Effect of oxygen concentration and temperature on compatibility of ODS steel with liquid, Stagnant Pb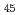 Bi
Bi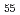
None
古川 智弘 
 ; M
; M ller, G.*; Schumacher, G.*; Weisenburger, A.*; Heinzel, A.*; 青砥 紀身
ller, G.*; Schumacher, G.*; Weisenburger, A.*; Heinzel, A.*; 青砥 紀身 
Furukawa, Tomohiro; M ller, G.*; Schumacher, G.*; Weisenburger, A.*; Heinzel, A.*; Aoto, Kazumi
ller, G.*; Schumacher, G.*; Weisenburger, A.*; Heinzel, A.*; Aoto, Kazumi
鉛ビスマス(LBE)中における鉄鋼材料の腐食挙動に及ぼすLBE中酸素濃度の影響を調べるために、10-4、10-6および10-8wt%の酸素を含有した500Cから650 CのLBE中で10000時間までのODS鋼の腐食試験を実施した。その結果、550
CのLBE中で10000時間までのODS鋼の腐食試験を実施した。その結果、550 C以下の10-6wt%の酸素含有LBE中では母相上にスピネル層が形成しており腐食抑制効果が観察された。600Cの10-4および10-6wt%の酸素含有LBE中では液体金属腐食が複数の場所で観察された。一方、650
C以下の10-6wt%の酸素含有LBE中では母相上にスピネル層が形成しており腐食抑制効果が観察された。600Cの10-4および10-6wt%の酸素含有LBE中では液体金属腐食が複数の場所で観察された。一方、650 Cの10-8wt%酸素含有LBE中では酸化皮膜が母相上に形成されていないものの、液体金属腐食の挙動が観察されず健全であった。
Cの10-8wt%酸素含有LBE中では酸化皮膜が母相上に形成されていないものの、液体金属腐食の挙動が観察されず健全であった。
In order to investigate the effect of oxygen concentration in LBE on corrosion behavior, exposure test of an oxide dispersion strength martensitic type steel was performed in stagnant lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) containing 10 , 10
, 10 and 10
and 10 wt% of oxygen at 500-650
wt% of oxygen at 500-650 C up to 10,000 hours. Results of metallurgical analysis, it was obtained that the base metal was protected from liquid metal corrosion by the formation of a spinel layer under the test condition containing 10
C up to 10,000 hours. Results of metallurgical analysis, it was obtained that the base metal was protected from liquid metal corrosion by the formation of a spinel layer under the test condition containing 10 wt% of oxygen at 550
wt% of oxygen at 550 C or less. In LBE over 600
C or less. In LBE over 600 C containing 10
C containing 10 and 10
and 10 wt% of oxygen, liquid metal corrosion was observed at some places on the surface. At the condition of 650
wt% of oxygen, liquid metal corrosion was observed at some places on the surface. At the condition of 650 C containing 10
C containing 10 wt% of oxygen, although no oxide layer was observed on the surface, the base metal showed good compatibility with LBE.
wt% of oxygen, although no oxide layer was observed on the surface, the base metal showed good compatibility with LBE.