Electrically tunable spin injector free from the impedance mismatch problem
電気的に制御可能なインピーダンスミスマッチフリースピン流注入源
安藤 和也*; 高橋 三郎; 家田 淳一 

 ; 紅林 秀和*; Trypiniotis, T.*; Barnes, C. H. W.*; 前川 禎通; 齊藤 英治
; 紅林 秀和*; Trypiniotis, T.*; Barnes, C. H. W.*; 前川 禎通; 齊藤 英治
Ando, Kazuya*; Takahashi, Saburo; Ieda, Junichi; Kurebayashi, Hidekazu*; Trypiniotis, T.*; Barnes, C. H. W.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Injection of spin currents into solids is crucial for exploring spin physics and spintronics. There has been significant progress in recent years in spin injection into high-resistivity materials, for example, semiconductors and organic materials, which uses tunnel barriers to circumvent the impedance mismatch; the impedance mismatch between ferromagnetic metals and high-resistivity materials drastically limits the spin-injection efficiency. However, because of this problem, there is no route for spin injection into these materials through low-resistivity interfaces, that is, Ohmic contacts, even though this promises an easy and versatile pathway for spin injection without the need for growing high-quality tunnel barriers. Here we show experimental evidence that spin pumping enables spin injection free from this condition; room-temperature spin injection into GaAs from Ni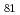 Fe
Fe through an Ohmic contact is demonstrated through dynamical spin exchange. Furthermore, we demonstrate that this exchange can be controlled electrically by applying a bias voltage across a Ni
through an Ohmic contact is demonstrated through dynamical spin exchange. Furthermore, we demonstrate that this exchange can be controlled electrically by applying a bias voltage across a Ni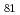 Fe
Fe /GaAs interface, enabling electric tuning of the spin-pumping efficiency.
/GaAs interface, enabling electric tuning of the spin-pumping efficiency.