AQUA,FLUENTコードによるADSターゲットモデル検証解析(IAHR国際会議[10th IWGAR]ベンチマーク計算)
Numerical ca1culation of the ADS target model with AQUA and FLUENT codes (IAHR [10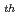 IWGAR ] Benchmark calculation)
IWGAR ] Benchmark calculation)
高田 孝; 山口 彰; 橋本 昭彦*
Takata, Takashi; Yamaguchi, Akira; not registered
液体金属を作動流体とした伝熱流動場の数値解析手法の妥当性を評価するために、IAHR(International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research)内のFluid Phenomena in Energy Exchange sectionで実施されているIWGAR(International Working Group of Advanced Nuclear Reactor Thermal hydraulic)ワーキンググループの第10回meeting(in Obninsk,July 2001)でNaKを用いたADSターゲットモデル実験のベンチマーク問題が取り上げられ、AQUA及びFlUENTコードによるベンチマーク計算を実施した。その結果、以下が明らかとなった。・整流版(Distributing guid)での流量配分が模擬ターゲット(Membrane)近傍の冷却材温度及び温度変動成分に与える影響は大きく、 模擬ターゲット中心部への冷却材の流入量が増えるにつれ、冷却材温度並びに温度変動成分は急速に減衰する傾向であった。 ・整流版以降に関しては、冷却材温度変動成分を若干高めに評価するものの概ね実験結果と解析結果とは一致していた。また流量配分に関する傾向としては、中心部への流入量が増加するにつれ中心部からの周囲への温度及び温度変動成分の拡散が抑制される傾向であった。 ・FLUENTコードでは中心部への冷却材流入量が多く、整流版以降の冷却材挙動に関し拡散を過小仮称評価する傾向であった。ただし、同様の傾向(中心部流入量が増加すると、整流版下流域での拡散が低下する)はAQUAコードでも確認された。 ・本ベンチマーク計算では、乱流モデルの有無による冷却材温度分布の差異がそれほど見られなかった。これは低Pr数流体であることと、それほど発達した乱流場では無かったことが理由と考えられる。
A benchmark problem was proposed to reproduce an experiment for target membrane structure cooling of Accelerator Driven System at the 10th meeting of IWGAR (International Working Group of Advanced Nuclear Reactors Thermal Hydraulic) by the fluid Phenomena in Energy Exchnges Section of IAHR (International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research). THe benchmark calculation has been carried out with AQUA and FLUENT codes to estimate the code validity for liquid metal thermal-hydraulics application. As a result of comparison between numerical analyses and experiment, it is concluded as follows: (1)Inlet flow rate at the distributing grid much affects a coolant temperature and temperature pulsation near the membrane. The coolant temperature descreases and the pulsation decays rapidly as the flow rate toward the membrane center increases. (2)On downstream of the distributing grid, numerical results agree with experimental data except that numerical analysis tends to overestimate the coolant temperature pulsation. Numerical results show that the decrease of coolant temperature and the dissipation of pulsation tend to be underestimated when the flow rate toward the membrane center increases. (3)In FLUENT code, the dissipation of coolant temperature is underestimated more than in AQUA code because FLUENT code tends to overestimate the flow rate toward the membrane center. But the same tendency of the dissipation behavior is shown in AQUA code. (4)A turbulent model is less influenced on the coolant behavior in this benchmark analysis. Because Prandtl (Pr) number of liquid metal is low and the turbulent flow is not developed sufficiently in the condition of the experiment.