Hydrothermal chloritization processes from biotite in the Toki granite, Central Japan; Temporal variations of the compositions of hydrothermal fluids associated with chloritization
Yuguchi, Takashi; Sasao, Eiji 

 ; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Nishiyama, Tadao*
; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Nishiyama, Tadao*
This paper describes the biotite chloritization process with a focus on mass transfer in the Toki granitic pluton, Central Japan, and also depicts the temporal variations in chemical characteristics of hydrothermal fluid associated with chloritization during the sub-solidus cooling of the pluton. Singular value decomposition (SVD) analysis results in chloritization reaction equations for eight mineral assemblages, leading to the quantitative assessment of mass transfer between the reactant and product minerals, and inflow and outflow of components through the hydrothermal fluid. The matrices for SVD analysis consist of arbitrary combinations of molar volume and closure component in the reactant and product minerals. The eight reactions represent the temporal variations of chemical characteristics of the hydrothermal fluid associated with chloritization: the progress of chloritization results in gradual increase of silicon, potassium and chlorine and gradual decrease of calcium and sodium in the hydrothermal fluid with temperature decrease. The biotite chloritization involves two essential formation processes: Formation Process 1, small volume decrease from biotite to chlorite and large inflow of metallic ions from the hydrothermal fluid, and Formation Process 2, large volume decrease and large outflow of metallic ions into hydrothermal fluid. Chlorite produced during Formation Process 1 dominates over that of Formation Process 2, resulting in the gradual decrease of metallic components in the hydrothermal fluid with chloritization progress. The combination of continuous reactions based on compositional variations in chlorite together with corresponding continuous Al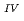 variations gives an indication of the temporal variations in rates of decreasing and increasing concentration of chemical components in the hydrothermal fluid associated with chloritization.
variations gives an indication of the temporal variations in rates of decreasing and increasing concentration of chemical components in the hydrothermal fluid associated with chloritization.