Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Okita, Shoichiro; Goto, Minoru
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/10
Kosaka, Wataru; Uchibori, Akihiro; Okano, Yasushi; Yanagisawa, Hideki*
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.1150 - 1163, 2023/08
The leakage of pressurized water from a steam generator (SG) and the progress after that are a key issue in the safety assessment or design of a SG in sodium-cooled fast reactor. The analysis code LEAP-III can evaluate a rate of water leakage during the long-term event progress, i.e., from the self-wastage initiated by an occurrence of a microscopic crack in a tube wall to the water leak detection and water/water-vapor blowdown. Since LEAP-III consists of semi-empirical formulae and one-dimensional equations of conservation, it has an advantage in short computation time. Thus, LEAP-III can facilitate the exploration of various new SG designs in the development of innovative reactors. However, there are several problems, such as an excessive conservative result in some case and the need for numerous experiments or preliminary analyses to determine tuning parameters of models in LEAP-III. Hence, we have developed a Lagrangian particle method code, which is characterized by a simpler computational principle and faster calculation. In this study, we have improved the existing particle pair search method for interparticle interaction in this code and developed an alternative model without the pair search. Through the trial analysis simulating in a tube bundle system, it was confirmed that new models reduced the computation time. In addition, it was shown that representative temperatures of the heat-transfer tubes evaluated by this particle method code, which is used to predict the tube failure in LEAP-III, were good agreement with that by SERAPHIM, which is a detailed mechanistic analysis method code.
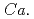 Methanoperedenaceae
MethanoperedenaceaeNishimura, Hiroki*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Fukuda, Akari*; Ishimura, Toyoho*; Amano, Yuki; Beppu, Hikari*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Suzuki, Yohei*
Environmental Microbiology Reports (Internet), 15(3), p.197 - 205, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:48.3(Environmental Sciences)The family 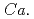 Methanoperedenaceae archaea mediate anaerobic oxidation of methane (AOM). We newly developed a high-pressure laboratory incubation system and investigated groundwater from 214- and 249-m deep boreholes at Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, Japan, where the high and low abundances of
Methanoperedenaceae archaea mediate anaerobic oxidation of methane (AOM). We newly developed a high-pressure laboratory incubation system and investigated groundwater from 214- and 249-m deep boreholes at Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, Japan, where the high and low abundances of 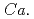 Methanoperedenaceae archaea have been revealed, respectively. We incubated the samples amended with or without amorphous Fe(III) and
Methanoperedenaceae archaea have been revealed, respectively. We incubated the samples amended with or without amorphous Fe(III) and  C-labelled methane at an in-situ pressure of 1.6 MPa. After three to seven-day incubation, AOM activities were not detected from the 249-m sample but from the 214-m sample. The AOM rates were 93.7
C-labelled methane at an in-situ pressure of 1.6 MPa. After three to seven-day incubation, AOM activities were not detected from the 249-m sample but from the 214-m sample. The AOM rates were 93.7 40.6 and 27.7
40.6 and 27.7 37.5 nM/day with and without Fe(III) amendment. Suspended particulates were not visible in the 249-m sample on the filter, while they were abundant and contained amorphous Fe(III) and Fe(III)-bearing phyllosilicates in the 214-m sample. This supports the in-situ activity of Fe(III)-dependent AOM in the deep subsurface borehole.
37.5 nM/day with and without Fe(III) amendment. Suspended particulates were not visible in the 249-m sample on the filter, while they were abundant and contained amorphous Fe(III) and Fe(III)-bearing phyllosilicates in the 214-m sample. This supports the in-situ activity of Fe(III)-dependent AOM in the deep subsurface borehole.
Matsushita, Hatsuki*; Kobayashi, Ren*; Sakai, Takaaki*; Kato, Shinya; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-13) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2022/09
During core disruptive accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors, the molten core material flows through flow channels, such as the control rod guide tubes, into the core inlet plenum under the core region. The molten core material can be cooled and solidified while impinging on a horizontal plate of the inlet plenum in a sodium coolant. However, the solidification and cooling behaviors of molten core materials impinged on a horizontal structure have not been sufficiently studied thus far. Notably, this is an important phenomenon that needs to be elucidated from the perspective of improving the safety of sodium-cooled fast reactors. Accordingly, a series of experiments on discharging a simulated molten core material (alumina: Al O
O ) into a sodium coolant on a horizontal structure was conducted at the experimental facility of the National Nuclear Center of the Republic of Kazakhstan. In this study, analyses on the sodium experiments using SIMMER-III as the fast reactor safety evaluation code were performed. The analysis methods were validated by comparing the results and experiment data. In addition, the cooling and solidification behaviors during jet impingement were evaluated. The results indicated that the molten core material exhibited fragmentation owing to the impingement on the horizontal plate and was, therefore, scattered toward the periphery. Furthermore, the simulated molten core material was evaluated to be cooled by sodium and subsequently solidified.
) into a sodium coolant on a horizontal structure was conducted at the experimental facility of the National Nuclear Center of the Republic of Kazakhstan. In this study, analyses on the sodium experiments using SIMMER-III as the fast reactor safety evaluation code were performed. The analysis methods were validated by comparing the results and experiment data. In addition, the cooling and solidification behaviors during jet impingement were evaluated. The results indicated that the molten core material exhibited fragmentation owing to the impingement on the horizontal plate and was, therefore, scattered toward the periphery. Furthermore, the simulated molten core material was evaluated to be cooled by sodium and subsequently solidified.
Kosaka, Wataru; Uchibori, Akihiro; Yanagisawa, Hideki*; Takata, Takashi; Jang, S.*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 88(905), p.21-00310_1 - 21-00310_9, 2022/01
If a pressurized water/water-vapor leaks from a heat transfer tube in a steam generator (SG) in a sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), sodium-water reaction forms high-velocity, high-temperature, and corrosive jet. It would damage the other tubes and might propagate the tube failure in the SG. Thus, it is important to evaluate the effect of the tube failure propagation for safety assessment of SFR. The computational code LEAP-III can evaluate water leak rate during the tube failure propagation with short calculation time, since it consists of empirical formulae and one-dimensional equations of conservation. One of the empirical models, temperature distribution evaluation model, evaluates the temperature distribution in SG as circular arc isolines determined by experiments and preliminary analyses instead of complicated real distribution. In order to improve this model to get more realistic temperature distribution, we have developed the Lagrangian particle method based on engineering approaches. In this study, we have focused on evaluating gas flow in a tube bundle system, and constructed new models for the gas-particles behavior around a tube to evaluate void fraction distribution near the tube. Through the test analysis simulating one target tube system, we confirmed the capability of the models and next topic to improve the models.
Okita, Shoichiro; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Fukaya, Yuji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(9), p.992 - 998, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kosaka, Wataru; Uchibori, Akihiro; Yanagisawa, Hideki*; Takata, Takashi; Jang, S.*
Dai-25-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2021/07
If a pressurized water/water-vapor leaks from a heat transfer tube in a steam generator (SG) in a sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), sodium-water reaction forms high-velocity, high-temperature, and corrosive jet. It would damage the other tubes and might propagate the tube failure in the SG. Thus, it is important to evaluate the effect of the tube failure propagation for safety assessment of SFR. The computational code LEAP-III can evaluate water leak rate during the tube failure propagation with short calculation time, since it consists of empirical formulae and one-dimensional equations of conservation. One of the empirical models, temperature distribution evaluation model, evaluates the temperature distribution in SG as circular arc isolines determined by experiments and preliminary analyses instead of complicated real distribution. In order to improve this model to get more realistic temperature distribution, we have developed the Lagrangian particle method based on engineering approaches. In this study, we have focused on evaluating gas flow in a tube bundle system, and constructed new models for the gas-particles behavior around a tube to evaluate void fraction distribution near the tube. Through the test analysis simulating one target tube system, we confirmed the capability of the models and next topic to improve the models.
Igarashi, Kai*; Onuki, Ryoji*; Sakai, Takaaki*; Kato, Shinya; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2020/08
Koizumi, Mitsuo; Goto, Jun*; Matsuki, Seishi*
Journal of Semiconductors, 39(8), p.082001_1 - 082001_5, 2018/08
Dynamic nuclear self-polarization (DYNASP) is a phenomenon observed in III-V semiconductors. When electrons of the valence band of a semiconductor are optically excited to the conduction band, a relaxation process of the conduction electrons induces a large nuclear polarization to suddenly occur below a critical temperature. Extending the original theoretical work of Dyakonov et al., we examined the effect of spin distribution of valence electrons excited by the circularly polarized light and the effect of external magnetic field on the phenomenon of the nuclear self-polarization. We found that the nuclear polarization is achieved even above the critical temperatures by the effect of electron polarization and of the external magnetic field. To investigate the phenomenon experimentally, we constructed an apparatus for low-temperature experiments.
Suzuki, Hideya; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Kurosawa, Tatsuya; Shibata, Mitsunobu; Kawasaki, Tomohiro; Urabe, Shunichi*; Matsumura, Tatsuro
Analytical Sciences, 32(4), p.477 - 479, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:67.95(Chemistry, Analytical)An impeccable, high-performance new reagent called alkyl diamide amine (ADAAM) was examined from the viewpoint of mutual separation of Am(III) and Eu(III). ADAAM has three donor atoms, one soft N-donor atom and two hard O-donor atoms, in the central frame. The combination of soft and hard atoms affords a tridentate donor set of atoms that ensures remarkable extractability and selectivity of Am(III) and Eu(III) in highly acidic media.
Guo, L.*; Morita, Koji*; Tobita, Yoshiharu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(2), p.271 - 280, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:54.6(Nuclear Science & Technology)Cheng, S.; Matsuba, Kenichi; Isozaki, Mikio; Kamiyama, Kenji; Suzuki, Toru; Tobita, Yoshiharu
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 85, p.740 - 752, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:90.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)Cheng, S.; Matsuba, Kenichi; Isozaki, Mikio; Kamiyama, Kenji; Suzuki, Toru; Tobita, Yoshiharu
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2015/05
Awual, M. R.; Hasan, M. M.*; Shahat, A.*; Naushad, M.*; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Chemical Engineering Journal, 265, p.210 - 218, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:261 Percentile:99.35(Engineering, Environmental)Suzuki, Toru; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Kawada, Kenichi; Tagami, Hirotaka; Sogabe, Joji; Matsuba, Kenichi; Ito, Kei; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 47(3), p.240 - 252, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:91.1(Nuclear Science & Technology)Cheng, S.; Matsuba, Kenichi; Isozaki, Mikio; Kamiyama, Kenji; Suzuki, Toru; Tobita, Yoshiharu
Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, 2015, p.964327_1 - 964327_14, 2015/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)La Haye, R. J.*; Prater, R.*; Buttery, R. J.*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Isayama, Akihiko; Maraschek, M. E.*; Urso, L.*; Zohm, H.*
Nuclear Fusion, 46(4), p.451 - 461, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:151 Percentile:97.52(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Arisaka, Makoto; Kimura, Takaumi; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Yoshida, Zenko
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 408-412, p.1307 - 1311, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.58(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Yoshio*; Murata, Miho*; Kimura, Takaumi
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 408-412, p.1246 - 1251, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:75.1(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
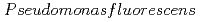
Nankawa, Takuya; Suzuki, Yoshinori*; Ozaki, Takuo; Onuki, Toshihiko; Francis, A. J.*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 408-412, p.1329 - 1333, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.56(Chemistry, Physical)We studied the biodegradation of Eu(III)-malic acid complexes by 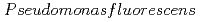 . Ten milimolar Malic acid was degraded in the absence and in the presence of Eu(III) of 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2 mM. The degradation rate of malic acid increased with decreasing the ratios of Eu(III) to malic acid. These results suggest that the toxicity of Eu(III) can be masked through its complexation with malic acid. The degradation of malic acid was followed by the production of unidentified metabolites which were associated with Eu(III). One of the unidentified organic acids was analysed to be pyruvic acid. Our findings suggest that metabolites can influence the environmental behavior of Eu(III) by biologically transformed through subsequent complexation with Eu(III).
. Ten milimolar Malic acid was degraded in the absence and in the presence of Eu(III) of 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2 mM. The degradation rate of malic acid increased with decreasing the ratios of Eu(III) to malic acid. These results suggest that the toxicity of Eu(III) can be masked through its complexation with malic acid. The degradation of malic acid was followed by the production of unidentified metabolites which were associated with Eu(III). One of the unidentified organic acids was analysed to be pyruvic acid. Our findings suggest that metabolites can influence the environmental behavior of Eu(III) by biologically transformed through subsequent complexation with Eu(III).