Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 SR studies on copper minerals
SR studies on copper mineralsFujihara, Masayoshi; Okabe, Hirotaka*; Koda, Akihiro*
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.13_1 - 13_6, 2024/12
Quantum states are difficult to observe experimentally. In addition, ideal model materials have not been found for some of the lattice systems in which exotic quantum states are predicted to be realized. Numerous candidates for low-dimensional quantum magnets are hidden in copper minerals, and the number of candidates is increasing every year. We succeeded to synthesize seven copper minerals by imitating the environment where they are discovered and reported their quantum states. The properties of pulsed muons are very suitable for investigating the spin state of artificial copper minerals.
He, X.*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Iizuka, Riko*; Okajima, Hajime*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Goto, Hirotada*; et al.
Journal of Molecular Structure, 1310, p.138271_1 - 138271_8, 2024/08
High-pressure responses of the O-D F hydrogen bonds in deuterated magnesium hydroxyfluoride were investigated using neutron powder diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. The Rietveld analysis at ambient conditions revealed a chemical formula of Mg(OD)
F hydrogen bonds in deuterated magnesium hydroxyfluoride were investigated using neutron powder diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. The Rietveld analysis at ambient conditions revealed a chemical formula of Mg(OD)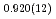 F
F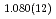 and hydroxyl group/fluorine disorder (OD/F disorder) in the crystal structure, which gave rise to two hydrogen-bonding configurations. The Rietveld analysis showed the hydrogen-bonding geometries remains up to 9.8 GPa, indicating no pressure-induced strengthening of hydrogen bonds. The Raman spectra at ambient conditions showed three hydroxyl stretching bands at 2613, 2694, and 2718 cm
and hydroxyl group/fluorine disorder (OD/F disorder) in the crystal structure, which gave rise to two hydrogen-bonding configurations. The Rietveld analysis showed the hydrogen-bonding geometries remains up to 9.8 GPa, indicating no pressure-induced strengthening of hydrogen bonds. The Raman spectra at ambient conditions showed three hydroxyl stretching bands at 2613, 2694, and 2718 cm . The high frequencies of the O-D stretching modes indicated that the hydroxyls should be involved in weak or none hydrogen-bonding interactions. Up to 20.2 GPa, the mode initially centered at 2694 cm
. The high frequencies of the O-D stretching modes indicated that the hydroxyls should be involved in weak or none hydrogen-bonding interactions. Up to 20.2 GPa, the mode initially centered at 2694 cm displayed a pressure-induced blue shift, revealing no strengthening of hydrogen bonds under compression. We discuss the existence of hydrogen bonds and the causes of the blue-shifting hydroxyls at ambient and at high pressures.
displayed a pressure-induced blue shift, revealing no strengthening of hydrogen bonds under compression. We discuss the existence of hydrogen bonds and the causes of the blue-shifting hydroxyls at ambient and at high pressures.
Li, L.*; Miyamoto, Goro*; Zhang, Y.*; Li, M.*; Morooka, Satoshi; Oikawa, Katsunari*; Tomota, Yo*; Furuhara, Tadashi*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 184, p.221 - 234, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Mori, Yuichiro*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Takano, Masahiro*; Kakizawa, Sho*; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 634, p.118673_1 - 118673_8, 2024/05
To investigate silicon effects on the hydrogen-induced volume expansion of iron, neutron diffraction and X-ray diffraction experiments were conducted to examine hcp-Fe Si
Si under high pressures and high temperatures. Neutron diffraction experiments were performed on the deuterated hcp-Fe
under high pressures and high temperatures. Neutron diffraction experiments were performed on the deuterated hcp-Fe Si
Si at 13.5 GPa and 900 K, and at 12.1 GPa and 300 K. By combining the P-V-T equation of state of hcp-Fe
at 13.5 GPa and 900 K, and at 12.1 GPa and 300 K. By combining the P-V-T equation of state of hcp-Fe Si
Si , present results indicate that the hydrogen-induced volume expansion of hcp-Fe
, present results indicate that the hydrogen-induced volume expansion of hcp-Fe Si
Si is 10% greater than that of pure hcp iron. Using the obtained values, we estimated the hydrogen content that would reproduce the density deficit in the inner core, which was 50% less than that without the effect of silicon. Possible hydrogen content,
is 10% greater than that of pure hcp iron. Using the obtained values, we estimated the hydrogen content that would reproduce the density deficit in the inner core, which was 50% less than that without the effect of silicon. Possible hydrogen content,  , in the inner core and the outer core was calculated to be 0.07 and 0.12-0.15, respectively, when reproducing the density deficit of the inner core with hcp-Fe
, in the inner core and the outer core was calculated to be 0.07 and 0.12-0.15, respectively, when reproducing the density deficit of the inner core with hcp-Fe Si
Si Hx.
Hx.
Micheau, C.; Ueda, Yuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Yamada, Norifumi*; Yamada, Masako*; Moussaoui, S. A.*; Makombe, E.*; Meyer, D.*; Berthon, L.*; et al.
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 401, p.124372_1 - 124372_12, 2024/05
Supramolecular organization of extractant molecules impacts metal ions separation behavior. Probing bulk and interfacial structures of the relevant systems is expected to provide key insights into the metal ion selectivity and kinetic aspects. The supramolecular features of two solvent extraction systems based on malonamide extractants THMA in toluene and DBMA in n-heptane were studied using small-angle X-ray scattering for the organic bulk phases, as well as interfacial tension and neutron reflectivity measurements for the interfaces. In the bulk solution, THMA forms dimeric/trimeric associates but no aggregates in toluene, while DBMA forms large aggregates in n-heptane. On the other hand, THMA accumulates in a diffuse layer at the interface at high THMA concentration, whereas DBMA forms a compact but thinner layer. After Pd(II) extraction, the thickness of interfacial layers decreases in the case of THMA, and totally vanishes in the case of DBMA. Based on these new structural information, two mechanisms are proposed for Pd(II) and Nd(III) extraction with malonamides. In toluene, THMA associates slightly accumulate in the vicinity of the interface, then coordinate Pd(II) and diffuse into the organic bulk phase. In n-heptane, DBMA aggregates adsorb at the interface then pick up Nd(III) cations in their polar cores and finally diffuse into the bulk.
Shamoto, Shinichi; Akatsu, Mitsuhiro*; Chang, L.-J.*; Nemoto, Yuichi*; Ieda, Junichi
Applied Physics Letters, 124(11), p.112402_1 - 112402_5, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0The magnon excitation by ultrasound injection in Y Fe
Fe O
O is studied by inelastic neutron scattering. Both longitudinal and transverse ultrasound injections enhanced the inelastic neutron scattering intensity.
is studied by inelastic neutron scattering. Both longitudinal and transverse ultrasound injections enhanced the inelastic neutron scattering intensity.
 -Ga
-Ga O
O (001)
(001)Tsai, Y. H.*; Kobata, Masaaki; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tanida, Hajime; Kobayashi, Toru; Yamashita, Yoshiyuki*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(11), p.112105_1 - 112105_5, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 -MgAgSb
-MgAgSbLi, J.*; Li, X.*; Zhang, Y.*; Zhu, J.*; Zhao, E.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Avdeev, M.*; Liu, P.-F.*; Sui, J.*; et al.
Applied Physics Reviews (Internet), 11(1), p.011406_1 - 011406_8, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Applied)Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Hiroi, Kosuke; Oba, Yojiro*; Nagakawa, Yoshiyasu*; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Shibayama, Yuki; Ikeda-Fukazawa, Tomoko*
Carbohydrate Polymers, 327, p.121538_1 - 121538_11, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Applied)We describe non-toxic, tough nanocellulose (NC) hydrogels formed from chemically unmodified NC by cellulose crystalline transformation and subsequent freeze cross-linking reaction. Using low-concentration NaOH and freezing together induced the crystalline transformation of NC from cellulose I to II via freeze concentration. After the crystalline transformation, cross-linking between the NC and CA in the freeze concentration layer (FCL) provided a strong NC network structure, forming NC hydrogels with high mechanical strength. The freeze-cross-linked NC hydrogel easily retained powder adsorbents in its inner space by mixing the NC-NaOH sol and the powder, and the hydrogel showed high removal efficiency for heavy metals. The results highlight the versatility of chemically unmodified celluloses in developing functional materials, suggest possible practical applications.
 O
O -75MoO
-75MoO binary glasses composed of isolated MoO
binary glasses composed of isolated MoO

Masuno, Atsunobu*; Munakata, Sae*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yaji, Toyonari*; Kosugi, Yoshihisa*; Shimakawa, Yuichi*
Inorganic Chemistry, 63(12), p.5701 - 5708, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.05(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Transparent and brown La O
O -MoO
-MoO binary glasses were prepared in bulk form using a levitation technique. The glass-forming range was limited, with the primary composition being approximately 25 mol% La
binary glasses were prepared in bulk form using a levitation technique. The glass-forming range was limited, with the primary composition being approximately 25 mol% La O
O . This glass exhibited a clear crystallization at 546
. This glass exhibited a clear crystallization at 546  C, while determining its glass transition temperature was difficult. Notably, despite its amorphous nature, the glass possessed a density and packing density comparable to those of crystalline La
C, while determining its glass transition temperature was difficult. Notably, despite its amorphous nature, the glass possessed a density and packing density comparable to those of crystalline La Mo
Mo O
O . X-ray absorption fine structure and Raman scattering analyses revealed that the glass structure closely resembles La
. X-ray absorption fine structure and Raman scattering analyses revealed that the glass structure closely resembles La Mo
Mo O
O due to the presence of isolated MoO
due to the presence of isolated MoO
 units, whereas disordered atomic arrangement around La atoms was confirmed. The glass demonstrated transparency ranging from 378 to 5500 nm, and the refractive index at 1.0
units, whereas disordered atomic arrangement around La atoms was confirmed. The glass demonstrated transparency ranging from 378 to 5500 nm, and the refractive index at 1.0  m was estimated to be 2.0. The optical bandgap energy was 3.46 eV, which was slightly smaller than that of La
m was estimated to be 2.0. The optical bandgap energy was 3.46 eV, which was slightly smaller than that of La Mo
Mo O
O . Additionally, the glass displayed a transparent region ranging from 6.5 to 8.0
. Additionally, the glass displayed a transparent region ranging from 6.5 to 8.0  m. This occurrence results from the decreased diversity of MoO
m. This occurrence results from the decreased diversity of MoO units and connectivity of Mo-O-Mo, which resulted in the reduced overlap of multiphonon absorption. This glass formation, with its departure from conventional glass-forming rules, resulted in distinctive glasses with crystal-like atomic arrangements.
units and connectivity of Mo-O-Mo, which resulted in the reduced overlap of multiphonon absorption. This glass formation, with its departure from conventional glass-forming rules, resulted in distinctive glasses with crystal-like atomic arrangements.
Hasemi, Hiroyuki; Takahashi, Ryuta*; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kawamura, Seiko; Komine, Ryota
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 41, p.011003_1 - 011003_5, 2024/03
 He spin filter and small-angle X-ray scattering
He spin filter and small-angle X-ray scatteringRyoki, Akiyuki*; Watanabe, Fumi*; Okudaira, Takuya*; Takahashi, Shingo*; Oku, Takayuki; Hiroi, Kosuke; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Nakamura, Yo*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 160(11), p.114907_1 - 114907_9, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 neutron diffraction revealing the achievement of excellent combination of strength and ductility in metastable austenitic steel by grain refinement
neutron diffraction revealing the achievement of excellent combination of strength and ductility in metastable austenitic steel by grain refinementMao, W.; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Morooka, Satoshi; Gao, S.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 176, p.69 - 82, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The yield stress of Fe-24Ni-0.3C (wt.%) metastable austenitic steel increased 3.5 times (158  551 MPa) when the average grain size decreased from 35
551 MPa) when the average grain size decreased from 35  m (coarse-grained [CG]) to 0.5
m (coarse-grained [CG]) to 0.5  m (ultrafine-grained [UFG]), whereas the tensile elongation was kept large (0.87
m (ultrafine-grained [UFG]), whereas the tensile elongation was kept large (0.87  0.82).
0.82).  neutron diffraction measurements of the CG and UFG Fe-24Ni-0.3C steels were performed during tensile deformation at room temperature to quantitatively elucidate the influence of grain size on the mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms. The initial stages of plastic deformation in the CG and UFG samples were dominated by dislocation slip, with deformation-induced martensitic transformation (DIMT) also occurring in the later stage of deformation. Results show that grain refinement increases the initiation stress of DIMT largely and suppresses the rate of DIMT concerning the strain, which is attributed to the following effects. (i) Grain refinement increased the stabilization of austenite and considerably delayed the initiation of DIMT in the
neutron diffraction measurements of the CG and UFG Fe-24Ni-0.3C steels were performed during tensile deformation at room temperature to quantitatively elucidate the influence of grain size on the mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms. The initial stages of plastic deformation in the CG and UFG samples were dominated by dislocation slip, with deformation-induced martensitic transformation (DIMT) also occurring in the later stage of deformation. Results show that grain refinement increases the initiation stress of DIMT largely and suppresses the rate of DIMT concerning the strain, which is attributed to the following effects. (i) Grain refinement increased the stabilization of austenite and considerably delayed the initiation of DIMT in the  111
111 //LD (LD: loading direction) austenite grains, which were the most stable grains for DIMT. As a result, most of the
//LD (LD: loading direction) austenite grains, which were the most stable grains for DIMT. As a result, most of the  111
111 //LD austenite grains in the UFG specimens failed to transform into martensite. (ii) Grain refinement also suppressed the autocatalytic effect of the martensitic transformation. Nevertheless, the DIMT with the low transformation rate in the UFG specimen was more efficient in increasing the flow stress and more appropriate to maintain uniform deformation than that in the CG specimen during deformation. The above phenomena mutually contributed to the excellent combination of strength and ductility of the UFG metastable austenitic steel.
//LD austenite grains in the UFG specimens failed to transform into martensite. (ii) Grain refinement also suppressed the autocatalytic effect of the martensitic transformation. Nevertheless, the DIMT with the low transformation rate in the UFG specimen was more efficient in increasing the flow stress and more appropriate to maintain uniform deformation than that in the CG specimen during deformation. The above phenomena mutually contributed to the excellent combination of strength and ductility of the UFG metastable austenitic steel.
Nankawa, Takuya; Sekine, Yurina; Matsumura, Daiju; Hiroi, Kosuke; Takata, Shinichi; Kamiya, Yoshimi*; Honda, Takayuki*
Langmuir, 40(11), p.5725 - 5730, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The chemical reaction between Fe and lacquer has been used to create the black color lacquer since ancient times. Here, the chemical state of Fe ions in black lacquer was investigated by using X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES), extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS), and Fourier transform-infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. Fe(II) or Fe(III) was added to the lacquer paste to prepare black lacquer films by air drying, heating, or UV irradiation. The XANES spectral features of all the film samples were similar, meaning that the Fe ions in the samples existed in the trivalent state regardless of the oxidation state of the initially added Fe. The corresponding Fourier transforms of the EXAFS spectra around the Fe K-edge were used to investigate Fe sites in the lacquer films. The spectra of all the film samples were similar shapes, but the peak intensities decreased in the order air dried  heated
heated  UV irradiated films. This result indicates that heating and UV irradiation made the coordination structure of Fe in the lacquer non-uniform, and that heating caused the greatest non-uniformity. The complementary use of XANES, XAFS, and FT-IR spectroscopy is highly effective for non-destructive analysis of black lacquer in precious cultural artifacts.
UV irradiated films. This result indicates that heating and UV irradiation made the coordination structure of Fe in the lacquer non-uniform, and that heating caused the greatest non-uniformity. The complementary use of XANES, XAFS, and FT-IR spectroscopy is highly effective for non-destructive analysis of black lacquer in precious cultural artifacts.
Gong, W.; Gholizadeh, R.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Aizawa, Kazuya; Harjo, S.
Magnesium Technology 2024, p.89 - 90, 2024/03
Miura, Yasufumi*; Suzuki, Kenji*; Morooka, Satoshi; Shobu, Takahisa
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 8(1), p.1_1 - 1_14, 2024/03
Yoshimoto, Masataka*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Watanabe, Kenta*; Shimizu, Keisuke*; Horisawa, Yuhei*; Kobayashi, Takeshi*; Tsurita, Hanae*; Suzuki, Kota*; Kanno, Ryoji*; Hirayama, Masaaki*
Sustainable Energy & Fuels (Internet), 8(6), p.1236 - 1244, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)Photo-rechargeable systems, which can efficiently convert and store solar energy into chemical energy within single devices, are essential to harness sunlight effectively. Photo-(de)intercalation plays a pivotal role in the functionality of photorechargeable systems. Nevertheless, the photo-(de)intercalation process has not been conclusively confirmed owing to potential interference from side reactions, such as the decomposition of liquid electrolytes and the elution of electrode materials. In this study, we successfully demonstrated photo-responsive Li -deintercalation using an all-solid-state thin-film battery comprised of epitaxially-grown anatase TiO
-deintercalation using an all-solid-state thin-film battery comprised of epitaxially-grown anatase TiO doped with Nb (a-TiO
doped with Nb (a-TiO :Nb) as the cathode. Under light irradiation, Li
:Nb) as the cathode. Under light irradiation, Li -deintercalation occurred and was subsequently reversibly intercalated into a-TiO
-deintercalation occurred and was subsequently reversibly intercalated into a-TiO :Nb during discharge.
:Nb during discharge.
Higuchi, Yuki*; Yoshimune, Wataru*; Kato, Satoru*; Hibi, Shogo*; Setoyama, Daigo*; Isegawa, Kazuhisa*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Nozaki, Hiroshi*; Harada, Masashi*; et al.
Communications Engineering (Internet), 3, p.33_1 - 33_7, 2024/02
Ishida, Takekazu*; Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 214(3-4), p.152 - 157, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Applied)Shinohara, Yuya*; Iwashita, Takuya*; Nakanishi, Masahiro*; Osti, N. C.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nirei, Masami; Dmowski, W.*; Egami, Takeshi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 128(6), p.1544 - 1549, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)