高速炉配管合流部におけるサーマルストライピング条件の解析的検討(I); 配管合流部における流速比に関する検討
Numerical investigation on thermal striping conditions for a tee junction of LMFBR coolant pipes (I); Investigation on velocity ratio between the coolant pipes
村松 壽晴
not registered
高速炉の炉心出口近傍では、炉心構成要素毎の熱流力特性(集合体発熱量、集合体流量)の違いから、炉心燃料集合体間あるいは炉心燃料集合体-制御棒集合体間などで冷却材に温度差が生じ、それらが混合する過程で不規則な温度ゆらぎ挙動が発生する。この温度ゆらぎを伴った冷却材が炉心上部機構各部(整流筒、制御棒上部案内管、炉心出口温度計装ウェルなど)の表面近傍を通過すると、冷却材中の不規則な温度ゆらぎが構造材中に伝播し、その材料は高サイクル熱疲労を受ける(サーマルストライピング)。特に、冷却材として液体金属ナトリウムを使用する高速炉では、大きな熱伝導率を持つナトリウムの性質から、この熱疲労に対する配慮が必要となる。本研究では、高速炉配管合流部におけるサーマルストライピング条件を解析的に検討するため、内径の等しい90゜エルボ付き主配管と枝管から成る配管系合流部に対し、流速比をパラメータ(主配管流速/枝管流速:0.25,0.50,1.00,2.00および4.00)としたサーマルストライピング解析を、直接シミュレーションコードDINUS-3で行った。得られた結果は、次の通りである。(1)配管合流部下流側に形成される温度ゆらぎ挙動は、主配管流れと枝管からの噴流との相互干渉により生じる比較的周波数の低い変動( 7.0Hz)に、枝管外縁から放出される比較的周波数の高い変動(
7.0Hz)に、枝管外縁から放出される比較的周波数の高い変動( 10.0Hz)が重量したものである。(2)主配管内天井面における温度ゆらぎ振幅のピーク値は、主配管内流速を増加させることによって減少した後増加する傾向を示し、その発生箇所位置は主配管内下流側に移動する。(3)主配管内床面における温度ゆらぎ振幅のピーク値は、主配管内流速を増加させることによって増加する傾向となり、その発生箇所位置は主配管内下流側に移動する。今後の研究では、配管径比、流量比、合流部上流のエルボ個数、レイノルズ数、温度差などの効果を含め、実験的研究による現象論的な考察結果を加味しながら、挙動の定量化を図ってゆく必要がある。
10.0Hz)が重量したものである。(2)主配管内天井面における温度ゆらぎ振幅のピーク値は、主配管内流速を増加させることによって減少した後増加する傾向を示し、その発生箇所位置は主配管内下流側に移動する。(3)主配管内床面における温度ゆらぎ振幅のピーク値は、主配管内流速を増加させることによって増加する傾向となり、その発生箇所位置は主配管内下流側に移動する。今後の研究では、配管径比、流量比、合流部上流のエルボ個数、レイノルズ数、温度差などの効果を含め、実験的研究による現象論的な考察結果を加味しながら、挙動の定量化を図ってゆく必要がある。
This report presents numeical results on thermal striping charactelistics at a tee junction of LMFBR coolant pipe, carried out using a direct numerical simulation code DINUS-3. In the numerical investigations, it was considered a tee junction system consisted of a main pipe (1.33 cm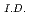 ) with a 90
) with a 90 elbow and a branch pipe having same inner diameter to the main pipe, and five velocity ratio conditions between both the pipes, i,e., (V
elbow and a branch pipe having same inner diameter to the main pipe, and five velocity ratio conditions between both the pipes, i,e., (V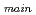 / V
/ V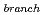 ) = 0.25; 0.5; 1.0; 2.0 and 4.0. From the numerical investigations, the following characteristics were obtained: (1)Temperature fluctuations in the downstream region of the tee junction were formulated by lower frequency components (< 7.0Hz) due to the iteractions between main pipe flows and jet flows from the branch pipe, and higher frequency components (> 10.0 Hz) generated by the vortex released frequency from the outer edge of the branch pipe jet flows. (2)On the top plane of the main pipe, peak values of the temperature fluctuation amplitude was decreased with increasing flow velocity in the main pipe, and its position was shifted to downstream direction of the main pipe by the increase of the main pipe flow velocity. (3)On the bottom plane of the main pipe, contrary to (2), peak values of the temperature fluctuation amplitude was increased with increasing flow velocity in the main pipe.
) = 0.25; 0.5; 1.0; 2.0 and 4.0. From the numerical investigations, the following characteristics were obtained: (1)Temperature fluctuations in the downstream region of the tee junction were formulated by lower frequency components (< 7.0Hz) due to the iteractions between main pipe flows and jet flows from the branch pipe, and higher frequency components (> 10.0 Hz) generated by the vortex released frequency from the outer edge of the branch pipe jet flows. (2)On the top plane of the main pipe, peak values of the temperature fluctuation amplitude was decreased with increasing flow velocity in the main pipe, and its position was shifted to downstream direction of the main pipe by the increase of the main pipe flow velocity. (3)On the bottom plane of the main pipe, contrary to (2), peak values of the temperature fluctuation amplitude was increased with increasing flow velocity in the main pipe.