Experimental investigation and validation of neutral beam current drive for ITER through ITPA joint experiments
ITPA装置間比較実験によるITERのための中性粒子ビーム電流駆動についての実験研究と検証
鈴木 隆博; Akers, R.*; Gates, D. A.*; G nter, S.*; Heidbrink, W. W.*; Hobirk, J.*; Luce, T. C.*; 村上 和功*; Park, J. M.*; Turnyanskiy, M.*; ITPA Integrated Operation Scenarios Topical Group*
nter, S.*; Heidbrink, W. W.*; Hobirk, J.*; Luce, T. C.*; 村上 和功*; Park, J. M.*; Turnyanskiy, M.*; ITPA Integrated Operation Scenarios Topical Group*
Suzuki, Takahiro; Akers, R.*; Gates, D. A.*; G nter, S.*; Heidbrink, W. W.*; Hobirk, J.*; Luce, T. C.*; Murakami, Masanori*; Park, J. M.*; Turnyanskiy, M.*; ITPA Integrated Operation Scenarios Topical Group*
nter, S.*; Heidbrink, W. W.*; Hobirk, J.*; Luce, T. C.*; Murakami, Masanori*; Park, J. M.*; Turnyanskiy, M.*; ITPA Integrated Operation Scenarios Topical Group*
国際トカマク物理活動(ITPA)の下で、世界の主要な4つのトカマク装置(AUG(独国), DIII-D(米国), JT-60U(日本)、及びMAST(英国))において周辺部中性粒子ビーム(NB)駆動電流分布を測定し理論を検証するための国際装置間比較実験を実施した。さまざまな装置での実験を行い、プラズマ電流0.6-1.2MA,トロイダル磁場0.3-3.7T, NBの加速エネルギー67-350keVと広いダイナミックレンジの実験条件に渡ってNB駆動電流分布(あるいは全電流分布のNBCDによる変化)を測定し、NB駆動電流とその空間分布の測定結果は、比較的小さい高速イオンの拡散係数(0-0.5m /s)を仮定した理論計算で説明できることがわかった。また、AUG及びDIII-Dの結果によると、低い加熱パワーのときにはNB駆動電流分布は高速イオンの拡散係数として0m
/s)を仮定した理論計算で説明できることがわかった。また、AUG及びDIII-Dの結果によると、低い加熱パワーのときにはNB駆動電流分布は高速イオンの拡散係数として0m /sを仮定した理論計算で説明できる一方で、高い加熱パワー(AUGでは5MW、DIII-Dでは7.2MW)の時には0.3-0.5m
/sを仮定した理論計算で説明できる一方で、高い加熱パワー(AUGでは5MW、DIII-Dでは7.2MW)の時には0.3-0.5m /s程度の拡散係数を仮定した理論計算が最もよく実験と合致するとの結果を得た。背景プラズマ乱流による高速イオンの散乱とそれによる再分配と考えられる。測定したNB駆動電流と
/s程度の拡散係数を仮定した理論計算が最もよく実験と合致するとの結果を得た。背景プラズマ乱流による高速イオンの散乱とそれによる再分配と考えられる。測定したNB駆動電流と
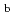 =0を仮定した計算との比について、高速イオンの静電的乱流輸送の指標である
=0を仮定した計算との比について、高速イオンの静電的乱流輸送の指標である
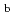 /
/
 及び電磁的乱流輸送の指標であるトロイダル
及び電磁的乱流輸送の指標であるトロイダル 値への依存性を調べ、ITERの周辺部NB電流駆動について議論する。
値への依存性を調べ、ITERの周辺部NB電流駆動について議論する。
Joint experiments investigating the off-axis neutral beam current drive (NBCD) capability to be utilized for advanced operation scenario development in ITER was conducted in 5 tokamaks (AUG, DIII-D, JT-60U, MAST and NSTX) through the ITPA. We discuss results obtained in the joint experiments, where the toroidal field, 
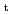 , covered 0.3-3.7 T, the plasma current,
, covered 0.3-3.7 T, the plasma current, 
 , 0.6-1.2 MA, and the beam energy, Eb, 67-350 keV. A current profile broadened by off-axis NBCD was observed in MAST. In DIII-D, good agreement between the measured and calculated NB driven current profile was observed. In JT-60U, agreement between measured and calculated NBCD location was obtained, when the NBCD location (0.3-0.6 in
, 0.6-1.2 MA, and the beam energy, Eb, 67-350 keV. A current profile broadened by off-axis NBCD was observed in MAST. In DIII-D, good agreement between the measured and calculated NB driven current profile was observed. In JT-60U, agreement between measured and calculated NBCD location was obtained, when the NBCD location (0.3-0.6 in  /
/ ), heating power (6-13 MW), triangularity
), heating power (6-13 MW), triangularity  (0.25-0.45), and
(0.25-0.45), and 
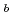 (85 and 350 keV) were widely scanned. In AUG (at low
(85 and 350 keV) were widely scanned. In AUG (at low 
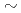 0.2) and DIII-D, introduction of a fast ion diffusion coefficient of
0.2) and DIII-D, introduction of a fast ion diffusion coefficient of 
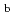 0.3-0.5 m
0.3-0.5 m /s in the calculation gave better agreement at high heating power (5 and 7.2 MW), suggesting anomalous transport of fast ions by turbulence. It was found through these ITPA joint experiments that NBCD related physics quantities reasonably agree with calculations (with
/s in the calculation gave better agreement at high heating power (5 and 7.2 MW), suggesting anomalous transport of fast ions by turbulence. It was found through these ITPA joint experiments that NBCD related physics quantities reasonably agree with calculations (with 
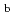 = 0-0.5 m
= 0-0.5 m /s) in all devices when there is no MHD activity except ELMs. Proximity of measured off-axis beam driven current to the corresponding calculation with
/s) in all devices when there is no MHD activity except ELMs. Proximity of measured off-axis beam driven current to the corresponding calculation with 
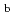 = 0 has been discussed for ITER in terms of a theoretically predicted scaling of fast-ion diffusion that depends on
= 0 has been discussed for ITER in terms of a theoretically predicted scaling of fast-ion diffusion that depends on 
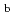 /
/
 for electrostatic turbulence or
for electrostatic turbulence or 
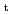 for electromagnetic turbulence.
for electromagnetic turbulence.