Male-sterility induced by  -ray irradiation of African nightshade (
-ray irradiation of African nightshade (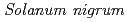 L. ssp.
L. ssp. 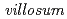 ) seed
) seed
アフリカンナイトシェード(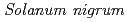 L. ssp.
L. ssp. 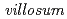 )種子に対する
)種子に対する 線照射により誘発された雄性不稔性
線照射により誘発された雄性不稔性
Ojiewo, C. O.*; Agong, S. G.*; 村上 賢治*; 田中 淳; 長谷 純宏; 桝田 正治*
Ojiewo, C. O.*; Agong, S. G.*; Murakami, Kenji*; Tanaka, Atsushi; Hase, Yoshihiro; Masuda, Masaharu*
アフリカンナイトシェード(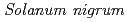 L. spp.
L. spp. 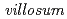 )はアフリカでよく消費される葉野菜であるが、発芽から開花・結実までの期間が短いことから葉の収量が比較的少ない。つまり、生殖生長の開始後、花粉や種子,果実の発達に養分が送られるため、葉に対する養分の転流が少なくなることが原因である。本研究では、雄性不稔性を利用することによって、養分の転流を葉に向けることにより収量を増加させることを考え、
)はアフリカでよく消費される葉野菜であるが、発芽から開花・結実までの期間が短いことから葉の収量が比較的少ない。つまり、生殖生長の開始後、花粉や種子,果実の発達に養分が送られるため、葉に対する養分の転流が少なくなることが原因である。本研究では、雄性不稔性を利用することによって、養分の転流を葉に向けることにより収量を増加させることを考え、 線の種子照射により得られたさまざまな変異体を調査した。照射種子の発芽率,生存率,種子稔性並びに雄性不稔変異体誘発率から、100Gyの
線の種子照射により得られたさまざまな変異体を調査した。照射種子の発芽率,生存率,種子稔性並びに雄性不稔変異体誘発率から、100Gyの 線が変異誘発に最適であると考えられた。M2世代で選抜された雄性不稔変異体には4つのタイプ、すなわち、(1)稔性は無いが酢酸カーミンで花粉が染色される個体、(2)酢酸カーミンで花粉が染色されない個体、(3)花粉が形成されない個体、及び(4)花粉量が著しく少ない個体、が見られた。本研究で得られた雄性不稔変異体は、生殖や果実形成を制限することによって、葉の収量の増加につながると期待される。
線が変異誘発に最適であると考えられた。M2世代で選抜された雄性不稔変異体には4つのタイプ、すなわち、(1)稔性は無いが酢酸カーミンで花粉が染色される個体、(2)酢酸カーミンで花粉が染色されない個体、(3)花粉が形成されない個体、及び(4)花粉量が著しく少ない個体、が見られた。本研究で得られた雄性不稔変異体は、生殖や果実形成を制限することによって、葉の収量の増加につながると期待される。
The leaf yields of vegetables belonging to the 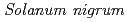 complex are limited by prolific early flowering and berry set. Source-sink limitations and imbalances occur after anthesis, with dry matter partitioning directed more to pollen, seed and fruit formation and development. Each of these processes is associated with high respiratory costs, in competition with leaf expansion and productivity. To use male-sterility to redistribute biological biomass towards greater economic leaf yield, a range of mutants inducible by irradiation of seed with
complex are limited by prolific early flowering and berry set. Source-sink limitations and imbalances occur after anthesis, with dry matter partitioning directed more to pollen, seed and fruit formation and development. Each of these processes is associated with high respiratory costs, in competition with leaf expansion and productivity. To use male-sterility to redistribute biological biomass towards greater economic leaf yield, a range of mutants inducible by irradiation of seed with  -rays was investigated. On the basis of overall plant development from germination, seedling survival, production of M2 selfed-seed and the frequency of male-sterile mutants, 100 Gy of
-rays was investigated. On the basis of overall plant development from germination, seedling survival, production of M2 selfed-seed and the frequency of male-sterile mutants, 100 Gy of  -rays was determined to be the optimum dose. Four male-sterile mutant types were isolated during the Spring-Summer season from the M2 screen: (1) an acetocarmine-stained nonviable pollen type which stained black with potassium iodide solution (T-1); (2) a defective pollen type not stainable with acetocarmine (T-2); (3) a pollen-less type with defective anthers (T-3); and (4) an extremely low pollen-producing type (T-4). An intermediate type (T-1/2) had a mixture of acetocarmine stainable and defective non-stainable pollen. All T-1, and some T-3 mutants were partially restored and set berries with selfed-seed, while T-1/2 set non-seeded berries in the Autumn-Winter season. Eliminating the reproductive function and subsequently fruits, which are the major sink organs of the plant, is expected to enable the male-sterile mutants isolated in this study to use the biomass no longer allocated to pollen (and eventually to berry and seed production), for extra leaf production.
-rays was determined to be the optimum dose. Four male-sterile mutant types were isolated during the Spring-Summer season from the M2 screen: (1) an acetocarmine-stained nonviable pollen type which stained black with potassium iodide solution (T-1); (2) a defective pollen type not stainable with acetocarmine (T-2); (3) a pollen-less type with defective anthers (T-3); and (4) an extremely low pollen-producing type (T-4). An intermediate type (T-1/2) had a mixture of acetocarmine stainable and defective non-stainable pollen. All T-1, and some T-3 mutants were partially restored and set berries with selfed-seed, while T-1/2 set non-seeded berries in the Autumn-Winter season. Eliminating the reproductive function and subsequently fruits, which are the major sink organs of the plant, is expected to enable the male-sterile mutants isolated in this study to use the biomass no longer allocated to pollen (and eventually to berry and seed production), for extra leaf production.