Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sakasegawa, Hideo; Nomura, Mitsuo; Sawayama, Kengo; Nakayama, Takuya; Yaita, Yumi*; Yonekawa, Hitoshi*; Kobayashi, Noboru*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Hiyama, Toshiaki*; Murata, Eiichi*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 153, p.104396_1 - 104396_9, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)When dismantling centrifuges in uranium-enrichment facilities, decontamination techniques must be developed to remove uranium-contaminated surfaces of dismantled parts selectively. Dismantled uranium-contaminated parts can be disposed of as nonradioactive wastes or recycled after decontamination appropriate for clearance. previously, we developed a liquid decontamination technique using acidic electrolyzed water to remove uranium-contaminated surfaces. However, further developments are still needed for its actual application. Dismantled parts have various uranium-contaminated surface features due to varied operational conditions, inhomogeneous decontamination using iodine heptafluoride gas, and changes in long-term storage conditions after dismantling. Here, we performed liquid decontamination on specimens with varying uranium-contaminated surfaces cut from a centrifuge made of low-carbon steel. From the results, the liquid decontamination can effectively remove the uranium-contaminated surfaces, and radioactive concentrations fell below the target value within twenty minutes. Although the required time should also depend on dismantled parts' sizes and shapes in their actual application, we demonstrated that it could be an effective decontamination technique for uranium-contaminated steels of dismantled centrifuges.
Koma, Yoshikazu; Ashida, Takashi; Meguro, Yoshihiro; Miyamoto, Yasuaki; Sasaki, Toshiki; Yamagishi, Isao; Kameo, Yutaka; Terada, Atsuhiko; Hiyama, Toshiaki; Koyama, Tomozo; et al.
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference; Nuclear Energy at a Crossroads (GLOBAL 2013) (CD-ROM), p.736 - 743, 2013/09
Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (F1NPS), TEPCO, was severely damaged with the hydrogen explosions caused by losing their cooling functions due to the earthquake and the tsunami occurred on March 11, 2011. Radioactive wastes generated from the current FINPS and future their decommission and demolition are greater huge amount than those from general reactors and nuclear fuel facilities. Toward accomplishing safe and reasonable management of the wastes, great effort of R&Ds has been strongly required and performed in bringing together the knowledge and experience of all of Japan. This report outlines the current status of the R&Ds performed in JAEA.
Taguchi, Shigeo; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Surugaya, Naoki; Kurosawa, Akira; Hiyama, Toshiaki; Tanaka, Tatsuhiko*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 288(2), p.435 - 441, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.16(Chemistry, Analytical)Yamamoto, Masahiko; Ishibashi, Atsushi; Nagayama, Tetsuya; Surugaya, Naoki; Kurosawa, Akira; Hiyama, Toshiaki
JAEA-Technology 2010-040, 28 Pages, 2010/12
Precise analysis of plutonium is necessary for material control and safeguards in nuclear facility. Thus, controlled-potential coulometry, which yields absolute results and high precision, was applied for the determination of plutonium. The coulometry system and sample pretreatment procedures were optimized following ISO12183:2005. Plutonium sample prepared from NBL CRM-126 Pu metal was measured and agreed well with certified value. For spike preparation of isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS), plutonium solution was prepared from MOX powder. Plutonium content was 15.5995 mgPu/g. The uncertainty was calculated by ISO/BIPM Guide to the Expression of Uncertainties in Measurements. The relative expanded uncertainty was 0.023% with confidence interval of 95%. The results were in good agreement with those obtained by IDMS. Thus the proposed coulometry method was successfully applied for the determination of plutonium at the highest level of precision and accuracy.
Taguchi, Shigeo; Surugaya, Naoki; Kurosawa, Akira; Hiyama, Toshiaki; Tanaka, Tatsuhiko*
Bunseki Kagaku, 59(11), p.1035 - 1041, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.69(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
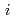 Hex-BTP/SiO
Hex-BTP/SiO -P resin
-P resinSurugaya, Naoki; Sano, Yuichi; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Kurosawa, Akira; Hiyama, Toshiaki
Nuclear Energy and the Environment; ACS Symposium Series 1046, p.131 - 139, 2010/10
Taguchi, Shigeo; Surugaya, Naoki; Kurosawa, Akira; Hiyama, Toshiaki; Tanaka, Tatsuhiko*
Bunseki Kagaku, 58(10), p.901 - 907, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)An on-line analysis system using a solid-phase extraction column coupled to electrochemical detection has been developed for rapid determination of small amounts of uranium in liquid wastes of spent nuclear-fuel reprocessing plants. A sample solution with a concentration of 3 M HNO was loaded onto the column: packed with U/TEVA
was loaded onto the column: packed with U/TEVA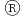 resin. The interference elements were rinsed by passing 3 M HNO
resin. The interference elements were rinsed by passing 3 M HNO through the column. The adsorbed uranium was eluted with 0.1 M HNO
through the column. The adsorbed uranium was eluted with 0.1 M HNO . The eluate was directly introduced into a flow-electrolysis cell. The result of five repeated analyses for a standard solution containing 2.5
. The eluate was directly introduced into a flow-electrolysis cell. The result of five repeated analyses for a standard solution containing 2.5  g (0.1 mL at 25
g (0.1 mL at 25  g mL
g mL ) of uranium was found to be 2.5
) of uranium was found to be 2.5  0.025
0.025  g (mean
g (mean  1
1  ). The detection limit calculated from 3 times the standard deviation of background current was 56 ng. The analysis time required for one sample was within 5 min. The recoveries of uranium in actual nuclear waste reprocessing solutions were 92%
). The detection limit calculated from 3 times the standard deviation of background current was 56 ng. The analysis time required for one sample was within 5 min. The recoveries of uranium in actual nuclear waste reprocessing solutions were 92%  112%.
112%.
 Sr in highly radioactive liquid waste by alkaline precipitation separation/liquid scintillation counting technique
Sr in highly radioactive liquid waste by alkaline precipitation separation/liquid scintillation counting techniqueOnuma, Takashi; Surugaya, Naoki; Hiyama, Toshiaki
Bunseki Kagaku, 58(7), p.633 - 638, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)An analytical method with a liquid scintillation counting technique for the determination of  Sr in the presence of other elements was developed by deriving a calculation formula to remove their influence. Generally the analysis of
Sr in the presence of other elements was developed by deriving a calculation formula to remove their influence. Generally the analysis of  Sr is performed using the radioactive equilibrium of a generation process of
Sr is performed using the radioactive equilibrium of a generation process of  Y with
Y with  Sr separated from a sample. In this study, a new disintegration calculating formula that enable us remove influences by the coexistence nuclides to analyze
Sr separated from a sample. In this study, a new disintegration calculating formula that enable us remove influences by the coexistence nuclides to analyze  Sr in highly radioactive liquid wastes of spent-fuel reprocessing plants was derived and the formula was validated by experimental approaches. It was found that
Sr in highly radioactive liquid wastes of spent-fuel reprocessing plants was derived and the formula was validated by experimental approaches. It was found that  Sr was analyzed without any influences when a sample contains nuclides that have a long half life and radioactive equilibrium is small enough compared with a generation of
Sr was analyzed without any influences when a sample contains nuclides that have a long half life and radioactive equilibrium is small enough compared with a generation of  Y. The relative standard deviation of the analysis by the proposed method was equal to or less than 3%.
Y. The relative standard deviation of the analysis by the proposed method was equal to or less than 3%.
Okano, Masanori; Kuno, Takehiko; Nemoto, Hirokazu*; Yamada, Keiji; Watahiki, Masaru; Hiyama, Toshiaki
Proceedings of INMM 50th Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2009/07
no abstracts in English
Surugaya, Naoki; Hiyama, Toshiaki; Watahiki, Masaru
Analytical Sciences, 24(6), p.739 - 744, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.14(Chemistry, Analytical)A robotized sample preparation method for the determination of Pu, which is recovered by extraction reprocessing of spent nuclear fuel, by isotope dilution mass spectrometry is described. The automated system has a six-axis industrial robot, whose motility is very fast, accurate and flexible, installed in a glove box. The automation of the weighing and diluting steps enables operator-unattended sample pretreatment for highly precise analyses of Pu in aqueous solutions. By the developed system, Pu concentration in HNO medium was successfully determined with a set of subsequent mass spectrometric measurements. The relative uncertainty in determining the concentration of Pu by isotope dilution mass spectrometry using this system for sample pretreatment was estimated to be less than 0.1 rel.% (
medium was successfully determined with a set of subsequent mass spectrometric measurements. The relative uncertainty in determining the concentration of Pu by isotope dilution mass spectrometry using this system for sample pretreatment was estimated to be less than 0.1 rel.% ( =2), which is equal to that expected of a talented analyst. The operation time required was the same as that by a skilled operator.
=2), which is equal to that expected of a talented analyst. The operation time required was the same as that by a skilled operator.
Surugaya, Naoki; Taguchi, Shigeo; Sato, Soichi; Watahiki, Masaru; Hiyama, Toshiaki
Analytical Sciences, 24(3), p.377 - 380, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:17.16(Chemistry, Analytical)A simple and rapid spectrophotometric method has been developed for the determination of Pu in highly radioactive liquid waste. This method uses Nd(III) as an internal standard, which enables us to determine the concentration of Pu and to authenticate the whole analytical scheme as well. A Nd(III) standard was mixed with a sample solution and Pu was quantitatively oxidized to Pu(VI) with Ce(IV) in a nitric acid medium, having maximum absorbance at 830 nm. The spectrophotometric measurement of Pu(VI) was subsequently performed to determine the concentration compared with maximum absorbance of Nd(III) at 795nm. The proposed method was validated through comparison experiments with isotope dilution mass spectrometry and was successfully applied to the analysis for the nuclear waste management at spent nuclear fuel reprocessing plants.
Surugaya, Naoki; Hiyama, Toshiaki; Verbruggen, A.*; Wellum, R.*
Analytical Sciences, 24(2), p.247 - 252, 2008/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:23.22(Chemistry, Analytical)A stable solid spike for the measurement of uranium and plutonium content in nitric acid solutions of spent nuclear fuel by isotope dilution mass spectrometry has been prepared at the European Commission Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements in Belgium. The spike contains about 50 mg of uranium with a 19.838%  U enrichment and 2 mg of plutonium with a 97.766%
U enrichment and 2 mg of plutonium with a 97.766%  Pu abundance in each individual ampoule. The dried materials were covered with a thin film of cellulose acetate butyrate as a protective organic stabilizer to resist shocks encountered during transportation and to eliminate flaking-off during long-term storage. It was found that the cellulose acetate butyrate has good characteristics, maintaining a thin film for a long time, but readily dissolving on heating with nitric acid solution. The solid spike containing cellulose acetate butyrate was certified as reference material IRMM-1027f with certified quantities:
Pu abundance in each individual ampoule. The dried materials were covered with a thin film of cellulose acetate butyrate as a protective organic stabilizer to resist shocks encountered during transportation and to eliminate flaking-off during long-term storage. It was found that the cellulose acetate butyrate has good characteristics, maintaining a thin film for a long time, but readily dissolving on heating with nitric acid solution. The solid spike containing cellulose acetate butyrate was certified as reference material IRMM-1027f with certified quantities:  U and
U and  Pu amounts and uranium and plutonium amount ratios, and was validated by analyzing spent fuel dissolver solutions of the Tokai reprocessing plant in Japan.
Pu amounts and uranium and plutonium amount ratios, and was validated by analyzing spent fuel dissolver solutions of the Tokai reprocessing plant in Japan.
Taguchi, Shigeo; Surugaya, Naoki; Sato, Soichi; Kurosawa, Akira; Watahiki, Masaru; Hiyama, Toshiaki
JAEA-Technology 2006-040, 76 Pages, 2006/07
A spectrophotometric determination using neodymium as an internal standard has been developed for safeguards verification analysis of plutonium in highly radioactive liquid waste which is produced by the reprocessing of spent nuclear fuel. The method offers reduced sample preparation and analysis time compared to isotope dilution mass spectrometry. It uses neodymium as an internal standard, which allows for determining an index for the authentication of the analytical operation and the instrument conditions. The sample was mixed with a known amount of neodymium as an internal standard. Subsequently, plutonium was quantitatively oxidized to Pu(IV) by the addition of Ce(IV). Plutonium concentration was calculated from a relation between Nd(III)/Pu(VI) molar extinction coefficient ratio and their absorbance ratio. The expanded uncertainty of the repeated analysis of plutonium (n=5) was found to be  15mgL
15mgL (confidence interval 95%) for a highly radioactive liquid waste sample (173mgL
(confidence interval 95%) for a highly radioactive liquid waste sample (173mgL ). The determination limit was calculated to be 6mgL
). The determination limit was calculated to be 6mgL (ten fold's the standard deviation). This method was validated through comparison experiments with isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The analytical results of plutonium in highly radioactive liquid waste using this method were agree well with values obtained using isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The proposed method was successfully applied for the independent on-site safeguards analysis at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant.nt on-site safeguards analysis at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant.
(ten fold's the standard deviation). This method was validated through comparison experiments with isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The analytical results of plutonium in highly radioactive liquid waste using this method were agree well with values obtained using isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The proposed method was successfully applied for the independent on-site safeguards analysis at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant.nt on-site safeguards analysis at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant.
Taguchi, Shigeo; Surugaya, Naoki; Sato, Soichi; Kurosawa, Akira; Watahiki, Masaru; Hiyama, Toshiaki
JAEA-Technology 2006-041, 58 Pages, 2006/06
We have developed a method of spectrophotometric determination of plutonium ( 10
10 M) in highly radioactive liquid waste for safeguards verification analysis. The method offers reduced sample preparation and analysis time compared to isotope dilution mass spectrometry. It uses neodymium as an internal standard, which allows for determining an index for the authentication of the analytical scheme and the inspection procedure. The relative expanded uncertainty of the repeated analysis (n = 5) was 8.9 % (coverage factor k = 2) for a highly radioactive liquid waste sample(173 mgL
M) in highly radioactive liquid waste for safeguards verification analysis. The method offers reduced sample preparation and analysis time compared to isotope dilution mass spectrometry. It uses neodymium as an internal standard, which allows for determining an index for the authentication of the analytical scheme and the inspection procedure. The relative expanded uncertainty of the repeated analysis (n = 5) was 8.9 % (coverage factor k = 2) for a highly radioactive liquid waste sample(173 mgL ). The determination limit was calculated to be 6 mgL
). The determination limit was calculated to be 6 mgL (ten fold's the standard deviation). This method was validated through comparison experiments with isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The analytical results of plutonium in highly radioactive liquid waste using this method were in good agreement with those obtained using isotope dilution mass spectrometry. It is to be noted that the neodymium standard is intended to be provided by the inspector so that an inspector can check the instrument conditions as well as the analytical scheme. The proposed method was successfully applied for the independent on-site safeguards analysis at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant.
(ten fold's the standard deviation). This method was validated through comparison experiments with isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The analytical results of plutonium in highly radioactive liquid waste using this method were in good agreement with those obtained using isotope dilution mass spectrometry. It is to be noted that the neodymium standard is intended to be provided by the inspector so that an inspector can check the instrument conditions as well as the analytical scheme. The proposed method was successfully applied for the independent on-site safeguards analysis at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant.
Kitagawa, Osamu; Suzuki, Yoshimasa; Kurosawa, Akira; Watahiki, Masaru; Hiyama, Toshiaki
JAEA-Technology 2006-031, 29 Pages, 2006/03
Using the correlation between electric conductivity and acidity in solution, we have investigated an analytical method that is able to determine acidity in the nitric acid solution by measuring electric conductivity of sample diluted with distilled water, and correcting the electric conductivity for plutonium(Pu) and uranium(U) using multivariate analysis method. We obtained good results as follows, (1) Acidity in the nitric acid solutions containing Pu and U obtained by this method was good agreement, within 10%, compared with the acidity measured by potentiometric titration method. (2) For plutonium nitrate solution and plutonium-uranium mixed nitrate solution, the repeatability and reproducibility for the measurement of electric conductivity at 25.0 C were less than 0.52%, and 1.53% respectively. (3) Impurities such as americium and iron in the solutions did not influence to the measurement of electric conductivity, if total amounts of these impurities were less than 1% compared with those of Pu and U. From the results described above, electric conductivity measuring method has been applying to analysis of acidity in the nitric acid solutions containing Pu and U at high concentration handled in Plutonium Conversion Development Facility. Furthermore, this method can be expected for the application to analysis of acidity in nitric acid solutions containing Pu and U for reprocessing process.
C were less than 0.52%, and 1.53% respectively. (3) Impurities such as americium and iron in the solutions did not influence to the measurement of electric conductivity, if total amounts of these impurities were less than 1% compared with those of Pu and U. From the results described above, electric conductivity measuring method has been applying to analysis of acidity in the nitric acid solutions containing Pu and U at high concentration handled in Plutonium Conversion Development Facility. Furthermore, this method can be expected for the application to analysis of acidity in nitric acid solutions containing Pu and U for reprocessing process.
Taguchi, Shigeo; Surugaya, Naoki; Sato, Soichi; Hiyama, Toshiaki
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2005/10
AA spectrophotometric determination of plutonium in highly radioactive liquid waste has been developed for safeguards verification analysis. The method offers reduced sample preparation and analysis time compared to isotope dilution mass spectrometry. It uses neodymium as an internal standard, which allows for determining an index for the authentication of the analytical scheme and the inspection procedure. The relative expanded uncertainty of the repeated analysis of plutonium (n = 5) was found to be 8.9 % (coverage factor k = 2) for a typical highly radioactive liquid waste sample (172 mg/L). The determination limit was calculated to be 6.1 mg/L (ten fold's the standard deviation). This method was validated through comparison experiments with isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The analytical results of plutonium in highly radioactive liquid waste using this method were in good agreement with those obtained using isotope dilution mass spectrometry. It is to be noted that the neodymium standard is intended to be provided by the International Atomic Energy Agency so that an inspector can check the instrument conditions as well as the analytical scheme. The proposed method was successfully applied to independent on-site safeguards analysis at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant.
Sato, Soichi*; Suzuki, Toru*; Hiyama, Toshiaki*; Watanabe, Kazuo
Bunseki, 2005(8), p.451 - 457, 2005/08
no abstracts in English
Sato, Soichi; Suzuki, Toru; Hiyama, Toshiaki; Watanabe, Kazuo*
Bunseki, 2005(8), p.451 - 457, 2005/08
Focusing on the cover layer materials (as the Radon Barrier Materials), which could have the effect to restrain the radon from scattering into the air and the effect of the radiation shielding, we produced the radon barrier materials with crude bentonite on an experimental basis, using the rotary type comprehensive unit for grinding and mixing, through which we carried out the evaluation of the characteristics thereof.
Taguchi, Shigeo; Surugaya, Naoki; Sato, Soichi; Kitao, Takahiko; Hina, Tetsuro; Toshiaki, Hiyama,
Dai-25-Kai Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nihon Shibu Nenji Taikai Rombunshu, p.120 - 127, 2004/00
For the determination of Pu in the high active liquid waste (HALW), isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS) has been applied to verification analysis at Tokai Reprocessing Plant. IDMS has been considered as the most reliable analytical technique for accountability measurement of Pu in spent fuel reprocessing plant. However, it takes quite long time for inspector to obtain an analytical result because inspection sample has to be transported to safeguards analytical laboratory for off-site analysis. In order to overcome this disadvantage, a rapid verification analysis of Pu in HALW by conventional spectrophotometer using Nd as an internal standard was proposed to achieve on-site verification measurements. In this method, Nd standard is intended to be provided by International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) so that an inspector can independently control it not only as an internal standard but also as an authentication purpose. The validation analysis was carried out by comparing with IDMS. It was found that the values of Pu concentration obtained by proposed method were in good agreement with those obtained by IDMS. Therefore the proposed method can be expected for the application to the verification analysis.
Surugaya, Naoki; Taguchi, Shigeo; Sato, Soichi; Kitao, Takahiko; Hina, Tetsuro; Hiyama, Toshiaki,
Proceedings of 45th INMM Annual Meeting, (112), p.33 - 34, 2004/00
A technique of measuring rapidly and correctly the concentration of Pu contained in the high radioactive liquid waste in a reprocessing plant has been developed. This method is based on spectrophotometry using Nd as an internal standard, and can be expected the application as measurement technology for the safeguards which has been utilizing the conventional method of isotope dilution mass spectrometry. This report describes the measurement principle and the result of the examination which used a real sample.