Laser-induced fluorescence and infrared spectroscopic studies on the specific solvation of tris(1-(2-thienyl)-4,4,4-trifluoro-1,3-butanedionato)europium(III) in an ionic liquid
Okamura, Hiroyuki 

 ; Sakae, Hiroki*; Kidani, Keiji*; Hirayama, Naoki*; Aoyagi, Noboru
; Sakae, Hiroki*; Kidani, Keiji*; Hirayama, Naoki*; Aoyagi, Noboru 

 ; Saito, Takumi*; Shimojo, Kojiro
; Saito, Takumi*; Shimojo, Kojiro 

 ; Naganawa, Hirochika
; Naganawa, Hirochika 
 ; Imura, Hisanori*
; Imura, Hisanori*
The extraction constant and the two-phase stability constant of tris(2-thenoyltrifluoroacetonato) europium(III) between 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ([C mim][Tf
mim][Tf N]) as an ionic liquid and an aqueous phase were determined by considering the extraction equilibria. Specific solute-solvent interactions between the neutral Eu(III) chelate and [C
N]) as an ionic liquid and an aqueous phase were determined by considering the extraction equilibria. Specific solute-solvent interactions between the neutral Eu(III) chelate and [C mim][Tf
mim][Tf N] molecules were revealed from the relationships between the distribution constant of the enol form of 2-thenoyltrifluoroacetone (Htta) and the distribution constant (
N] molecules were revealed from the relationships between the distribution constant of the enol form of 2-thenoyltrifluoroacetone (Htta) and the distribution constant (
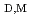 ) of the neutral Eu(III) chelate. The coordination environment of Eu
) of the neutral Eu(III) chelate. The coordination environment of Eu in the neutral Eu(III) chelate in [C
in the neutral Eu(III) chelate in [C mim][Tf
mim][Tf N] was investigated by time-resolved laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy and infrared absorption spectroscopy. Both methods consistently indicated that not only the Eu(III)chelate extracted but also Eu(tta)
N] was investigated by time-resolved laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy and infrared absorption spectroscopy. Both methods consistently indicated that not only the Eu(III)chelate extracted but also Eu(tta) (H
(H O)
O) synthesized as a solid crystal were almost completely dehydrated in [C
synthesized as a solid crystal were almost completely dehydrated in [C mim][Tf
mim][Tf N] saturated with water. Consequently, the higher
N] saturated with water. Consequently, the higher 
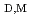 or extractability of the neutral Eu(III) chelate in the [C
or extractability of the neutral Eu(III) chelate in the [C mim][Tf
mim][Tf N] system can be ascribed to the dehydration of the Eu(III) chelate, which is caused by the specific solvation with [C
N] system can be ascribed to the dehydration of the Eu(III) chelate, which is caused by the specific solvation with [C mim][Tf
mim][Tf N] molecules.
N] molecules.