Measurement of neutron dose under criticality accident conditions at TRACY using ebonites
Murazaki, Minoru; Nobuhara, Fumiyoshi*; Iwai, Shohei*; Tonoike, Kotaro  ; Uchiyama, Gunzo
; Uchiyama, Gunzo 
Neutron doses under criticality accident conditions at TRACY were measured using ebnites, which are hard rubber containing sulfur. To evaluate a neutron dose, beta rays emitted from  P induced by
P induced by  S(n,p) reaction are measured with Geiger-M
S(n,p) reaction are measured with Geiger-M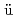 ller (GM) counter. A calibration factor (Gy/cpm), which is pre-determined using a
ller (GM) counter. A calibration factor (Gy/cpm), which is pre-determined using a  Cf source, is applied to the count rates to obtain neutron doses. Factors to correct for the difference between responses of
Cf source, is applied to the count rates to obtain neutron doses. Factors to correct for the difference between responses of  S(n,p) to the spectrum of
S(n,p) to the spectrum of  Cf source and to spectra of TRACY were calculated and applied to the doses. Ebonites were exposed by TRACY with and without the water reflector. Neutron doses in TRACY without a reflector were evaluated with an uncertainty of less than about 40%. On the other hand, average of neutron doses in TRACY with the water reflector were accurate. By these measurements, it was found that ebonites can be used as a neutron dosimeter for criticality accidents.
Cf source and to spectra of TRACY were calculated and applied to the doses. Ebonites were exposed by TRACY with and without the water reflector. Neutron doses in TRACY without a reflector were evaluated with an uncertainty of less than about 40%. On the other hand, average of neutron doses in TRACY with the water reflector were accurate. By these measurements, it was found that ebonites can be used as a neutron dosimeter for criticality accidents.