Inter-machine comparison of intrinsic toroidal rotation
Rice, J. E.*; Ince-Cushman, A.*; de Grassie, J. S.*; Eriksson, L.-G.*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Scarabosio, A.*; Bortolon, A.*; Burrell, K. H.*; Fenzi-Bonizec, C.*; Greenwald, M. J.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Hoang, G. T.*; Koide, Yoshihiko; Marmar, E. S.*; Pochelon, A.*; Podpaly, Y.*
Parametric scalings of the intrinsic (spontaneous, with no external momentum input) toroidal rotation observed on a large number of tokamaks have been combined with an eye toward revealing the underlying mechanism(s) and extrapolation to future devices. The intrinsic rotation velocity has been found to increase with plasma stored energy or pressure in JET, Alcator C-Mod, Tore Supra, DIII- D, JT-60U and TCV, and to decrease with increasing plasma current in some of these cases. Use of dimensionless parameters has led to a roughly unified scaling with Mach number in proportion to normalized beta, although a variety of Mach numbers works fairly well; scalings of the intrinsic rotation velocity with normalized gyro-radius or collisionality show no correlation. Whether this suggests the predominant role of MHD phenomena such as ballooning transport over turbulent processes in driving the rotation remains an open question. For an ITER discharge with 
 =2.6, an intrinsic rotation Alfv
=2.6, an intrinsic rotation Alfv n Mach number of M
n Mach number of M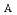
 0.02 may be expected from the above deduced scaling, possibly high enough to stabilize resistive wall modes without external momentum input.
0.02 may be expected from the above deduced scaling, possibly high enough to stabilize resistive wall modes without external momentum input.