Balance of the stored energies sustained by the internal and edge transport barriers and effects of ELMs and L-H transitions in JT-60U
JT-60Uにおける内部輸送障壁及び周辺輸送障壁が支える蓄積エネルギー間の相関と、ELM及びLH遷移の効果
鎌田 裕; 吉田 麻衣子; 坂本 宜照; 小出 芳彦; 大山 直幸; 浦野 創; 神谷 健作; 鈴木 隆博; 諫山 明彦; JT-60チーム
Kamada, Yutaka; Yoshida, Maiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Koide, Yoshihiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Urano, Hajime; Kamiya, Kensaku; Suzuki, Takahiro; Isayama, Akihiko; JT-60 Team
先進トカマクプラズマにおける圧力分布を決定する物理機構を理解するため、周辺輸送障壁と内部輸送障壁の相関を研究した。(1)Type-I ELMのあるHモードにおいて、周辺ペデスタル部のポロイダルベータ( p-ped)は、全ポロイダルベータ(
p-ped)は、全ポロイダルベータ( p-tot)とともにほぼ直線的に上昇することを、広いプラズマ電流領域で明らかにした。また、この関係がプラズマ断面の三角度とともに強くなることを見いだした。(2)ペデスタル蓄積エネルギー(Wped)の増加とともにELMのプラズマ中への侵入距離が深くなり、最終的に内部輸送障壁に達する。この状態になると、内部輸送障壁位置(半径)はそれ以上広がることができなくなり、また、その障壁は弱くなる。このようにして、全熱化蓄積エネルギー(Wth)に対する内部輸送障壁内での蓄積エネルギー(WITB)及びペデスタル蓄積エネルギー(Wped)が一定となる。また、Type I ELMによる周辺部のトロイダル運動量の減少は、熱エネルギーの減少に比べて大きいこと、さらに、ELM侵入距離はトロイダル回転の方がイオン温度よりも深く、内部輸送障壁内部に達することを見いだした。これが内部輸送障壁の劣化につながっているかも知れない。
p-tot)とともにほぼ直線的に上昇することを、広いプラズマ電流領域で明らかにした。また、この関係がプラズマ断面の三角度とともに強くなることを見いだした。(2)ペデスタル蓄積エネルギー(Wped)の増加とともにELMのプラズマ中への侵入距離が深くなり、最終的に内部輸送障壁に達する。この状態になると、内部輸送障壁位置(半径)はそれ以上広がることができなくなり、また、その障壁は弱くなる。このようにして、全熱化蓄積エネルギー(Wth)に対する内部輸送障壁内での蓄積エネルギー(WITB)及びペデスタル蓄積エネルギー(Wped)が一定となる。また、Type I ELMによる周辺部のトロイダル運動量の減少は、熱エネルギーの減少に比べて大きいこと、さらに、ELM侵入距離はトロイダル回転の方がイオン温度よりも深く、内部輸送障壁内部に達することを見いだした。これが内部輸送障壁の劣化につながっているかも知れない。
For understanding of the physics processes determining the radial profiles of the kinetic plasma parameters in the advanced tokamak plasmas, correlation between the edge and the internal transport barriers (ETB and ITB) has been studied. We fond that the edge pedestal beta, 
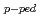 , increases almost linearly with the total
, increases almost linearly with the total 
 , over a wide range of the plasma current for the type I ELMing H-mode, and the dependence becomes stronger with increasing triangularity. This dependence is not due to the profile stiffness. However, with increasing the stored energy inside the ITB radius (W
, over a wide range of the plasma current for the type I ELMing H-mode, and the dependence becomes stronger with increasing triangularity. This dependence is not due to the profile stiffness. However, with increasing the stored energy inside the ITB radius (W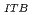 ), the total thermal stored energy (W
), the total thermal stored energy (W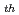 ) increases and then the pedestal stored energy (W
) increases and then the pedestal stored energy (W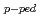 ) increases. With increasing W
) increases. With increasing W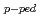 , the ELM penetration depth expands more inward and finally reaches the ITB-foot radius. At this situation, the ITB radius cannot move outward and the ITB strength becomes weak. Then the fractions of W
, the ELM penetration depth expands more inward and finally reaches the ITB-foot radius. At this situation, the ITB radius cannot move outward and the ITB strength becomes weak. Then the fractions of W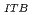 and W
and W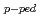 to W
to W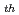 become almost constant. We also found that the type I ELM expels/decreases edge toroidal momentum larger than ion thermal energy. The ELM penetration radius for toroidal rotation tends to be deeper than that for ion temperature, and can exceeds the ITB radius. The ELM affected area is deeper for CO rotating plasmas than CTR rotating ones. The ELM affected area is deeper in the order of the toroidal rotation (V
become almost constant. We also found that the type I ELM expels/decreases edge toroidal momentum larger than ion thermal energy. The ELM penetration radius for toroidal rotation tends to be deeper than that for ion temperature, and can exceeds the ITB radius. The ELM affected area is deeper for CO rotating plasmas than CTR rotating ones. The ELM affected area is deeper in the order of the toroidal rotation (V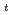 ), the ion temperature (T
), the ion temperature (T ) and then the electron temperature (Te). The L-H transition also changes the V
) and then the electron temperature (Te). The L-H transition also changes the V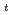 -profile more significantly than the Ti-profile. After the L-H transition, in the ELM-free phase, the pedestal V
-profile more significantly than the Ti-profile. After the L-H transition, in the ELM-free phase, the pedestal V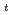 sifts into the CTR direction deeply and suddenly, and after that the pedestal V
sifts into the CTR direction deeply and suddenly, and after that the pedestal V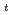 and T
and T evolves in the similar timescale. The change in V
evolves in the similar timescale. The change in V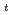 by ELM and L-H transition may affect degradation / evolution of ITBs.
by ELM and L-H transition may affect degradation / evolution of ITBs.