Vicinage Effect on Secondary-electron Yield from Amorphous Carbon Foils Induced by Swift H
 and C
and C
 Ions
Ions
Narumi, Kazumasa; Takahashi, Yasuyuki*; Chiba, Atsuya; Saito, Yuichi; Yamada, Keisuke; Ishikawa, Norito 

 ; Sugai, Hiroyuki*; Maeda, Yoshihito
; Sugai, Hiroyuki*; Maeda, Yoshihito
62.5-300-keV/u H
 and C
and C
 ions were incident on self-supporting amorphous carbon foils of 2-100
ions were incident on self-supporting amorphous carbon foils of 2-100  g/cm
g/cm thickness, which was tilted by 45
thickness, which was tilted by 45 to the beam axis. Secondary eletrons (SE) emitted in the forward and backward directions from a carbon foil were detected by two microchannel-plate (MCP) detectors placed at the both sides of the target holder in parallel with the target. Particles transmitted through the foil were detected with a solid-state detector placed at the backside of the target on the beam axis, which made it possible to measure the energy and the number of the transmitted particles. The forward and backward SE yields per incident projectile
to the beam axis. Secondary eletrons (SE) emitted in the forward and backward directions from a carbon foil were detected by two microchannel-plate (MCP) detectors placed at the both sides of the target holder in parallel with the target. Particles transmitted through the foil were detected with a solid-state detector placed at the backside of the target on the beam axis, which made it possible to measure the energy and the number of the transmitted particles. The forward and backward SE yields per incident projectile 
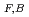 were determined from the pulse-height distributions of the forward and backward MCP signals, respectively, which are proportional to the number of detected SE's. The vicinage effect was evaluated with the ratios of the forward and backward SE yields R
were determined from the pulse-height distributions of the forward and backward MCP signals, respectively, which are proportional to the number of detected SE's. The vicinage effect was evaluated with the ratios of the forward and backward SE yields R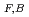 =
= 
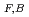 (2)/2
(2)/2
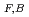 (1), where
(1), where 
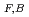 (2) and
(2) and 
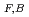 (1) are SE yields induced by bombardment with diatomic and monatomic ions with the same velocity, respectively. The origin of the vicinage effect on the SE yield will be discussed based on the observed foil-thickness and velocity dependence of the vicinage effect.
(1) are SE yields induced by bombardment with diatomic and monatomic ions with the same velocity, respectively. The origin of the vicinage effect on the SE yield will be discussed based on the observed foil-thickness and velocity dependence of the vicinage effect.