Comparative analysis of flavonoid biosynthesis genes between 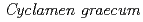 and its white-flowered mutant
and its white-flowered mutant
Akita, Yusuke; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Shimada, Akihiko; Kitamura, Satoshi; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Narumi, Issei
To reveal the relationship between floral pigmentation and flavonoid biosynthesis genes in cyclamen (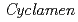 species), we analyzed flower pigments from wild-type cyclamen (
species), we analyzed flower pigments from wild-type cyclamen (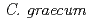 ) and its white-flowered mutant. Analysis with high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) showed that major anthocyanins of the wild-type petal were malvidin 3,5-diglucosides. The white-flowered mutant possessed smaller amount of anthocyanins but higher amount of flavonols than the wild-type, suggesting the change of metabolic flow by disruption of anthocyanin biosynthesis. By degenerate-PCR with total RNAs from wild-type petals, we isolated some flavonoid biosynthesis gene. RT-PCR using a specific primer set for each gene demonstrated that the expression of
) and its white-flowered mutant. Analysis with high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) showed that major anthocyanins of the wild-type petal were malvidin 3,5-diglucosides. The white-flowered mutant possessed smaller amount of anthocyanins but higher amount of flavonols than the wild-type, suggesting the change of metabolic flow by disruption of anthocyanin biosynthesis. By degenerate-PCR with total RNAs from wild-type petals, we isolated some flavonoid biosynthesis gene. RT-PCR using a specific primer set for each gene demonstrated that the expression of 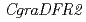 decreased in white-flowered mutant compared with wild-type, whereas the expressions of other genes did not appear to differ greatly. The genomic construction of
decreased in white-flowered mutant compared with wild-type, whereas the expressions of other genes did not appear to differ greatly. The genomic construction of 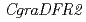 was not different between wild-type and white-flowered mutant, inferring that reduced expression of
was not different between wild-type and white-flowered mutant, inferring that reduced expression of 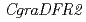 correlates with white-flowered mutation. These results suggest that
correlates with white-flowered mutation. These results suggest that 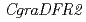 is involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway in
is involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway in 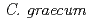 , and the white-flowered mutation could be caused by transcriptional regulation of
, and the white-flowered mutation could be caused by transcriptional regulation of 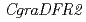 gene.
gene.