Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 continuous air monitor for the measurement of highly radioactive alpha-emitting particulates (
continuous air monitor for the measurement of highly radioactive alpha-emitting particulates ( -aerosols) under high humidity environment
-aerosols) under high humidity environmentTsubota, Yoichi; Honda, Fumiya; Tokonami, Shinji*; Tamakuma, Yuki*; Nakagawa, Takahiro; Ikeda, Atsushi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1030, p.166475_1 - 166475_7, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:30.99(Instruments & Instrumentation)In the long-lasting decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), the dismantling of nuclear fuel debris (NFD) remaining in the damaged reactors is an unavoidable but significant issue with many technical difficulties. The dismantling is presumed to involve mechanical cutting, generating significant concentrations of particulates containing  -radionuclides (
-radionuclides ( -aerosols) that pose significant health risk upon inhalation. In order to minimize the radiation exposure of workers with
-aerosols) that pose significant health risk upon inhalation. In order to minimize the radiation exposure of workers with  -aerosols during the dismantling/decommissioning process at 1F, it is essential to monitor the concentration of
-aerosols during the dismantling/decommissioning process at 1F, it is essential to monitor the concentration of  -aerosols at the point of initial generation, i.e. inside the primary containment vessels (PCV) of the damaged reactors. Toward this end, an
-aerosols at the point of initial generation, i.e. inside the primary containment vessels (PCV) of the damaged reactors. Toward this end, an  monitoring system for
monitoring system for  -aerosols (
-aerosols ( alpha air monitor: IAAM) was developed and its technical performance was investigated under the conditions expected for the actual environments at 1F. IAAM was confirmed to fulfill four technical requirements: (1) steady operation under high humidity, (2) operation without using filters, (3) capability of measuring a high counting rate of
alpha air monitor: IAAM) was developed and its technical performance was investigated under the conditions expected for the actual environments at 1F. IAAM was confirmed to fulfill four technical requirements: (1) steady operation under high humidity, (2) operation without using filters, (3) capability of measuring a high counting rate of  -radiation, and (4) selective measurement of
-radiation, and (4) selective measurement of  -radiation even under high radiation background with
-radiation even under high radiation background with  /
/ -rays. IAAM is capable of selectively measuring
-rays. IAAM is capable of selectively measuring  -aerosols with a concentration of 3.3
-aerosols with a concentration of 3.3  10
10 Bq/cm
Bq/cm or higher without saturation under a high humid environment (100%-relative humidity) and under high background with
or higher without saturation under a high humid environment (100%-relative humidity) and under high background with  /
/ -radiation (up to 100 mSv/h of
-radiation (up to 100 mSv/h of  -radiation). These results demonstrate promising potential of IAAM to be utilized as a reliable monitoring system for
-radiation). These results demonstrate promising potential of IAAM to be utilized as a reliable monitoring system for  -aerosols during the dismantling of NFD, as well as the whole long-lasting decommissioning of 1F.
-aerosols during the dismantling of NFD, as well as the whole long-lasting decommissioning of 1F.
Takada, Chie; Kurihara, Osamu*; Kanai, Katsuta; Nakagawa, Takahiro; Tsujimura, Norio; Momose, Takumaro
NIRS-M-252, p.3 - 11, 2013/03
A massive earthquake and tsunami on March 11, 2011 resulted in an enormous amount of release of radioactivity to the environment. On the day after the earthquake occurrence, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) started emergency radiological monitoring. The measurements with whole body counter (WBC) for the staff members who had returned from Fukushima started at the end of March. The measured activity of  I due to inhalation for emergency staff varied from LLD to 7 kBq, which corresponded to a range of estimated initial intakes of
I due to inhalation for emergency staff varied from LLD to 7 kBq, which corresponded to a range of estimated initial intakes of  1 to 60 kBq when extrapolated back to the date on which the staff started the operation in Fukushima. The measured activity of
1 to 60 kBq when extrapolated back to the date on which the staff started the operation in Fukushima. The measured activity of  Cs and
Cs and  Cs were both in the ranges of LLD - 3 kBq. The range of initial intake of
Cs were both in the ranges of LLD - 3 kBq. The range of initial intake of  Cs to
Cs to  I was 11 when taking a median from all the measurements. The maximum committed effective dose of 0.8 mSv was recorded for a worker, a member of the 2nd monitoring team dispatched from March 13 to 14.
I was 11 when taking a median from all the measurements. The maximum committed effective dose of 0.8 mSv was recorded for a worker, a member of the 2nd monitoring team dispatched from March 13 to 14.
 I in the thyroids of employees involved in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident
I in the thyroids of employees involved in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accidentKurihara, Osamu*; Kanai, Katsuta; Nakagawa, Takahiro; Takada, Chie; Tsujimura, Norio; Momose, Takumaro; Furuta, Sadaaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 50(2), p.122 - 129, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.8(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Nakagawa, Takahiro; Takada, Chie; Tsujimura, Norio
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.140 - 143, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)Radiation workers engaging in the fabrication of MOX fuels are exposed to neutrons, and hence thermoluminescent albedo dosemeters (TLAD) need to be used at JAEA-NCL. Because estimating the doses using TLADs are susceptible to the neutron energy spectrum, the authors have issued TLADs incorporating Solid-State Nuclear Tracks Detectors (SSNTDs) to selected workers who are routinely exposed to neutrons and been analyzing the relationship between the SSNTD and the TLAD (T/Rf) over the past 6 years. Consequently, the  /
/
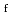 in each year was 10-20 (3.363 mm
in each year was 10-20 (3.363 mm )/(mSv
)/(mSv  Cs eq.), which is smaller than the data during 1991-1993, although the neutron spectra had not changed compared with that of the early 1990s. This decrease of the
Cs eq.), which is smaller than the data during 1991-1993, although the neutron spectra had not changed compared with that of the early 1990s. This decrease of the  /
/
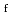 implies that the ratio of work carried out nearby the gloveboxes to total work decreased.
implies that the ratio of work carried out nearby the gloveboxes to total work decreased.
Takada, Chie; Nakagawa, Takahiro; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Tsujimura, Norio; Takayasu, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakagawa, Takahiro; Takada, Chie; Sekine, Nobuyuki*; Takayasu, Tetsuya*; Tsujimura, Norio; Momose, Takumaro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakagawa, Takahiro; Horikoshi, Yoshinori; Ito, Yasuhisa; Ito, Kimio; Momose, Takumaro; Takada, Chie
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakagawa, Takahiro; Takada, Chie; Sekine, Nobuyuki*; Takayasu, Tetsuya*; Tsujimura, Norio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takada, Chie; Nakagawa, Takahiro; Tsujimura, Norio
no journal, ,
Study on source term for emergency action plan on a criticality accident.
Takada, Chie; Nakagawa, Takahiro; Tsujimura, Norio; Terakado, Yoshinori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakagawa, Takahiro; Takada, Chie; Tsujimura, Norio; Yamazaki, Takumi; Kashimura, Shinya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakagawa, Takahiro; Takada, Chie; Takayasu, Tetsuya*; Kashimura, Shinya*; Tago, Itaru
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kanai, Katsuta; Kurihara, Osamu*; Takada, Chie; Nakagawa, Takahiro; Morishita, Yuki; Hokama, Tomonori; Takimoto, Misaki; Maruo, Yoshihiro; Momose, Takumaro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakagawa, Takahiro; Takada, Chie; Kanai, Katsuta; Murayama, Takashi; Miyauchi, Hideaki; Suzuki, Takehiko; Sato, Yoshitaka; Ezaki, Hiroko; Imahashi, Atsushi; Isozaki, Kohei; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamazaki, Takumi; Takada, Chie; Nakagawa, Takahiro; Ishikawa, Hisashi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakagawa, Takahiro; Takada, Chie; Yamazaki, Takumi; Momose, Takumaro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takada, Chie; Nakagawa, Takahiro; Yamazaki, Takumi; Ishikawa, Hisashi; Momose, Takumaro
no journal, ,
A special monitoring was performed for the persons working at Central Building in Tokai Reprocessing Plant in September, 2013. One person of the monitored subjects was estimated that he took a tiny amount of radioactive materials accidentally.
Takimoto, Misaki; Takada, Chie; Nakagawa, Takahiro; Yamazaki, Takumi; Ishikawa, Hisashi; Momose, Takumaro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 rays
raysYamazaki, Takumi; Takada, Chie; Nakamura, Keisuke; Sagawa, Naoki; Hoshi, Katsuya; Nakagawa, Takahiro; Takimoto, Misaki; Tanimura, Yoshihiko*; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Momose, Takumaro; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray field with low dose rate
-ray field with low dose rateKojima, Naomi; Nakagawa, Takahiro; Yamazaki, Takumi; Takimoto, Misaki; Takada, Chie
no journal, ,
In late years, Electronic Personal Dosemeter (EPD) has been widely used because of its useful specifications: indicating measurement values on site, lower detect limits than glass badge. However, an investigation of its response characteristic is difficult to perform using actual low dose rate  -ray. The investigation needs sheildings of a entire irradiation room for reducing natural radiation. In this study, at the compact irradiation system with low dose rate which National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and technology developed,
-ray. The investigation needs sheildings of a entire irradiation room for reducing natural radiation. In this study, at the compact irradiation system with low dose rate which National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and technology developed,  -ray of
-ray of  Cs below 0.1
Cs below 0.1 Sv/h were irradiated to two models of EPD with recording function. Integrated dose and standard deviation for EPD were analyzed to investigate response characteristics for low dose rate radiation.
Sv/h were irradiated to two models of EPD with recording function. Integrated dose and standard deviation for EPD were analyzed to investigate response characteristics for low dose rate radiation.