Our values are in good agreement with the predicted ones by theoretical calculations.
and IP. Our values are in good agreement with the predicted ones by theoretical calculations.
Sato, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
The chemical and atomic properties of the heavy elements with atomic numbers Z  100, affected by strong relativistic effects, are studied at an-atom-at-a-time scale using the JAEA-ISOL. We successfully determined the first ionization potential (IP
100, affected by strong relativistic effects, are studied at an-atom-at-a-time scale using the JAEA-ISOL. We successfully determined the first ionization potential (IP ) values of heavy actinide elements from fermium (Fm, Z = 100) to lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) by using a surface ion-source installed in the Isotope Separator On-Line (ISOL) at the JAEA tandem accelerator facility. The adsorption behavior of Lr is being studied by a newly developed method combining vacuum chromatography with surface ionization in a metallic column/ionizer of the ISOL as well.
) values of heavy actinide elements from fermium (Fm, Z = 100) to lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) by using a surface ion-source installed in the Isotope Separator On-Line (ISOL) at the JAEA tandem accelerator facility. The adsorption behavior of Lr is being studied by a newly developed method combining vacuum chromatography with surface ionization in a metallic column/ionizer of the ISOL as well.
 Es target
Es targetAsai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Ito, Yuta; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Makii, Hiroyuki; Hirose, Kentaro; Orlandi, R.; Suzaki, Fumi; Aoki, Ryota; et al.
no journal, ,
Fission of neutron-rich heavy-actinide nuclei exhibits extremely characteristic fission-fragment mass distributions which differ significantly from those of typical actinide nuclei. In the present study, we have succeeded in producing those neutron-rich heavy-actinide nuclei with multinucleon transfer reactions using an extremely rare and short-lived  Es target bombarded with heavy-ion beam from the JAEA Tandem Accelerator. The products were mass-separated with an on-line isotope separator (ISOL), and spontaneous fission of
Es target bombarded with heavy-ion beam from the JAEA Tandem Accelerator. The products were mass-separated with an on-line isotope separator (ISOL), and spontaneous fission of  Fm,
Fm,  Fm,
Fm,  Md,
Md,  Lr was observed. Fission-fragment mass distributions and total kinetic energy distributions were obtained precisely, which provides us with important information to clarify the characteristic fission mechanism observed in this nuclear region.
Lr was observed. Fission-fragment mass distributions and total kinetic energy distributions were obtained precisely, which provides us with important information to clarify the characteristic fission mechanism observed in this nuclear region.