Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 and GeO
and GeO liquids
liquidsKawaguchi, Munemichi; Uno, Masayoshi*
Journal of Crystal Growth, 585, p.126590_1 - 126590_7, 2022/05
Phase-field mobility,  , and crystal growth rates in crystallization of 11 oxides or mixed oxides in undercooled silicates, SiO
, and crystal growth rates in crystallization of 11 oxides or mixed oxides in undercooled silicates, SiO and GeO
and GeO liquids were calculated with a simple phase-field model (PFM), and material dependence of the
liquids were calculated with a simple phase-field model (PFM), and material dependence of the  was discussed. Ratios between experimental crystal growth rates and the PFM simulation with
was discussed. Ratios between experimental crystal growth rates and the PFM simulation with 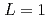 were confirmed to be proportional to a power of
were confirmed to be proportional to a power of 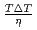 on the solid/liquid interface process during the crystal growth in a log-log plot. We determined that parameters,
on the solid/liquid interface process during the crystal growth in a log-log plot. We determined that parameters,  and
and  , of the
, of the 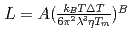 were
were 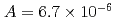 to
to 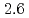 m
m J
J s
s and
and 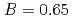 to
to 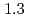 , which were unique for the materials. It was confirmed that our PFM simulation with the determined
, which were unique for the materials. It was confirmed that our PFM simulation with the determined  reproduced quantitively the experimental crystal growth rates. The
reproduced quantitively the experimental crystal growth rates. The  has a proportional relationship with the diffusion coefficient of a cation molar mass average per unit an oxygen molar mass at
has a proportional relationship with the diffusion coefficient of a cation molar mass average per unit an oxygen molar mass at 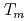 in a log-log graph. The
in a log-log graph. The  depends on the sum of the cation molar mass per the oxygen molar mass,
depends on the sum of the cation molar mass per the oxygen molar mass, 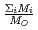 , in a compound. In
, in a compound. In 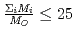 , the
, the  decreases with the cation molar mass increasing. The assumed cause is that the B represents the degree of the temperature dependence of the
decreases with the cation molar mass increasing. The assumed cause is that the B represents the degree of the temperature dependence of the  . Since the cation molar mass is proportional to an inertial resistance of the cation transfer, the
. Since the cation molar mass is proportional to an inertial resistance of the cation transfer, the  decreases with inverse of the cation molar mass. In crystallization of the silicates of heavy cation in
decreases with inverse of the cation molar mass. In crystallization of the silicates of heavy cation in 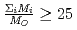 , the
, the  saturates at approximately 0.67, which leads to
saturates at approximately 0.67, which leads to 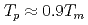 .
.
Yokota, Sho*; Chugo, Daisuke*; Hashimoto, Hiroshi*; Kawabata, Kuniaki
Proceedings of 25th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, p.910 - 911, 2016/08
The purpose of this paper is to experimentally investigate specific ranges of play (software backlash, deadzone) on the saddle type interface for the personal mobility (PM), and to implement them into the control scheme.
 lrradiated p-channel 6H-SiC MOSFETs; High total dose
lrradiated p-channel 6H-SiC MOSFETs; High total doseLee, K. K.; Oshima, Takeshi; Ito, Hisayoshi
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 50(1), p.194 - 200, 2003/02
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:84.34(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)p-channel SiC MOSFETs were fabricated on n-type 6H-SiC epitaxial layer. The effects of  -ray irradiation on the charecteristics of the MOSFETs were studied. Threshold voltage shifts to negative voltage side and the channel mobility reduces due to irradiation. Although the degradation of the channel mobility of the p-channel SiC MOSFETs is 10 times faster than n-channel SiC MOSFETs, p-channel SiC MOSFETs show 100 times stronger radiation resistance than Si MOSFETs. The values of interface traps and oxide-trapped-charge generated sue to irradiation were estimated from the subthreshold characteristics. As the result,it is concluded that the decrease in channel mobility can be explained by the generation of interface traps.
-ray irradiation on the charecteristics of the MOSFETs were studied. Threshold voltage shifts to negative voltage side and the channel mobility reduces due to irradiation. Although the degradation of the channel mobility of the p-channel SiC MOSFETs is 10 times faster than n-channel SiC MOSFETs, p-channel SiC MOSFETs show 100 times stronger radiation resistance than Si MOSFETs. The values of interface traps and oxide-trapped-charge generated sue to irradiation were estimated from the subthreshold characteristics. As the result,it is concluded that the decrease in channel mobility can be explained by the generation of interface traps.