表面硬化材のナトリウム中試験(II); 常温アルゴン中試験
In sodium tests of hard facing materials, 2; Test Result in room temperature argon
加納 茂機; 中山 紘一; 長谷川 成生; 小圷 亨; 中筋 孝; 滑川 優; 厚母 栄夫
Kano, Shigeki; Nakayama, Koichi; Hasegawa, Naruo; Koakutsu, Toru; Nakasuji, Takashi; Namekawa, Masaru; Atsumo, Hideo
ナトリウム冷却高速炉機器の摺動部材の開発研究として一連のナトリウム中試験が行なわれ,各種材料の短時間の摩擦,摩耗特性が明かにされている。本研究ではナトリウム中試験に供されてきた材料組合せを,一部の摺動部が位置するアルゴン雰囲気中で試験し,室温アルゴン中の摩擦,摩耗挙動を明かにするとともに450 ナトリウム中データと比較した。その結果次のことが明かとなった。静摩擦係数(
ナトリウム中データと比較した。その結果次のことが明かとなった。静摩擦係数( s)はアルゴン中においてほとんどの材料組合せが0.2以下であり,ナトリウム中より小さい。動摩擦係数(
s)はアルゴン中においてほとんどの材料組合せが0.2以下であり,ナトリウム中より小さい。動摩擦係数( k)はアルゴン中において荷重とともに変動する。又,アルゴン中とナトリウム中の
k)はアルゴン中において荷重とともに変動する。又,アルゴン中とナトリウム中の kの大小は材料組合せに依存する。摩耗量はアルゴン中において著しく,ナトリウム中で摩耗しないステライトおよびコルモノイもアルゴン中では摩耗する。摺動面はアルゴン中において塑性変形しやすく表面が粗くなり,摺動面のかたさはアルゴン中の方が小さくなる傾向がある。アルゴン中とナトリウム中の摩擦,摩耗特性には著しい差があり,アルゴン中データでナトリウム中挙動を推定することは困難である。高温アルゴン中の摩耗特性は常温アルゴン中のものより劣り,ナトリウム中との差がさらに大きくなると考えられる。
kの大小は材料組合せに依存する。摩耗量はアルゴン中において著しく,ナトリウム中で摩耗しないステライトおよびコルモノイもアルゴン中では摩耗する。摺動面はアルゴン中において塑性変形しやすく表面が粗くなり,摺動面のかたさはアルゴン中の方が小さくなる傾向がある。アルゴン中とナトリウム中の摩擦,摩耗特性には著しい差があり,アルゴン中データでナトリウム中挙動を推定することは困難である。高温アルゴン中の摩耗特性は常温アルゴン中のものより劣り,ナトリウム中との差がさらに大きくなると考えられる。
A series of experiments have been carried out to develop and screen friction and wear resistant materials used for sliding components of a sodium cooled reactor. Preceding studies 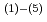 clarified the short-term friction and wear characteristics of various materials in 450
clarified the short-term friction and wear characteristics of various materials in 450 C sodium. A present study relates to clarify friction and wear behavior in argon environment, where a part of sliding components are located, and compare test data in room temperature argon with those in 450do sodium. The results obtained are as follows: (1)Static friction coefficients (
C sodium. A present study relates to clarify friction and wear behavior in argon environment, where a part of sliding components are located, and compare test data in room temperature argon with those in 450do sodium. The results obtained are as follows: (1)Static friction coefficients ( s) in argon were almost lower than 0.2. They were apt to be lower than those in sodium. (2)Kinetic friction coefficients (
s) in argon were almost lower than 0.2. They were apt to be lower than those in sodium. (2)Kinetic friction coefficients ( k) in argon varied with load. The difference of
k) in argon varied with load. The difference of  k in argon and sodium depended on material combination. (3)Wear rates were remarkably high in argon. Wear rates of Colmonoy and Stellite were not detected in sodium, but were detected in argon. (4)Sliding surface was more roughened in argon, and hardness of sliding surface was almost lower in argon than in sodium. (5)There is the significant difference between friction and wear characteristics argon and those in sodium. Then, it is difficult that in-sodium behavior is estimated with in-argon data. (6)The above-mentioned difference in room temperature argon and 450
k in argon and sodium depended on material combination. (3)Wear rates were remarkably high in argon. Wear rates of Colmonoy and Stellite were not detected in sodium, but were detected in argon. (4)Sliding surface was more roughened in argon, and hardness of sliding surface was almost lower in argon than in sodium. (5)There is the significant difference between friction and wear characteristics argon and those in sodium. Then, it is difficult that in-sodium behavior is estimated with in-argon data. (6)The above-mentioned difference in room temperature argon and 450 C sodium will be greater when the test is carried out in higher temperature argon.
C sodium will be greater when the test is carried out in higher temperature argon.