SMAP1 is a positive regulator for 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid mediated actin degradation and acts independent of known auxin signaling pathway
SMAP1は、2,4-ジクロロフェノキシ酢酸を介したアクチンの分解の正の制御因子であり、既知のオーキシン情報伝達経路とは独立して働く
高橋 摩帆*; 大野 豊; Rahman, A.*
Takahashi, Maho*; Ono, Yutaka; Rahman, A.*
Traditionally, it is believed that plant hormone IAA and 2,4-D share a common signaling pathway. However, recent studies have challenged this idea both at physiological and genetic level. To provide a molecular explanation of 2,4-D specific action in Arabidopsis, we characterized the functionally unknown protein SMAP1. The molecular and cell biological analyses revealed that, (1) SMAP1 acts as a positive regulator for 2,4-D induced degradation of actin, cell division and cell elongation processes, and (2) the double mutant of 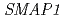 and
and 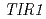 , a component of E3 ubuquitin ligaes, in root growth assay, shows complete insensitivity to 2,4-D at the concentration that inhibits eighty percent root growth in respective single mutants. Our results identify a novel 2,4-D specific biologically significant pathway in plants.
, a component of E3 ubuquitin ligaes, in root growth assay, shows complete insensitivity to 2,4-D at the concentration that inhibits eighty percent root growth in respective single mutants. Our results identify a novel 2,4-D specific biologically significant pathway in plants.