Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -ray bursts and extremely metal-poor stars; Black hole-forming supernovae with relativistic jets
-ray bursts and extremely metal-poor stars; Black hole-forming supernovae with relativistic jetsTominaga, Nozomu*; Maeda, Keiichi*; Umeda, Hideyuki*; Nomoto, Kenichi*; Tanaka, Masaomi*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Suzuki, Tomoharu*; Mazzali, P. A.*
Astrophysical Journal, 657(2, Part2), p.L77 - L80, 2007/03
Times Cited Count:116 Percentile:91.9(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Long-duration  -ray bursts (GRBs) are thought to be connected with luminous and energetic Type Ic supernovae [SNe, called hypernovae (HNe)] resulting from the black-hole (BH) forming collapse of massive stars. For GRBs 060505 and 060614, however, the expected SNe have not been detected. The upper limits to the SN brightness are about 100 times fainter than GRB-associated HNe (GRB-HNe), corresponding to the upper limits to the ejected
-ray bursts (GRBs) are thought to be connected with luminous and energetic Type Ic supernovae [SNe, called hypernovae (HNe)] resulting from the black-hole (BH) forming collapse of massive stars. For GRBs 060505 and 060614, however, the expected SNe have not been detected. The upper limits to the SN brightness are about 100 times fainter than GRB-associated HNe (GRB-HNe), corresponding to the upper limits to the ejected  Ni masses of
Ni masses of 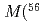 Ni)
Ni)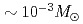 . SNe with a small amount of
. SNe with a small amount of  Ni ejection are observed as faint Type II SNe. HNe and faint SNe are thought to be responsible for the formaion of extremely metal-poor (EMP) stars. A relativistic jet-induced BH forming explosion of the 40
Ni ejection are observed as faint Type II SNe. HNe and faint SNe are thought to be responsible for the formaion of extremely metal-poor (EMP) stars. A relativistic jet-induced BH forming explosion of the 40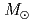 star is investigated and hydrodynamic and nucleosynthetic models are presented. These models can explain both GRB-HNe and GRBs without bright SNe in a unified manner. We suggest that GRBs without bright SNe are likely to synthesize
star is investigated and hydrodynamic and nucleosynthetic models are presented. These models can explain both GRB-HNe and GRBs without bright SNe in a unified manner. We suggest that GRBs without bright SNe are likely to synthesize 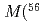 Ni)
Ni)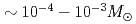 or
or 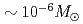 .
.