ウラン-プルトニウム混合酸化物燃料の融点評価
Melting temperature of uranium - plutonium mixed oxide fuel
石井 徹哉; 廣沢 孝志 

Ishii, Tetsuya; Hirosawa, Takashi
高速炉用ウランープルトニウム混合酸化物燃料の融点に関しては、従来、1960年代の知見に基づく評価が行なわれてきた。一方、80年代から最近にかけての融点実測値の拡充や測定精度の改善により、60年代の融点報告値の一部について下方修正を行なう必要があることや、燃焼に伴う融点変化に関して60年代の知見とは異なる傾向が認められるようになった。そこで、本研究では、現時点における最新の知見を考慮したMOX燃料の融点評価を行ない、得られた成果を高速炉の熱設計に反映することを目的とした。評価においては、予めUO -PuO
-PuO -PuO
-PuO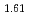 の擬3元系理想溶体モデルを仮定した上で、融点がPu濃度、O/M比、燃焼度に対する依存性を有するものとしてそれら依存性を独立に評価するとの方法を用いた。本研究で得られた融点評価式を、以下に示す。割愛上式中の
の擬3元系理想溶体モデルを仮定した上で、融点がPu濃度、O/M比、燃焼度に対する依存性を有するものとしてそれら依存性を独立に評価するとの方法を用いた。本研究で得られた融点評価式を、以下に示す。割愛上式中の TPuは融点のPu濃度依存性、
TPuは融点のPu濃度依存性、 TO/MはO/M依存性、
TO/MはO/M依存性、 TBuは燃焼度依存性をそれぞれ意味し、UO
TBuは燃焼度依存性をそれぞれ意味し、UO 融点(T0)からの変化量として整理している。なお熱設計上は、融点実測値に対して保守的な評価となることが必要とされるため、熱設計時には、上式に、上式より得られる評価値と実測値との最大差を定数項
融点(T0)からの変化量として整理している。なお熱設計上は、融点実測値に対して保守的な評価となることが必要とされるため、熱設計時には、上式に、上式より得られる評価値と実測値との最大差を定数項 Tとして加えた以下の式の使用を推奨する。割愛上式の適用範囲は、以下の通りである。Pu濃度:0
Tとして加えた以下の式の使用を推奨する。割愛上式の適用範囲は、以下の通りである。Pu濃度:0 PU
PU 60% O/M比:
60% O/M比: OM
OM 2.00 (O/Pu比換算で1.61以上2.0以下)
2.00 (O/Pu比換算で1.61以上2.0以下)
Fuel melting temperature is one of the major thermodynamical properties that is used for determining the design criteria on fuel temperature during irradiation in FBR. In general, it is necessary to evaluate the correlation of fuel melting temperature to confirm that the fuel temperature must be kept below the fuel melting temperature during irradiation at any conditions. The correlations of the melting temperature of uranium-plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel, typical FBR fuel, used to be estimated and formulized based on the measured values reported in 1960's and has been applied to the design. At present, some experiments have been accumulated with improved experimental techniques. And it reveals that the recent measured melting temperatures does not agree well to the data reported in 1960's and that some of the 1960's data should be modified by taking into account of the recent measurements. In this study, the experience of melting temperature up to now are summarized and evaluated in order to make the fuel pin design more reliable. The effect of plutonium content, oxygen to metal ratio and burnup on MOX fuel melting was examined based on the recent data under the UO - PuO
- PuO - PuO
- PuO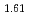 ideal solution model, and then formulized. The correlation obtained in this work is as-follows; T = T
ideal solution model, and then formulized. The correlation obtained in this work is as-follows; T = T +
+  T
T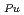 +
+  T
T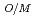 +
+  T
T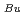 ----(A) T
----(A) T = 3120
= 3120  T
T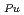 = -5.7537
= -5.7537 PU + 1.3631
PU + 1.3631 10
10
 PU
PU + 1.7952
+ 1.7952 10
10
 PU
PU
 T
T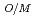 = -1.41
= -1.41  PU
PU  (2.00 - OP)/0.39 OP : OP =
(2.00 - OP)/0.39 OP : OP = 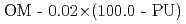 /(0.01
/(0.01 PU)
PU)  T
T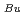 = -5.0
= -5.0 BU/10000 where T is the melting temperature (degree of K), PU is the weight fraction of PuO
BU/10000 where T is the melting temperature (degree of K), PU is the weight fraction of PuO in the mixed oxide fuel, OM is the oxygen to metal ratio, and BU is the burnup in the unit of MWd/MTM. respectively.
in the mixed oxide fuel, OM is the oxygen to metal ratio, and BU is the burnup in the unit of MWd/MTM. respectively.  T
T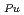 (plutonium content),
(plutonium content),  T
T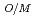 (O/M Ratio),
(O/M Ratio),  ...
...