Combinational effect of charged particle irradiation and alkaline pretreatment on hydriding property of a Mm-Ni based alloy
Kishimoto, Masahiko*; Abe, Hiroshi; Hiraki, Takeshi*; Uchida, Hirohisa*
We investigated combinational effects of electron/ion beam irradiation and KOH alkaline pretreatment on initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate of Mm-Ni based alloy. In previous studies, we have reported that the alkaline pretreatment of the alloy surface using LiOH, NaON or KOH accelerates the rate of the initial activation. For the surface modification of materials, an electron/ion beam irradiation is well known to produce a high density of vacancy type defects in materials and to be a quite useful method. These facts give the possibility that the hydrogen absorptivity in Mm-Ni based alloy is improved by the surface modification on using an electron/ion beam irradiations. In this study, we performed electron (e ) and proton ion (H
) and proton ion (H ) beam irradiation into MmNi
) beam irradiation into MmNi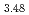 Co
Co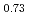 Mn
Mn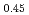 Al
Al (Mm = La
(Mm = La Ce
Ce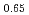 ) at TIARA (Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application), JAEA. For the electrochemical measurements of the initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate, either un-irraddiated or e
) at TIARA (Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application), JAEA. For the electrochemical measurements of the initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate, either un-irraddiated or e /H
/H beam irradiated MmNi
beam irradiated MmNi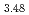 Co
Co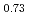 Mn
Mn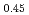 Al
Al was used as an anode. The hydrogen absorption rate of these samples with both 6M-KOH pretreatment and un-treatment was evaluated. Based on the obtained results, we discuss the correlation among e
was used as an anode. The hydrogen absorption rate of these samples with both 6M-KOH pretreatment and un-treatment was evaluated. Based on the obtained results, we discuss the correlation among e /H
/H beam irradiation, alkaline pretreatment and initial hydrogen absorption rate in Mm-Ni based alloy.
beam irradiation, alkaline pretreatment and initial hydrogen absorption rate in Mm-Ni based alloy.