Mutation rate and novel  mutants of
mutants of  induced by carbon ions
induced by carbon ions
Shikazono, Naoya; Yokota, Yukihiko*; Kitamura, Satoshi; Suzuki, Chihiro*; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Tano, Shigemitsu; Tanaka, Atsushi
Irradiation of  by carbon ions was carried out to investigate the mutational effect of ion particles in higher plants. Frequencies of embryonic lethals and chlorophyll deficient mutants were found to be significantly higher after carbon ion-irradiation than after electron-irradiation (11-fold and 7.8-fold per unit dose, respectively). During the isolation of mutants, two new classes of flavonoid mutants (
by carbon ions was carried out to investigate the mutational effect of ion particles in higher plants. Frequencies of embryonic lethals and chlorophyll deficient mutants were found to be significantly higher after carbon ion-irradiation than after electron-irradiation (11-fold and 7.8-fold per unit dose, respectively). During the isolation of mutants, two new classes of flavonoid mutants (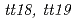 ) were isolated from carbon ion-mutagenized M2 plants. From PCR and sequence analysis, two of the three
) were isolated from carbon ion-mutagenized M2 plants. From PCR and sequence analysis, two of the three 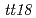 mutant alleles were found to have a small deletion within the
mutant alleles were found to have a small deletion within the 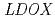 gene and the other was revealed to contain a rearrangement. Using the segregation rates, the mutation rate of carbon ions was estimated to be 17-fold higher than that of electrons. The isolation of novel mutants and the high mutation rate suggest that ion particles can be used as a valuable mutagen for plant genetics.
gene and the other was revealed to contain a rearrangement. Using the segregation rates, the mutation rate of carbon ions was estimated to be 17-fold higher than that of electrons. The isolation of novel mutants and the high mutation rate suggest that ion particles can be used as a valuable mutagen for plant genetics.