Numerical investigation on thermal striping conditions for a tee junction of LMFBR coolant pipes (I); Investigation on velocity ratio between the coolant pipes
not registered
This report presents numeical results on thermal striping charactelistics at a tee junction of LMFBR coolant pipe, carried out using a direct numerical simulation code DINUS-3. In the numerical investigations, it was considered a tee junction system consisted of a main pipe (1.33 cm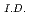 ) with a 90
) with a 90 elbow and a branch pipe having same inner diameter to the main pipe, and five velocity ratio conditions between both the pipes, i,e., (V
elbow and a branch pipe having same inner diameter to the main pipe, and five velocity ratio conditions between both the pipes, i,e., (V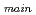 / V
/ V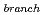 ) = 0.25; 0.5; 1.0; 2.0 and 4.0. From the numerical investigations, the following characteristics were obtained: (1)Temperature fluctuations in the downstream region of the tee junction were formulated by lower frequency components (< 7.0Hz) due to the iteractions between main pipe flows and jet flows from the branch pipe, and higher frequency components (> 10.0 Hz) generated by the vortex released frequency from the outer edge of the branch pipe jet flows. (2)On the top plane of the main pipe, peak values of the temperature fluctuation amplitude was decreased with increasing flow velocity in the main pipe, and its position was shifted to downstream direction of the main pipe by the increase of the main pipe flow velocity. (3)On the bottom plane of the main pipe, contrary to (2), peak values of the temperature fluctuation amplitude was increased with increasing flow velocity in the main pipe.
) = 0.25; 0.5; 1.0; 2.0 and 4.0. From the numerical investigations, the following characteristics were obtained: (1)Temperature fluctuations in the downstream region of the tee junction were formulated by lower frequency components (< 7.0Hz) due to the iteractions between main pipe flows and jet flows from the branch pipe, and higher frequency components (> 10.0 Hz) generated by the vortex released frequency from the outer edge of the branch pipe jet flows. (2)On the top plane of the main pipe, peak values of the temperature fluctuation amplitude was decreased with increasing flow velocity in the main pipe, and its position was shifted to downstream direction of the main pipe by the increase of the main pipe flow velocity. (3)On the bottom plane of the main pipe, contrary to (2), peak values of the temperature fluctuation amplitude was increased with increasing flow velocity in the main pipe.