Tunable nanometer electrode gaps by MeV ion irradiation
MeVイオン照射によって調整可能なナノメートルスケールの電極間隔
Cheang-Wong, J.-C.*; 鳴海 一雅; Sch rmann, G. M.*; Aziz, M. J.*; Golovchenko, J. A.*
rmann, G. M.*; Aziz, M. J.*; Golovchenko, J. A.*
Cheang-Wong, J.-C.*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Sch rmann, G. M.*; Aziz, M. J.*; Golovchenko, J. A.*
rmann, G. M.*; Aziz, M. J.*; Golovchenko, J. A.*
非晶質材料に特有のMeVイオン照射誘起塑性変形を利用したナノメートルスケールの間隔(ギャップ)を持つ電極の作製について報告する。非晶質金属Pd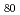 Si
Si で作製したサブミクロンサイズのギャップを持つ電極に、4.64MeV O
で作製したサブミクロンサイズのギャップを持つ電極に、4.64MeV O イオンを照射したところ、Pd
イオンを照射したところ、Pd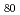 Si
Si の塑性変形が起こり、ギャップを完全に閉じることができた。そこで、電極間の電界放出に伴う電流-電圧(I-V)特性をその場測定することによって、イオン照射によるギャップサイズの変化を観察した。I-V特性はFowler-Nordheimトンネリングに一致した。これらの結果は、MeVイオン照射誘起塑性変形を利用してナノメートルスケールのギャップを持つ電極を作製する際に、I-V特性でフィードバックをかけることによって原子スケールの精度でギャップサイズを制御できることを示す。さらに、単一分子の電気特性の研究に必要な電極の作製及びその特性評価を可能にすると期待される。
の塑性変形が起こり、ギャップを完全に閉じることができた。そこで、電極間の電界放出に伴う電流-電圧(I-V)特性をその場測定することによって、イオン照射によるギャップサイズの変化を観察した。I-V特性はFowler-Nordheimトンネリングに一致した。これらの結果は、MeVイオン照射誘起塑性変形を利用してナノメートルスケールのギャップを持つ電極を作製する際に、I-V特性でフィードバックをかけることによって原子スケールの精度でギャップサイズを制御できることを示す。さらに、単一分子の電気特性の研究に必要な電極の作製及びその特性評価を可能にすると期待される。
We report the use of MeV ion-irradiation-induced plastic deformation of amorphous materials to fabricate electrodes with a nanometer-sized gap. Plastic deformation of the amorphous metal Pd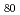 Si
Si is induced by 4.64 MeV O
is induced by 4.64 MeV O ion irradiation, allowing the complete closing of a sub-micrometer gap. We measure the evolving gap size in situ by monitoring the field emission current-voltage (I-V) characteristics between electrodes. The I-V behavior is consistent with Fowler-Nordheim tunneling. We show that feedback on this signal permits control of the gap size with atomic-scale precision, which we expect to permit precise fabrication and characterization of electrodes with nanometer gaps for the study of the electrical properties of single molecules.
ion irradiation, allowing the complete closing of a sub-micrometer gap. We measure the evolving gap size in situ by monitoring the field emission current-voltage (I-V) characteristics between electrodes. The I-V behavior is consistent with Fowler-Nordheim tunneling. We show that feedback on this signal permits control of the gap size with atomic-scale precision, which we expect to permit precise fabrication and characterization of electrodes with nanometer gaps for the study of the electrical properties of single molecules.