Living polymerization induced macro- and microdomain investigated by focusing ultra-small-angle neutron scattering
Motokawa, Ryuhei 

 ; Iida, You*; Zhao, Y.; Hashimoto, Takeji; Koizumi, Satoshi
; Iida, You*; Zhao, Y.; Hashimoto, Takeji; Koizumi, Satoshi
By utilizing a biconcave refractive neutron lens (MgF ), we constructed a focusing ultra-small-angle neutron scattering (USANS) spectrometer (SANS-J-II) at research reactor JRR3, Tokai Japan. SANS-J-II can successfully reach to
), we constructed a focusing ultra-small-angle neutron scattering (USANS) spectrometer (SANS-J-II) at research reactor JRR3, Tokai Japan. SANS-J-II can successfully reach to 
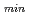 =0.0003
=0.0003 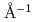 , where
, where  [= 4
[= 4 sin(
sin( )/
)/ ] is the magnitude of scattering vector given by wavelength
] is the magnitude of scattering vector given by wavelength  and scattering angle 2
and scattering angle 2 , and simultaneously cover conventional SANS region up to
, and simultaneously cover conventional SANS region up to  = 0.004
= 0.004 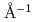 by using 5-inch size & high resolution position sensitive area photomultiplier with scintillator (ZnS). Focusing USANS, thus realized, plays an important role to investigate the time-evolution of hierarchically ordered structures in the living radical polymerization solution, preparing poly (methyl methacrylate)-
by using 5-inch size & high resolution position sensitive area photomultiplier with scintillator (ZnS). Focusing USANS, thus realized, plays an important role to investigate the time-evolution of hierarchically ordered structures in the living radical polymerization solution, preparing poly (methyl methacrylate)- 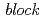 -polystyrene (PMMA-
-polystyrene (PMMA- -PS). In the reaction process to synthesize PS block chains from the end of PMMA block chain, we found the interplay between macro and microdomain structures as follows. Small-angle scattering at
-PS). In the reaction process to synthesize PS block chains from the end of PMMA block chain, we found the interplay between macro and microdomain structures as follows. Small-angle scattering at 
 0.001
0.001 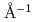 determined time-evolving microdomain structures; as the polymerization proceeds, (1) first by order-disorder transition, a lamellar microdomain appears and (2) second by order-order transitions, the morphologies of microdomains change to PS cylinder and successively to PS sphere. Ultra-small-angle scattering at
determined time-evolving microdomain structures; as the polymerization proceeds, (1) first by order-disorder transition, a lamellar microdomain appears and (2) second by order-order transitions, the morphologies of microdomains change to PS cylinder and successively to PS sphere. Ultra-small-angle scattering at 
 0.001
0.001 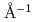 , exhibits power law scattering (
, exhibits power law scattering (

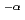 ) due to macrophase separation between PMMA-
) due to macrophase separation between PMMA- -PS and PS homopolymer, appeared as by product. The exponent
-PS and PS homopolymer, appeared as by product. The exponent  varies from 4 to 2, reflecting a grain boundary of macrodomain rich-in PMMA-
varies from 4 to 2, reflecting a grain boundary of macrodomain rich-in PMMA- -PS; when a lamellar microdomain appears, Porod law gives
-PS; when a lamellar microdomain appears, Porod law gives  = 4, whereas when cylinder and sphere appear,
= 4, whereas when cylinder and sphere appear,  = 2, due to inhomogeniety of the microdomain spatial distribution.
= 2, due to inhomogeniety of the microdomain spatial distribution.