Hydrothermal chloritization processes from biotite in the Toki granite, Central Japan; Temporal variations of the compositions of hydrothermal fluids associated with chloritization
土岐花崗岩体中の熱水変質による黒雲母の緑泥石化; 緑泥石化に伴う熱水流体の化学的特徴の変遷
湯口 貴史; 笹尾 英嗣 

 ; 石橋 正祐紀; 西山 忠男*
; 石橋 正祐紀; 西山 忠男*
Yuguchi, Takashi; Sasao, Eiji; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Nishiyama, Tadao*
花崗岩における地球化学的特徴の将来的な変遷を予測するためには、今日にいたるまでの花崗岩体で生じた現象(たとえば熱水変質や岩石-水反応)の長期的変遷を理解することが、重要な視点の1つとなる。そこで、本論文では中部日本に位置する土岐花崗岩体において黒雲母から緑泥石への熱水変質プロセスの解明を行った。花崗岩体の熱水変質の中で、黒雲母の緑泥石化は広い温度条件で生ずることが報告されており、かつ花崗岩体を通して普遍的に観察される。このため、変質に伴う鉱物と熱水流体間の物質移動に着目することで、花崗岩体内の熱水流体の化学的特徴の長期的な変遷を明らかにした。土岐花崗岩体中における緑泥石化に伴って生じる鉱物の組み合わせの違いは、熱水から流入する成分の相違に支配されることが明らかとなった。このことは、熱水に含有する化学成分の不均質性を示す。また、緑泥石化が進行するにつれ、熱水流体中のケイ素とカリウム,塩素が増大し、金属成分とカルシウムが減少する化学的特徴の経時的な変化を明らかにした。
This paper describes the biotite chloritization process with a focus on mass transfer in the Toki granitic pluton, Central Japan, and also depicts the temporal variations in chemical characteristics of hydrothermal fluid associated with chloritization during the sub-solidus cooling of the pluton. Singular value decomposition (SVD) analysis results in chloritization reaction equations for eight mineral assemblages, leading to the quantitative assessment of mass transfer between the reactant and product minerals, and inflow and outflow of components through the hydrothermal fluid. The matrices for SVD analysis consist of arbitrary combinations of molar volume and closure component in the reactant and product minerals. The eight reactions represent the temporal variations of chemical characteristics of the hydrothermal fluid associated with chloritization: the progress of chloritization results in gradual increase of silicon, potassium and chlorine and gradual decrease of calcium and sodium in the hydrothermal fluid with temperature decrease. The biotite chloritization involves two essential formation processes: Formation Process 1, small volume decrease from biotite to chlorite and large inflow of metallic ions from the hydrothermal fluid, and Formation Process 2, large volume decrease and large outflow of metallic ions into hydrothermal fluid. Chlorite produced during Formation Process 1 dominates over that of Formation Process 2, resulting in the gradual decrease of metallic components in the hydrothermal fluid with chloritization progress. The combination of continuous reactions based on compositional variations in chlorite together with corresponding continuous Al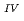 variations gives an indication of the temporal variations in rates of decreasing and increasing concentration of chemical components in the hydrothermal fluid associated with chloritization.
variations gives an indication of the temporal variations in rates of decreasing and increasing concentration of chemical components in the hydrothermal fluid associated with chloritization.