Simulations on the nonlinear mode coupling in multiple-scale drift-type turbulence with coherent flow structures
Li, J.*; Uzawa, Ken*; Lin, Z.*; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Miyato, Naoaki; Matsumoto, Taro; Dong, J. Q.*
The dynamics of secondary, anisotropic coherent structures behaving as a stationary wave, including zonal/mean flows, streamers and low-frequency long wavelength fluctuations, in multiple-scale turbulence in tokamak plasmas is investigated by performing 3D simulations as well as 2D modeling analyses. The role of nonlinear mode coupling is specifically discussed as a ubiquitous principal interaction mechanism in the dual processes of the generation and back-action of secondary structures on ITG and ETG turbulence. Here two new results are evidently presented on the importance of the mode coupling interaction: (1) While secondary zonal flows and long wavelength modes are generated through nonlinear mode coupling, the same back-action process can deform the spectral distribution in inertia range from the power-law scaling into an exponential-law dependence. The turbulence may be reduced due to the local and/or nonlocal free energy transfer to stable region. (2) Streamer-like long wavelength fluctuations driven by the most unstable ETG modes, can saturate slab ETG turbulence through producing a 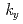 -mode coupling that corresponds to the toroidal mode coupling in tokamak plasma, suggesting a low ETG fluctuation level and electron transport. Furthermore, the effect of ITG generated zonal flows regarded as a wave-type mean flow on the generation of zonal flows in ETG turbulence is also discussed with an emphasis on the role of nonlinear mode coupling.
-mode coupling that corresponds to the toroidal mode coupling in tokamak plasma, suggesting a low ETG fluctuation level and electron transport. Furthermore, the effect of ITG generated zonal flows regarded as a wave-type mean flow on the generation of zonal flows in ETG turbulence is also discussed with an emphasis on the role of nonlinear mode coupling.