Application of KCl:Eu storage phosphors to wide-range neutron detection
storage phosphors to wide-range neutron detection
Sakasai, Kaoru 
 ; To, Kentaro
; To, Kentaro 
 ; Nakamura, Tatsuya
; Nakamura, Tatsuya 
 ; Takakura, Kosuke; Konno, Chikara
; Takakura, Kosuke; Konno, Chikara 
 ; Iwamoto, Yosuke
; Iwamoto, Yosuke 


Storage characteristics of KCl:Eu phosphor were investigated in order to apply the phosphor to wide-range neutron detection. For detection of both slow and fast neutrons,
phosphor were investigated in order to apply the phosphor to wide-range neutron detection. For detection of both slow and fast neutrons,  LiF powders and polyethylene powders were added to the phosphor at the same time. The optimization of the phosphor for maximum photostimulated luminescence yields have been performed and obtained at a polyethylene weight ratio of about 0.05 when the mixtures were irradiated by fast neutron with energy of 14.8 MeV, where the weight ratio of KCl:Eu
LiF powders and polyethylene powders were added to the phosphor at the same time. The optimization of the phosphor for maximum photostimulated luminescence yields have been performed and obtained at a polyethylene weight ratio of about 0.05 when the mixtures were irradiated by fast neutron with energy of 14.8 MeV, where the weight ratio of KCl:Eu phosphor to
phosphor to  LiF powders was fixed to be two to three. These experimental results well agreed with theoretical predictions by Monte Carlo simulation using PHITS code. The energy deposition by slow or intermediate neutrons was mainly due to charged particles as a result of nuclear reaction of
LiF powders was fixed to be two to three. These experimental results well agreed with theoretical predictions by Monte Carlo simulation using PHITS code. The energy deposition by slow or intermediate neutrons was mainly due to charged particles as a result of nuclear reaction of  Li(n,
Li(n, )T. According to relativistic calculation, the energy of alpha particles or tritons cannot be uniquely determined in a laboratory system but has a certain distribution even if incident neutron energy is fixed when neutron energy is high. The calculation showed that charged particles produced by nuclear reactions such as
)T. According to relativistic calculation, the energy of alpha particles or tritons cannot be uniquely determined in a laboratory system but has a certain distribution even if incident neutron energy is fixed when neutron energy is high. The calculation showed that charged particles produced by nuclear reactions such as 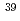 K(n,
K(n, ) or
) or  Cl(n,
Cl(n, ), in addition to protons by
), in addition to protons by  H(n,n)
H(n,n)  H reaction, will contribute the total energy deposition at high energy of incident neutrons.
H reaction, will contribute the total energy deposition at high energy of incident neutrons.