Core study on Pu-burning fast reactors loaded with minor actinides/FPs and research on material characteristics of fuels and targets for Pu/FP burning
Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; Fujita, Reiko*
As a study on technology utilization of advanced fast reactors, a core study on burning technology of actinides and FPs by fast reactors is carried out together with a research on material characteristics of fuels and targets for Pu/FP Burning. In the core study, a Pu-burning fast reactor corc was studied which can also burn minor actinides and FPs based upon the 600MWe Pu-burning fast reactor core with high Pu enrichment ( 40%). The criteria of core design were no significant change of core specification and small sodium void reactivity, and so on. In the core, minor actinides and FPs are loaded in the following way. (a)Core region ; loading of Pu/Np (Oxide fuel, Pu enrichment of
40%). The criteria of core design were no significant change of core specification and small sodium void reactivity, and so on. In the core, minor actinides and FPs are loaded in the following way. (a)Core region ; loading of Pu/Np (Oxide fuel, Pu enrichment of  40%) (b)Outside of core region ; the first layer
40%) (b)Outside of core region ; the first layer  loading of Am/Cm/rate earths mixed with ZrH
loading of Am/Cm/rate earths mixed with ZrH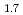 the second laycr
the second laycr  loading of Tc-99 mixed with ZrH
loading of Tc-99 mixed with ZrH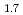 . The operation cycle length is 5 months and the averagc discharge burnup is about 80GWd/t. The burning capability of Pu, minor actinides and FPs is as follows ; (1)Pu burning rate ;
. The operation cycle length is 5 months and the averagc discharge burnup is about 80GWd/t. The burning capability of Pu, minor actinides and FPs is as follows ; (1)Pu burning rate ;  390kg/Year(
390kg/Year( 74kg/TWhe) (2)Burning rate of minor actinides;
74kg/TWhe) (2)Burning rate of minor actinides;  4.2%/Year(
4.2%/Year( 43kg/Year) (3)Burning rate of Tc-99;
43kg/Year) (3)Burning rate of Tc-99;  3.7%/Year(
3.7%/Year( 6.5kg/Year) The sodium void reactivity is very small. (0.1%
6.5kg/Year) The sodium void reactivity is very small. (0.1%  k/kk'=40cent) It is much smaller than that of the conventional fast reactors. This is the advantage of the core concept. The recent progress of material investigation of Pu, minor actinides and FP burning fuels was summaried. Also, basic characteristics of targets for FP burning was summalized, and the compatibility of the targets with ZrH
k/kk'=40cent) It is much smaller than that of the conventional fast reactors. This is the advantage of the core concept. The recent progress of material investigation of Pu, minor actinides and FP burning fuels was summaried. Also, basic characteristics of targets for FP burning was summalized, and the compatibility of the targets with ZrH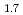 is evaluated.
is evaluated.