Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tanai, Kenji; Yamamoto, Mikihiko*; Seki, Yoshitaka*
JAEA-Research 2007-057, 71 Pages, 2007/07
In underground repositories for radioactive waste, significant quantities of gases may be generated as a result of metal corrosion. These gases may migrate through the engineered barrier system and the geological barrier. The potential impact of gas generation, accumulation and migration on the performances of the various barriers such as drainage of contaminated water from the repository and/or damaging of the engineered barriers due to a gas over-pressure should be assessed. The sensitivity analysis was carried out using the modified TOUGH2 model in order to clarify the impact of any input parameters. The following facts became clear as a result of this study. For the cementitious material (waste/cementitious filler), an impact of the absolute permeability and residual pore-water saturation was large. For the buffer material, absolute permeability of gas, capillary exclusion pressure and residual pore-water saturation was large.
Yamamoto, Mikihiko*; *; *
JNC TJ8400 2000-032, 153 Pages, 2000/02
Gas production resulting from mechanisms, which include metal corrosion and microbial degradation in TRU (TransUranic nuclide bearing) waste repository, can lead to overpressurisation and enhanced release of radionuclides. In this study, gas injection experiment and quantitative evaluation of gas flow properties in bentonite/sand mixture (70 weight percent of bentonite and 30 weight percent of quartz sand, 1.6 Mg/m of dry density) were carried out. Under the condition of cylindrical, constant volume geometry and axial flow, gas breakthrough phenomenon at which sharp increase of gas outflow rate after rapid rise in outflow rate of water was observed. Then an injection pressure rises to a peak value range from 2 MPa to 7 MPa higher than backpressure. Afterward, outflow rate of gas increased to a steady state value in the permeability range 10
of dry density) were carried out. Under the condition of cylindrical, constant volume geometry and axial flow, gas breakthrough phenomenon at which sharp increase of gas outflow rate after rapid rise in outflow rate of water was observed. Then an injection pressure rises to a peak value range from 2 MPa to 7 MPa higher than backpressure. Afterward, outflow rate of gas increased to a steady state value in the permeability range 10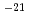 - 10
- 10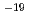 m
m . Outflow of water continued after gas breakthrough. When the gas injection pressure decreased, outflow rate of water declined coincidentally. An enhanced two-phase flow modei in which bentonite/sand gas flow sub-model, based on Kozeny-Carman model, is added to conventional two-phase flow model was used for simulation. Simulation results of gas injection test were compared with the test's data. Results of the simulation were in reasonably agreement with obtained experimental data. Also, two-dimensional calculation of gas migration in a multi-barrier repository of TRU waste was implemented. Parameter values used here without reseal pressure were identified through the simulation of the test's results. Comparing these results with other simulation results obtained by conventional two-phase flow model shows that the maximum pore pressure was almost same value between two different models. But estimated value of expelled water from cavern by enhanced two-phase flow model was less than the value from conventional two-phase flow calculation. Therefor in view of the expelled water, former ...
. Outflow of water continued after gas breakthrough. When the gas injection pressure decreased, outflow rate of water declined coincidentally. An enhanced two-phase flow modei in which bentonite/sand gas flow sub-model, based on Kozeny-Carman model, is added to conventional two-phase flow model was used for simulation. Simulation results of gas injection test were compared with the test's data. Results of the simulation were in reasonably agreement with obtained experimental data. Also, two-dimensional calculation of gas migration in a multi-barrier repository of TRU waste was implemented. Parameter values used here without reseal pressure were identified through the simulation of the test's results. Comparing these results with other simulation results obtained by conventional two-phase flow model shows that the maximum pore pressure was almost same value between two different models. But estimated value of expelled water from cavern by enhanced two-phase flow model was less than the value from conventional two-phase flow calculation. Therefor in view of the expelled water, former ...
Yamamoto, Mikihiko*; *; *
JNC TJ8400 2000-031, 29 Pages, 2000/02
no abstracts in English