Fundamental Study on HLW Glass Corrosion and Mineralization(III)
Inagaki, Yaohiro*
A large number of studies on aqueous corrosion of HLW glass have shown that the glass reacts with water to form more stable solid phases (alteration-phases or secondary phases). The process of alteration-phase formation is expected to play an important role in the radionuclide release from the glass, because it can affect both the glass dissolution rate and the retention of radionuclides in the phases. However, these processes of alteration and diffusion have not been evaluated in details. Therefore, a sound understanding of the glass corrosion mechanism under disposal conditions for long-term is expected to be essential for validation of the long-term performance. The purpose of this study (fiscal year 2001-2003) is to understand, qualitatively and quantitatively, the glass corrosion and associated elemetal release under assumed disposal conditions for long-term referring to geochemical mechanism in order to establish the validation for long-term corrosion/leaching model. This report (fiscal year 2003) discusses temperature dependence of the glass corrosion rate, effects of bentonite on the glass corrosion, and application of the results to the long-term corrosion model, on the basis of the results of corrosion tests performed with a simulated HLW galss, P0798, under various inditions. The conclusions are; 1) the glass corrosion rate can be analyzed by use of hydration(water diffusion) model, and values of the diffusion coefficient are evaluated to be 2 10
10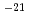 m
m /s (60
/s (60 C) to 5
C) to 5 10
10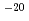 m
m /s (120
/s (120 C) with the activation energy of 52kJ/mol, 2) the presence of bentonite cannot affect the glass corrosion rate, but most of Cs released from the glass are sorbed on bentonite by ion-exchange, 3) application of the hydration (water diffusion) model to the long-term glass corrosion analysis indicates that the glass has higher potential than that evaluated in H12 report and the glass size is one of key parameters.
C) with the activation energy of 52kJ/mol, 2) the presence of bentonite cannot affect the glass corrosion rate, but most of Cs released from the glass are sorbed on bentonite by ion-exchange, 3) application of the hydration (water diffusion) model to the long-term glass corrosion analysis indicates that the glass has higher potential than that evaluated in H12 report and the glass size is one of key parameters.