Nuclear resonance fluorescence in U-238 using LaBr detectors for nuclear security
Hayakawa, Takehito; Negm, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Daito, Izuru*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Zen, H.*; Omer, M.* 
 ; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hajima, Ryoichi
; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hajima, Ryoichi
Recently, a nondestructive measurement method of shielded fissional isotopes such as  U or
U or  Pu has been proposed for the nuclear security. These isotopes are measured by using nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) with monochromatic energy
Pu has been proposed for the nuclear security. These isotopes are measured by using nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) with monochromatic energy  -ray beams generated by laser Compton-scattering (LCS). We have proposed that one measure scattered
-ray beams generated by laser Compton-scattering (LCS). We have proposed that one measure scattered  -rays from NRF with LCS
-rays from NRF with LCS  -ray beams using the LaBr
-ray beams using the LaBr (Ce) detectors. The LaBr
(Ce) detectors. The LaBr (Ce) crystals include internal radioisotopes of a meta-stable isotope
(Ce) crystals include internal radioisotopes of a meta-stable isotope 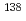 La and alpha decay chains from some actinides as
La and alpha decay chains from some actinides as 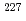 Ac. There is a broad pump at about 2 MeV. This pump is considered to be an overlap of
Ac. There is a broad pump at about 2 MeV. This pump is considered to be an overlap of  -rays from decay chains of some actinides but its detailed structure has not been established. Here we have measured NRF spectra of
-rays from decay chains of some actinides but its detailed structure has not been established. Here we have measured NRF spectra of  U using the LCS
U using the LCS  -rays with energy of about 2.5 MeV at the HIgS facility of the Duke University. The background has been evaluated using a simulation code GEAT4. The 9 peaks, 8 NRF
-rays with energy of about 2.5 MeV at the HIgS facility of the Duke University. The background has been evaluated using a simulation code GEAT4. The 9 peaks, 8 NRF  -rays plus the Compton scattered
-rays plus the Compton scattered  -ray of the incident beam, are finally assigned in an energy range of about 200 keV at about 2.5 MeV. The 8 integrated NRF cross-sections measured by LaBr
-ray of the incident beam, are finally assigned in an energy range of about 200 keV at about 2.5 MeV. The 8 integrated NRF cross-sections measured by LaBr (Ce) have been consistent with results by an HPGe detector. The three levels are newly assigned using the HPGe detector. Two of them are also measured by LaBr
(Ce) have been consistent with results by an HPGe detector. The three levels are newly assigned using the HPGe detector. Two of them are also measured by LaBr (Ce).
(Ce).