Implementation of a Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) system; An example application of PIV to wake-flows behind objects
Tokuhiro, Akira; Hishida, Koichi; Oki, Yoshihisa
Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) describes a velocity measurement technique for gas and liquid flows whereby, as the name implies, movement of tracer particles in motion with the flow are recorded as images. The particles are framr-to-frame "tracked by one of several correlation techniques from which a 2D vector field can be generated. A 3D vector field is also possible. The measurement method takes advantage of current computer, CCD camera and laser light technologies for its image processing needs. A laser light sheet is typically used to illuminate the tracer particles in the flow field of interest and when implemented accentuates the constrast between the particle and the transparent medium. One can also apply Laser Induced Fluorescence (LIF) in order to further distinguish the tracer particles, the transparent, continuous medium and any light reflecting surfaces in the flow field such as the interface of a gas bubble rising in a liquid. It is also possible to deduce the temperature field from LIF images. In the present work an introduction to PIV is given by way of an example. The selected flow configuration is that of wake-flow behind a bubble and its solid equivalent. By solid equivalent we mean a solid model with approximately the equivalent bubble breadth and volume. This two-component, two-phase flow aptly demonstrates the applicability of PIV to spatio-temporal flows. Use was additionally made of an Infrared Shadow Technique (IST) in order to capture the unlit image (shadow) of the bubble or solid within the flow field. By triggering both the laser and infrared light sources with the CCD camera, the shape of the object as well as the flow field was simultaneously recorded. Besides the 2D vector field, calculations of the vorticity, Reynolds stress and turbulent kinetic energy (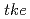 ) distributions were made. The results indicate that for counter-current flow (U
) distributions were made. The results indicate that for counter-current flow (U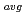 sim$0.245 m/s) of water in a square channel (100 mm) with a single air bubble of ...
sim$0.245 m/s) of water in a square channel (100 mm) with a single air bubble of ...